Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2021; 9(10): 2181-2191
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181
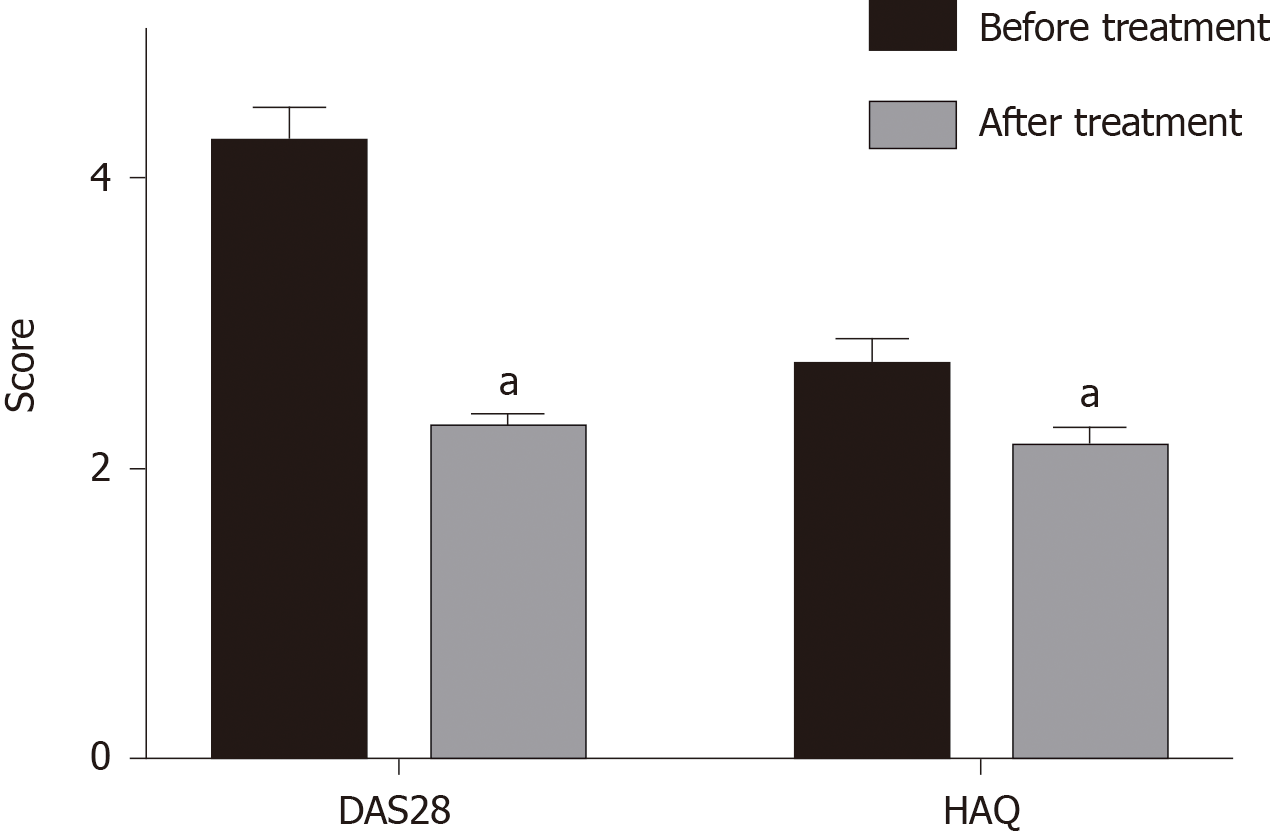
Figure 1 Effects of Iguratimod on Disease Activity Score 28 and Health Assessment Questionnaire score in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Compared to before treatment, aP < 0.05. DAS28: Disease Activity Score 28; HAQ: Health Assessment Questionnaire.
