Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2020; 8(6): 1158-1163
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1158
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1158
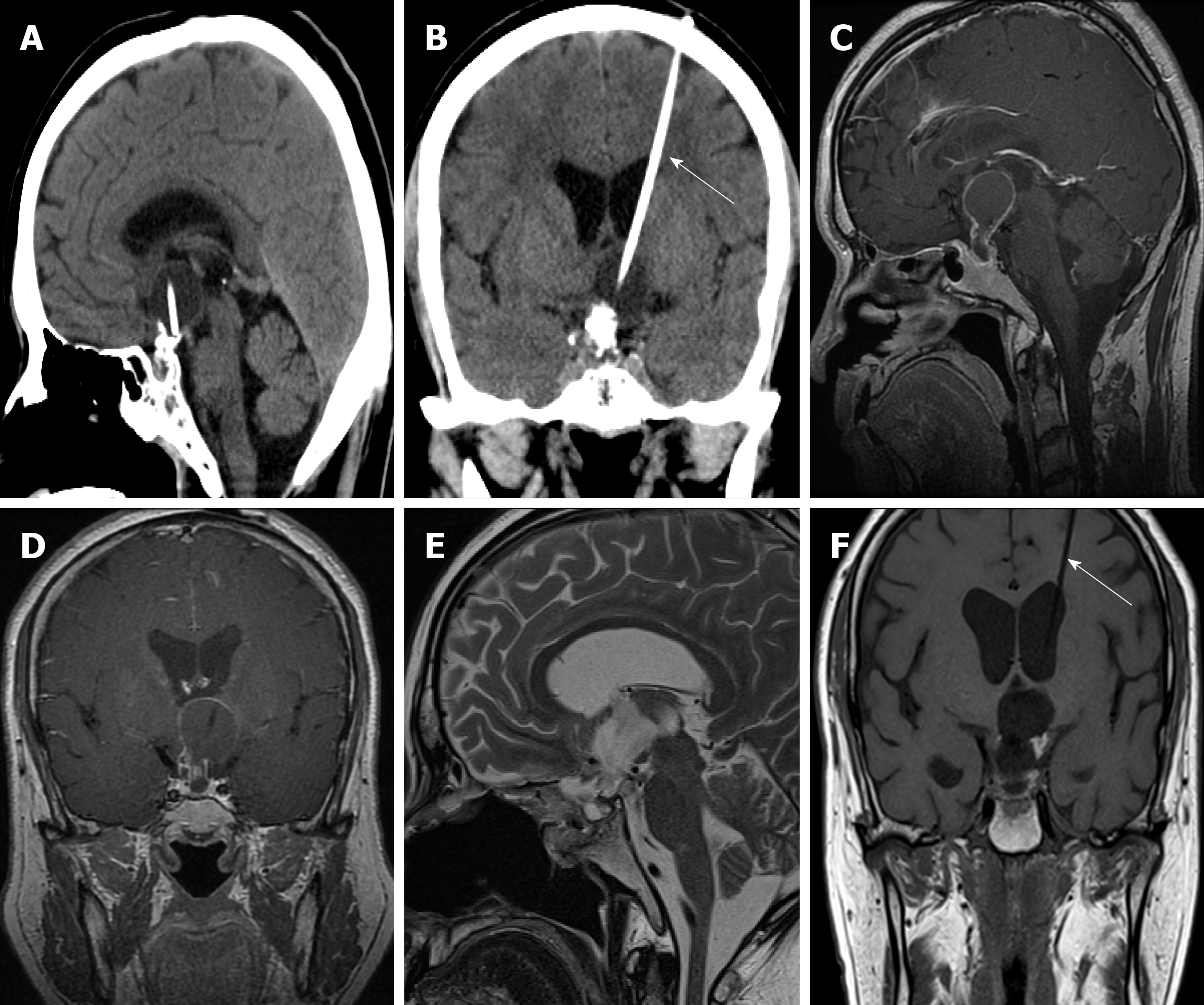
Figure 1 Imaging findings.
