Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2020; 8(9): 1735-1744
Published online May 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1735
Published online May 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1735
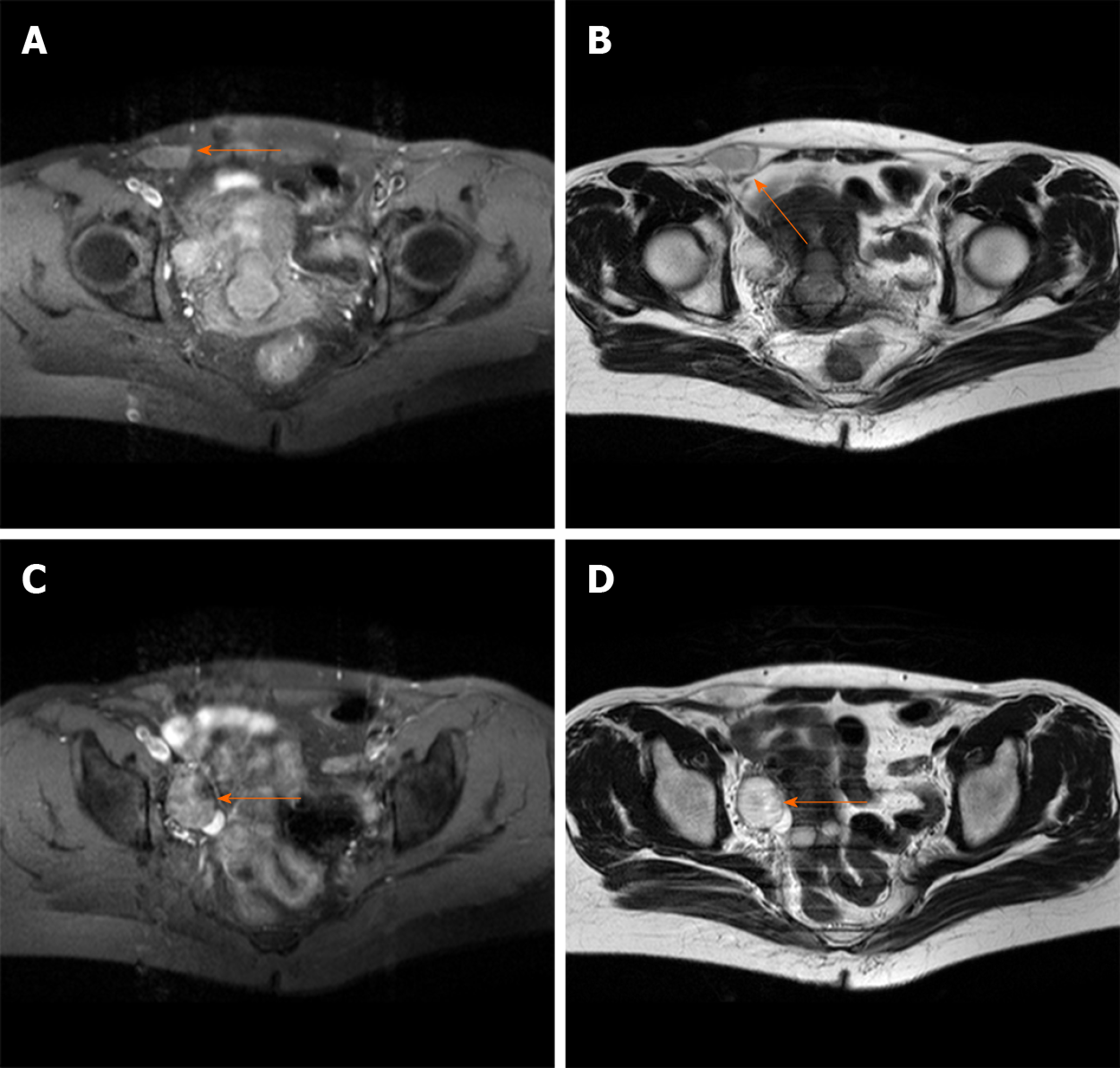
Figure 1 Pelvic cavity magnetic resonance imaging.
A and B: A liquid area in the right iliac fossa in T1 and T2-weighted images (2.7 cm × 1.3 cm × 2.6 cm); C and D: Oval mixed signal shadows with slightly longer T1 and T2-weighted image observed in the right adnexal area (2.6 cm × 3.0 cm).