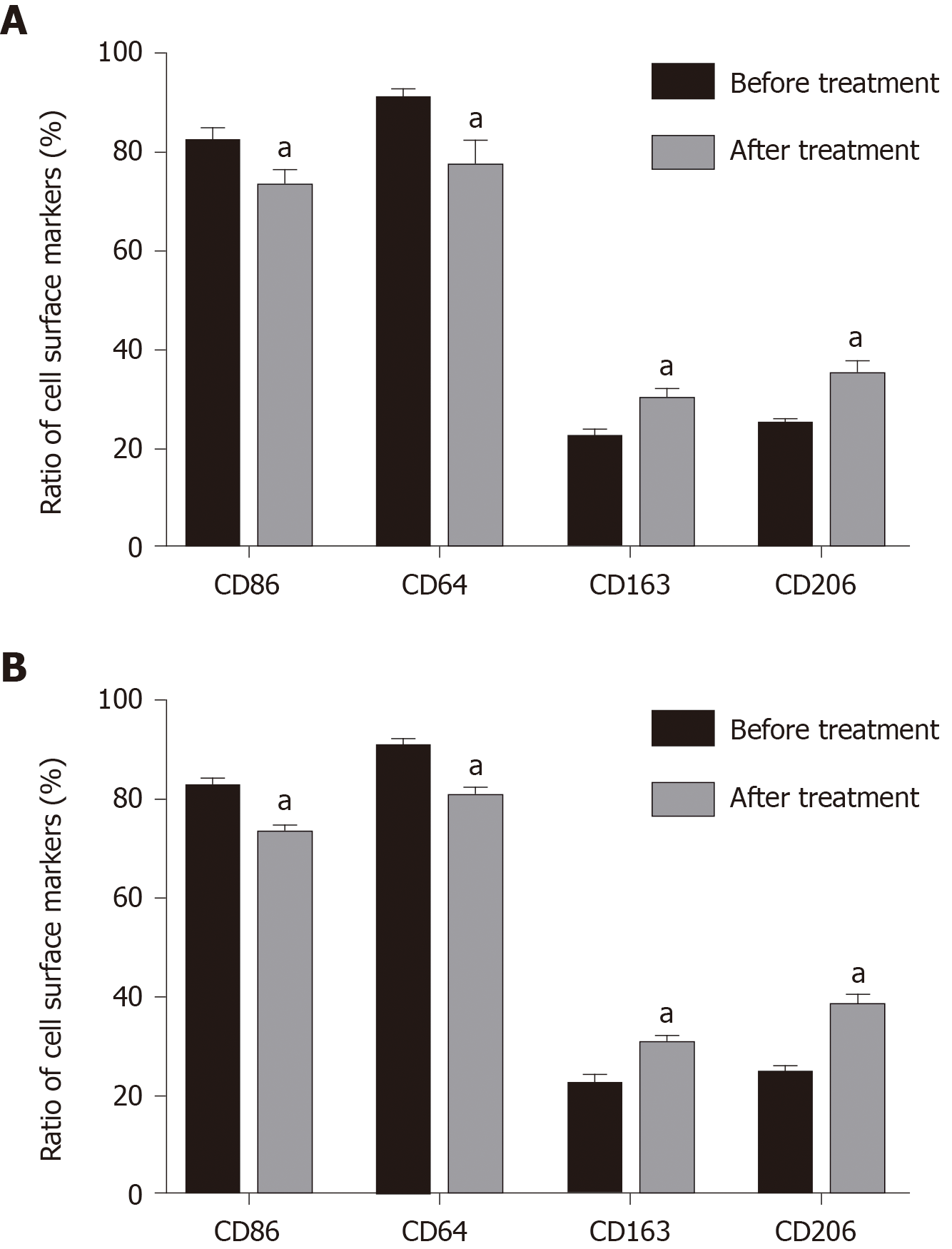
Figure 2 Effects of Iguratimod on cell polarity of mononuclear macrophages.
A: Effect of Iguratimod on monocyte polarity in peripheral blood; B: Effect of Iguratimod on macrophage polarity in joint effusion fluid. The results are expressed in %. Compared to before treatment, aP < 0.05.