A and B: Head computed tomography before transsphenoidal surgery showed calcified cystic mass components in the intra- and suprasellar region, and internal irradiation tube in the cystic cavity of the mass (white arrow); C and D: Magnetic resonance imaging before transsphenoidal surgery showed a 2.7 cm × 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm calcified cystic intra- and suprasellar mass, which was strongly enhanced after injection of contrast medium; E and F: Magnetic resonance imaging after transsphenoidal surgery showed complete tumor resection and irradiation tube was reserved (white arrow).
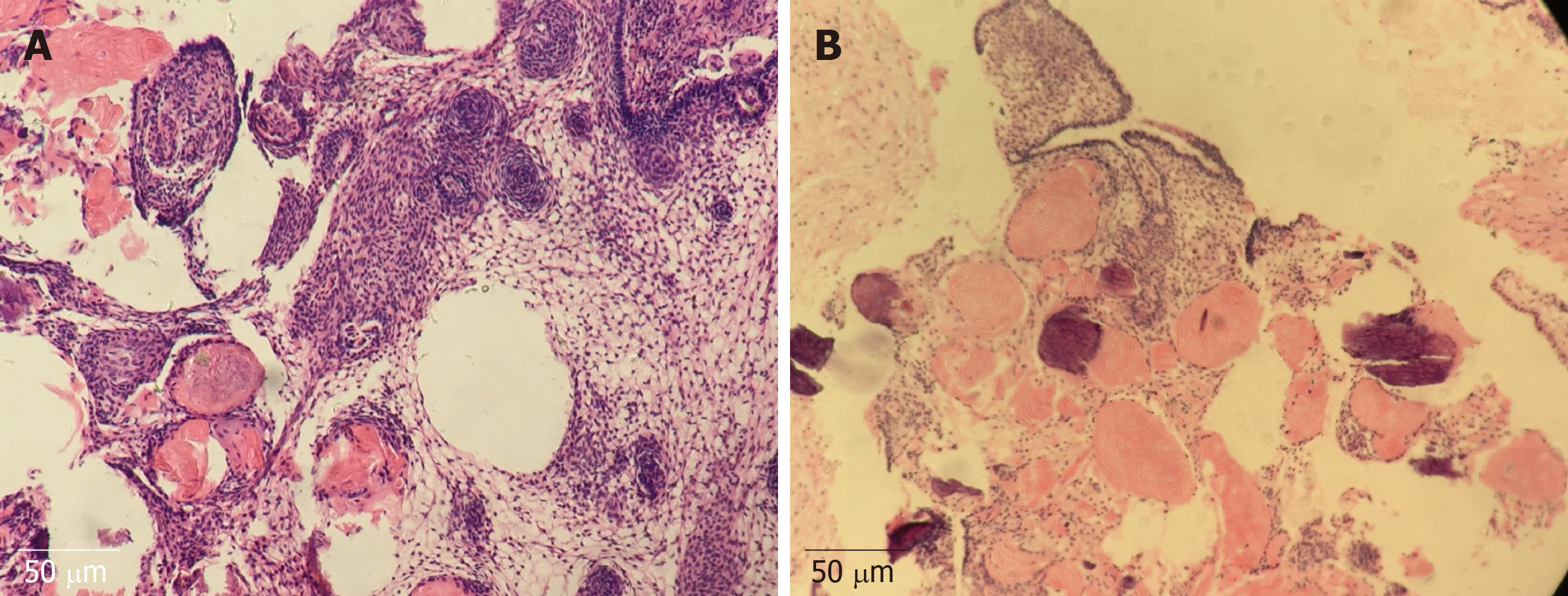
Figure 2 Histopathology examination of the tumor.
A and B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining showed adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma (× 100).
