Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2020; 8(24): 6456-6464
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6456
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6456
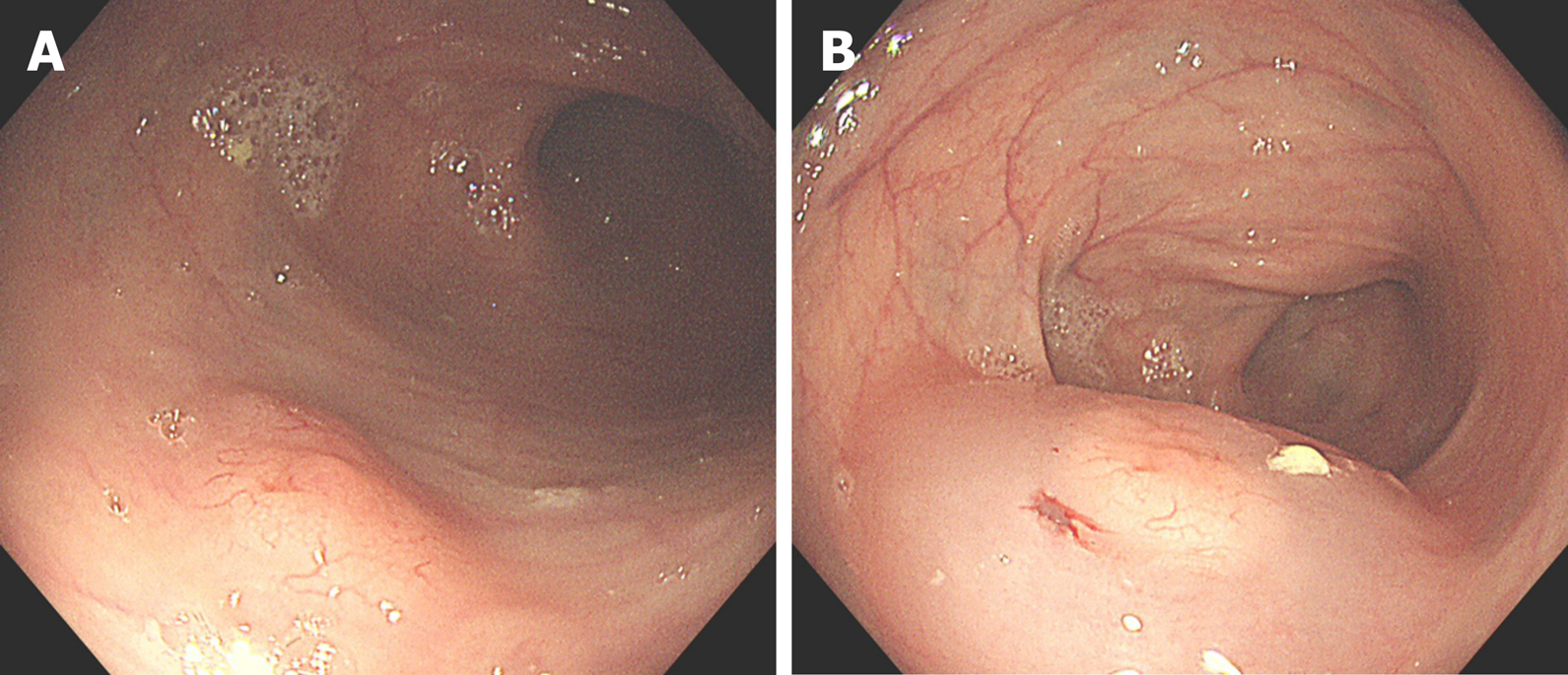
Figure 1 Colonoscopy.
A: A 1.2 cm × 0.8 cm flat polypoid lesion in the colon; B: The lesion after submucosal injection of normal saline into the colon.