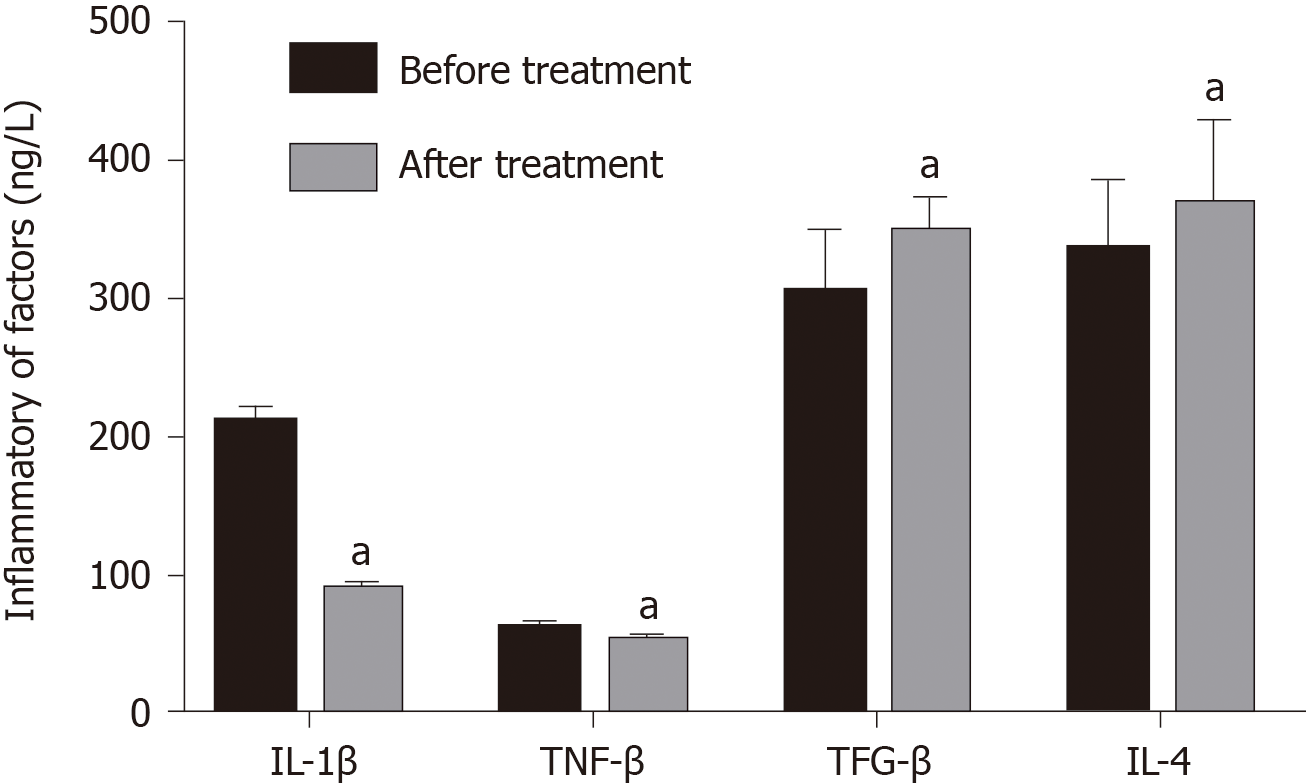
Figure 3 Effects of Iguratimod on interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-4 in joint effusion fluid.