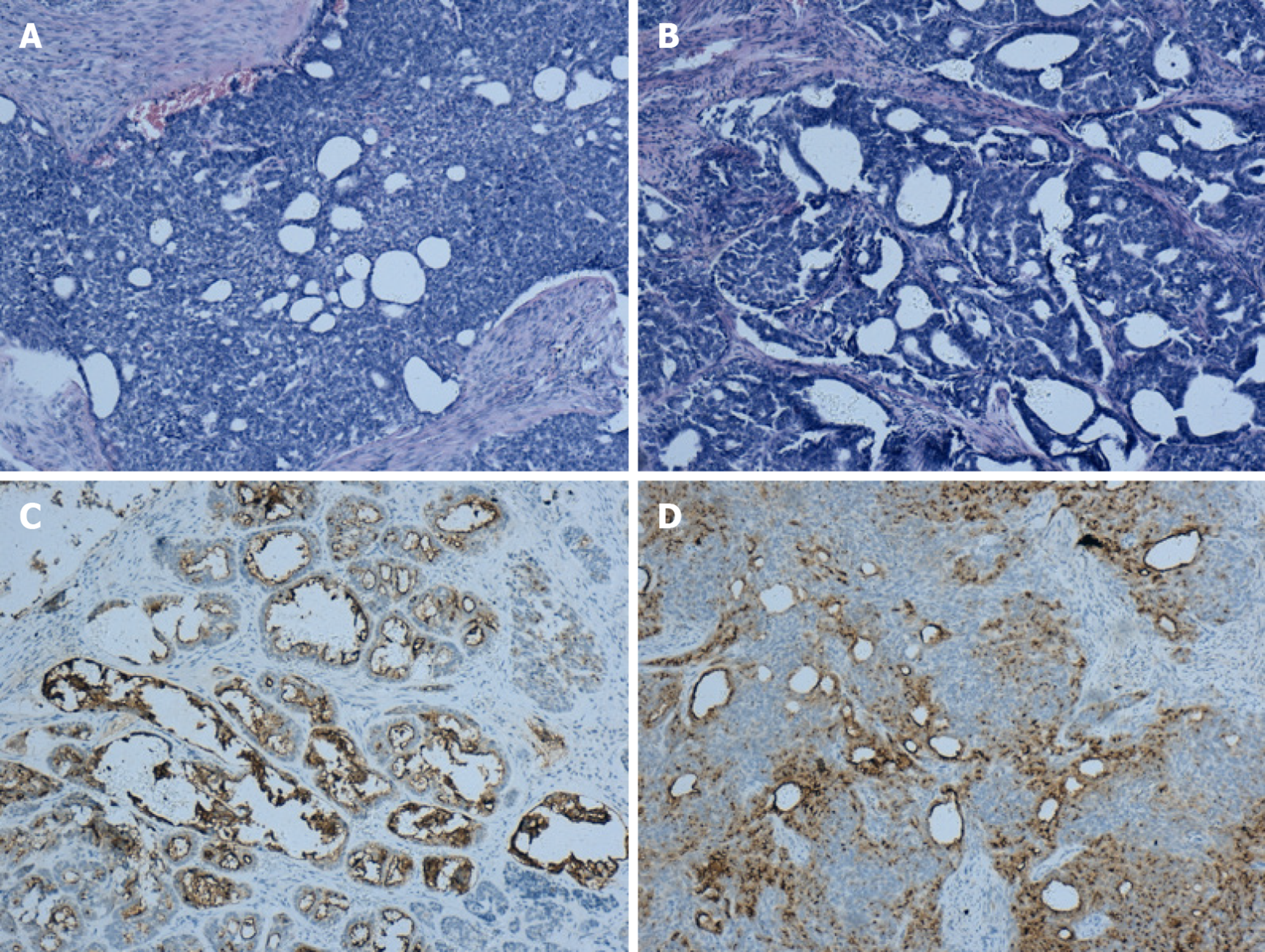
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical findings.
A: The lesion shows infiltrating tubular, papillary structures in the cervix (H&E, 100×); B: The lesion metastasis to the ovary shows the same pattern as that in the cervix (H&E, 100×); C: Positivity for CD10 staining in the cervix (H&E, 100×); D: Positivity for CD10 staining in the ovary (H&E, 100×).