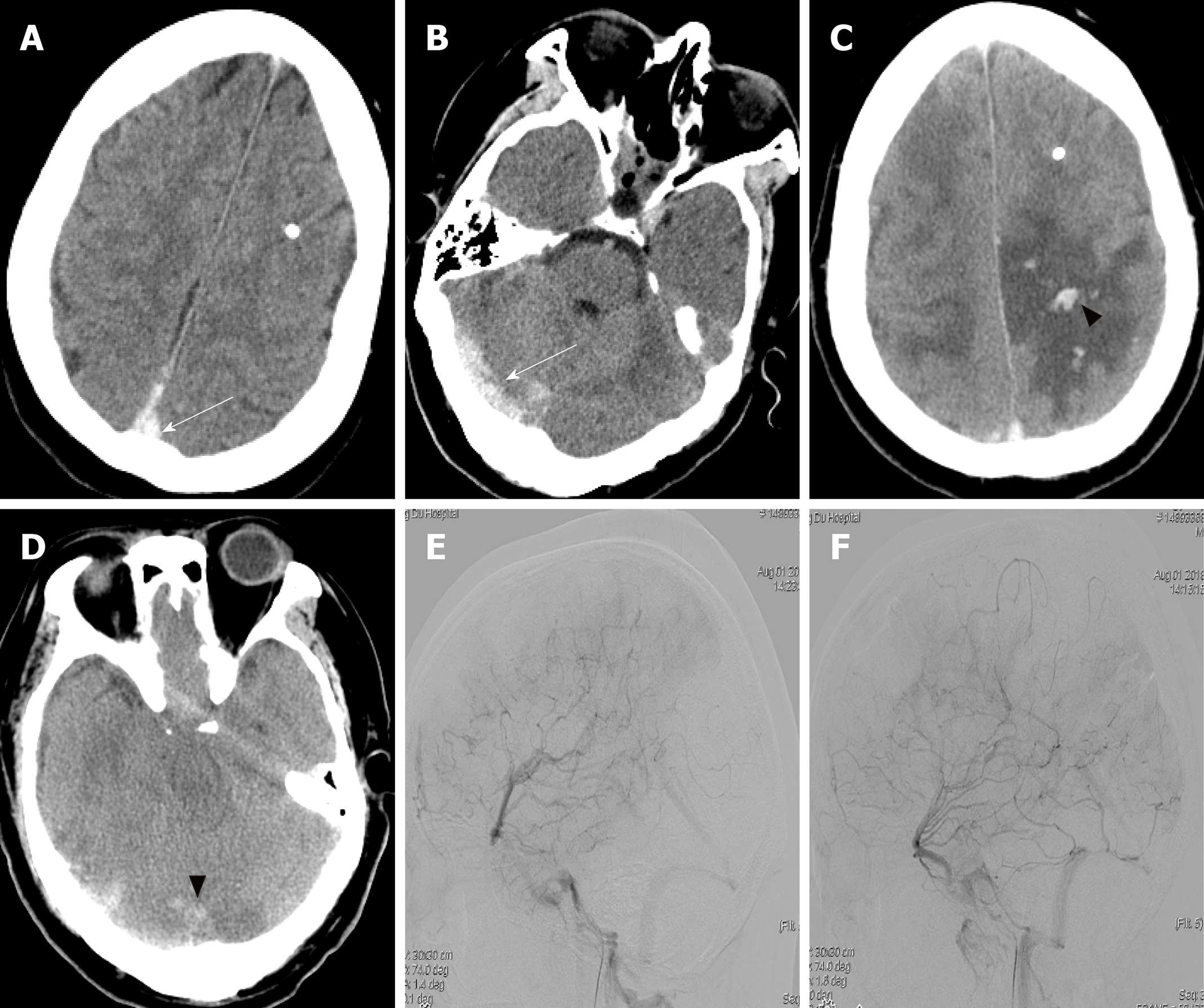
Figure 3 Imaging findings after readmission.
A and B: Head computed tomography on the first day after readmission showed a hyperdense shadow in the superior sagittal sinus and right transverse sinus (white arrow); C and D: Head computed tomography on the second day after readmission showed the presence of edema at the bilateral parietal lobe, and hemorrhage at the left parietal lobe and right occipital lobe (black arrowhead); E and F: Lateral view of the venous phase image of the left and right internal carotid artery of cerebral angiography illustrated the occlusion of the superior sagittal sinus.
- Citation: Chang T, Yang YL, Gao L, Li LH. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis following transsphenoidal surgery for craniopharyngioma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(6): 1158-1163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i6/1158.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1158