Compared with that before treatment, aP < 0.05. IL: Interleukin; TFG-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
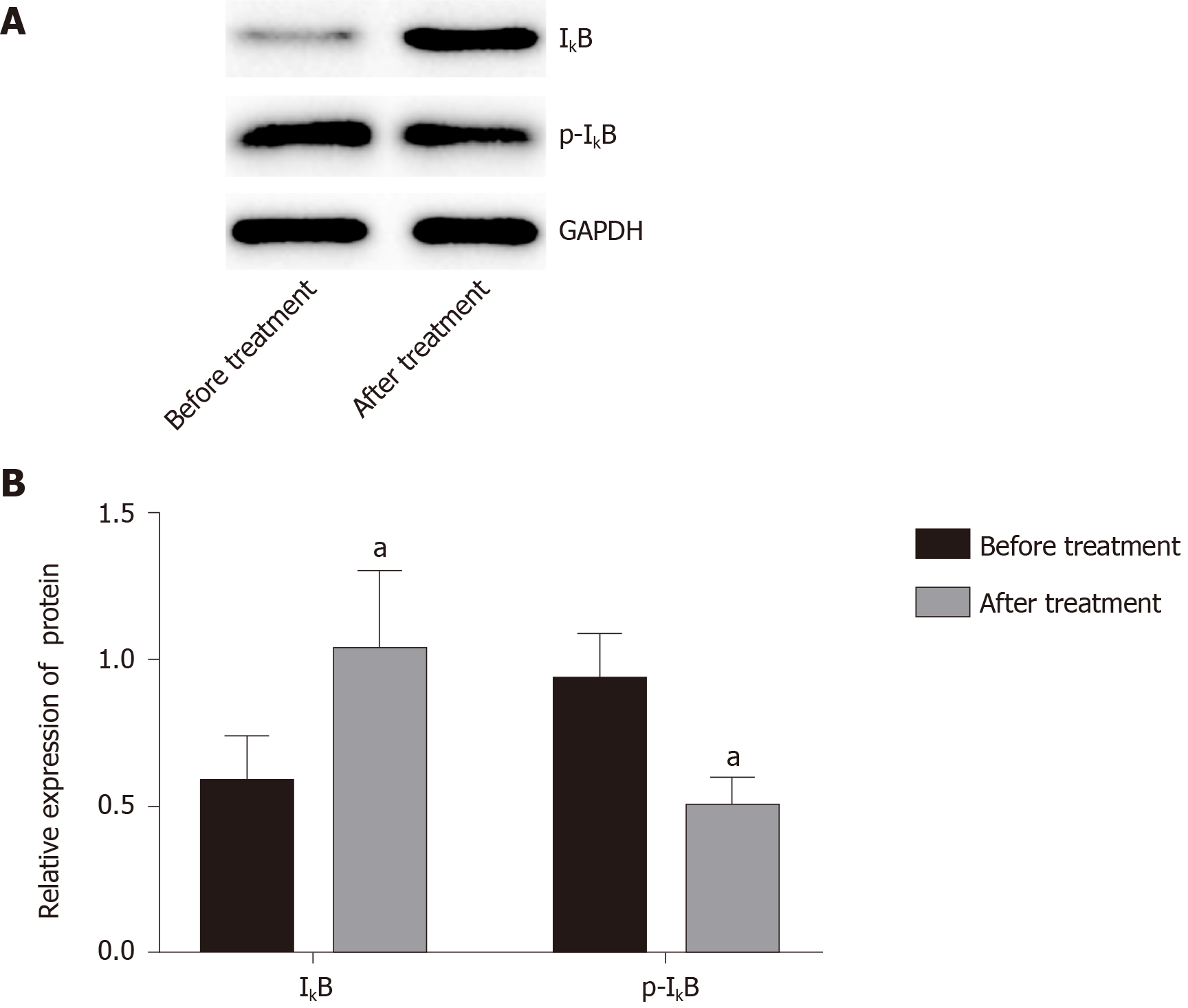
Figure 4 Effects of Iguratimod on nuclear factor-κB pathway in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
A: Western blot analysis of nuclear factor-κB pathway; B: Expression of inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (IκB) protein is the ratio of gray value of IκB to the gray value of internal reference glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and the relative expression of phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (p-IκB) protein is the ratio of the gray value of p-IκB to IκB. Compared with that before treatment, aP < 0.05.