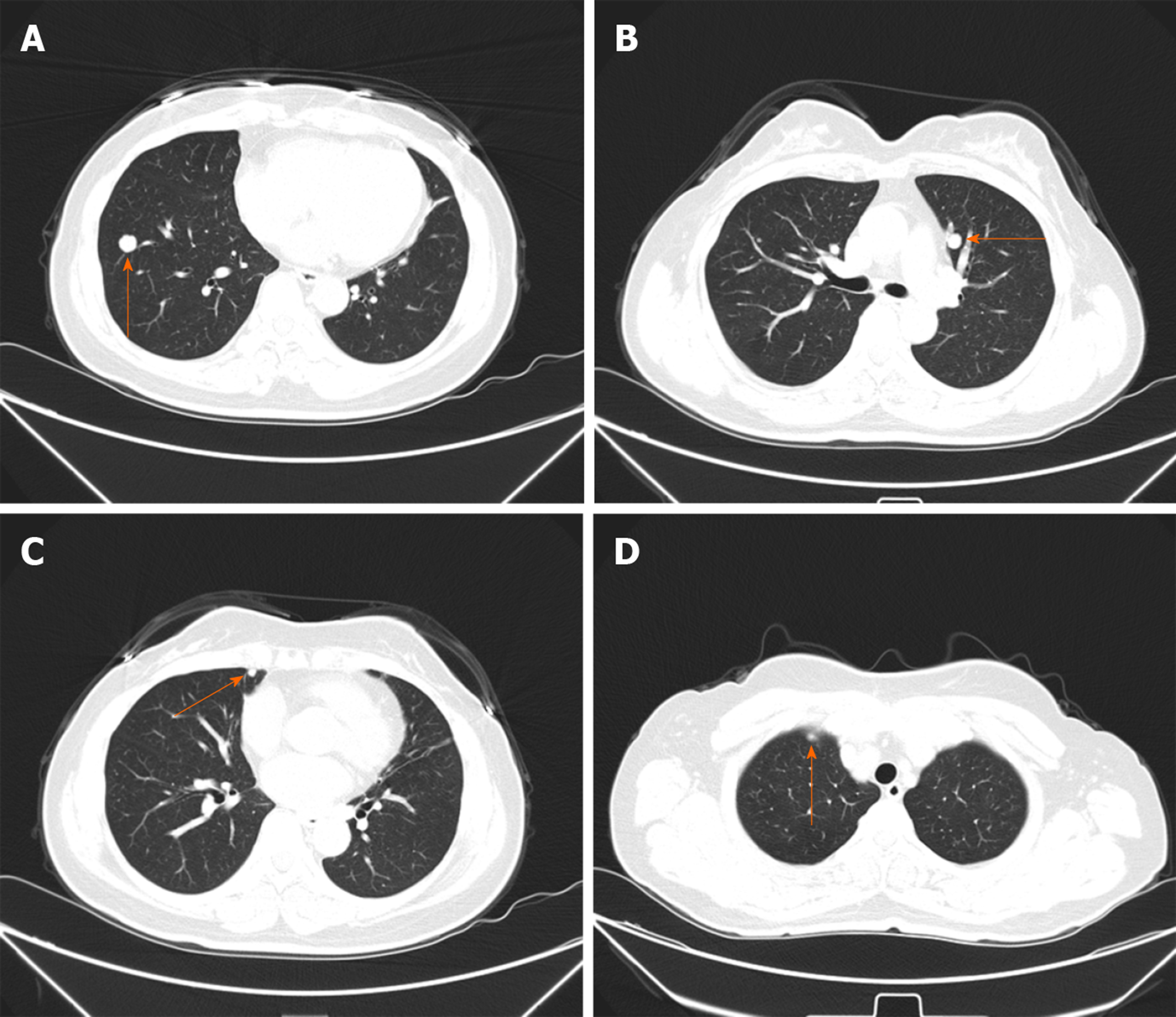
Figure 3 Thirty-two months later, multifocal lung nodules were found.
A-D: Multifocal lung metastatic nodules (orange arrows).
- Citation: Jiang LL, Tong DM, Feng ZY, Liu KR. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix with rare lung metastases: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(9): 1735-1744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i9/1735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1735