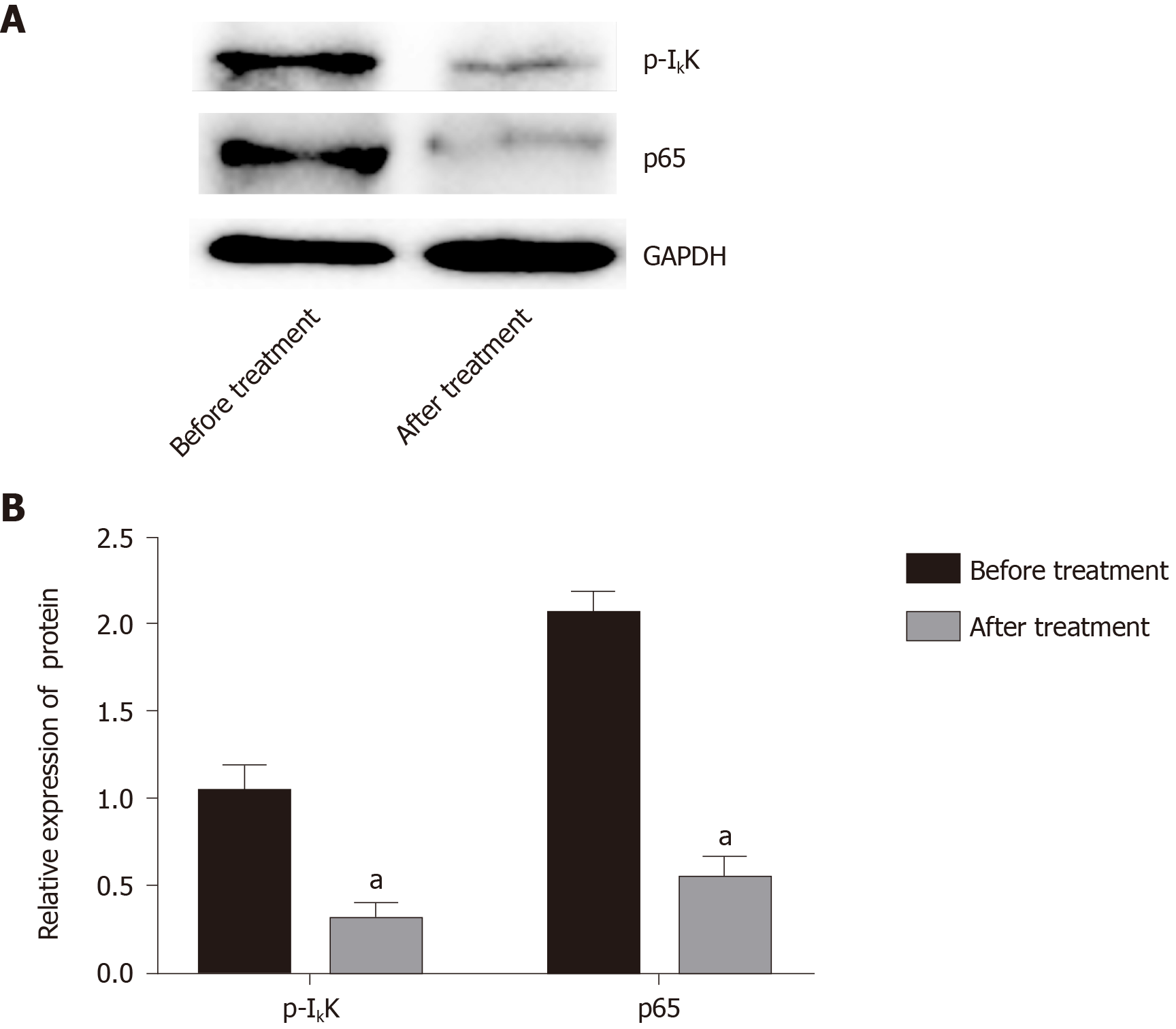
Figure 5 Changes of phosphorylated-inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB and p65 expression before and after treatment with Iguratimod.
A: Western blot analysis of the effect of Iguratimod on expression of phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB and p65; B: Ratio of phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (p-IκB) and p65 to the gray value of the internal reference glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) before and after treatment, aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Liu S, Song LP, Li RB, Feng LH, Zhu H. Iguratimod promotes transformation of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis by nuclear factor-κB pathway. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(10): 2181-2191
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i10/2181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181