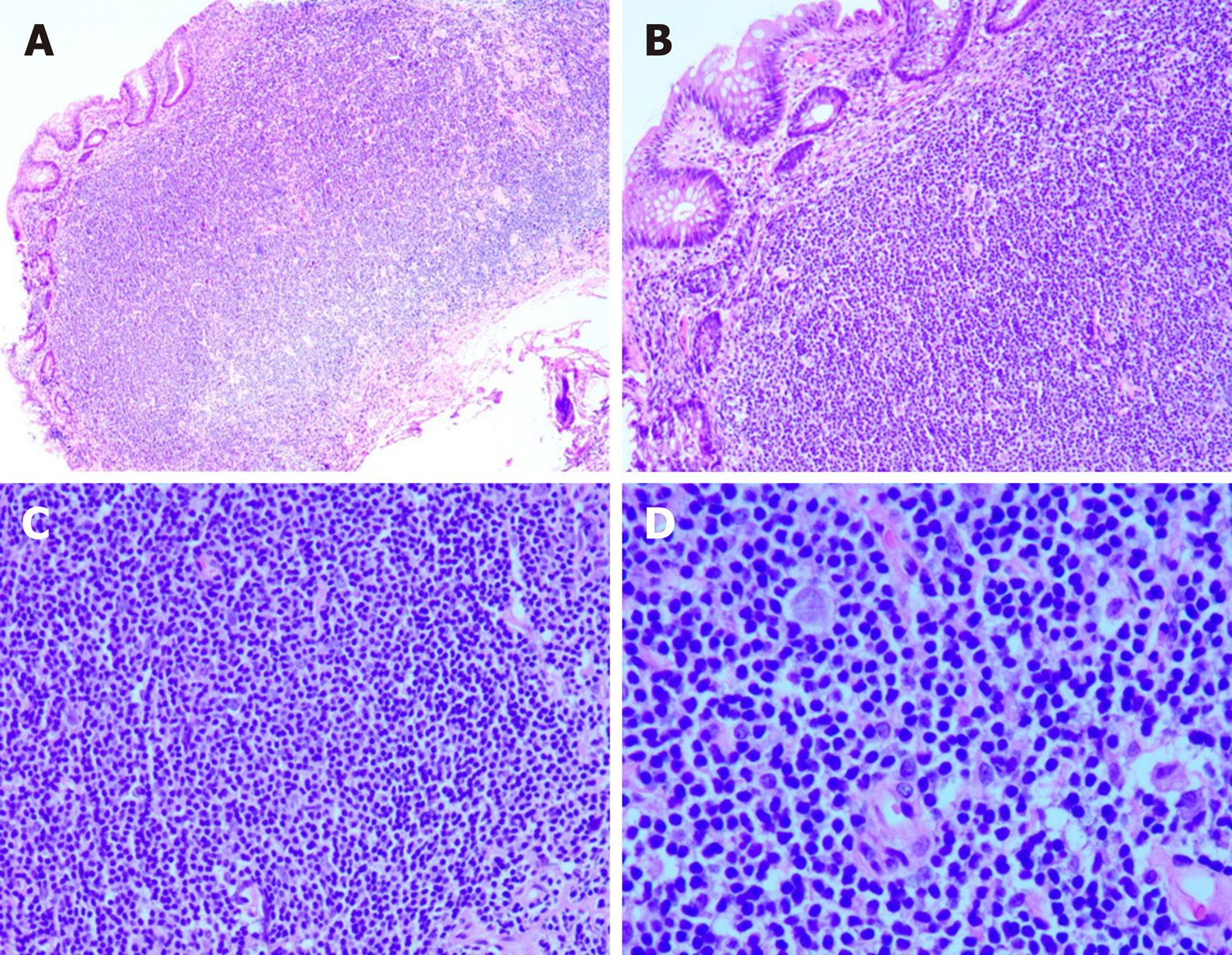
Figure 2 Histopathological findings.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (× 40); B: HE staining (× 100); C: HE staining (× 200); D: HE staining (× 400).
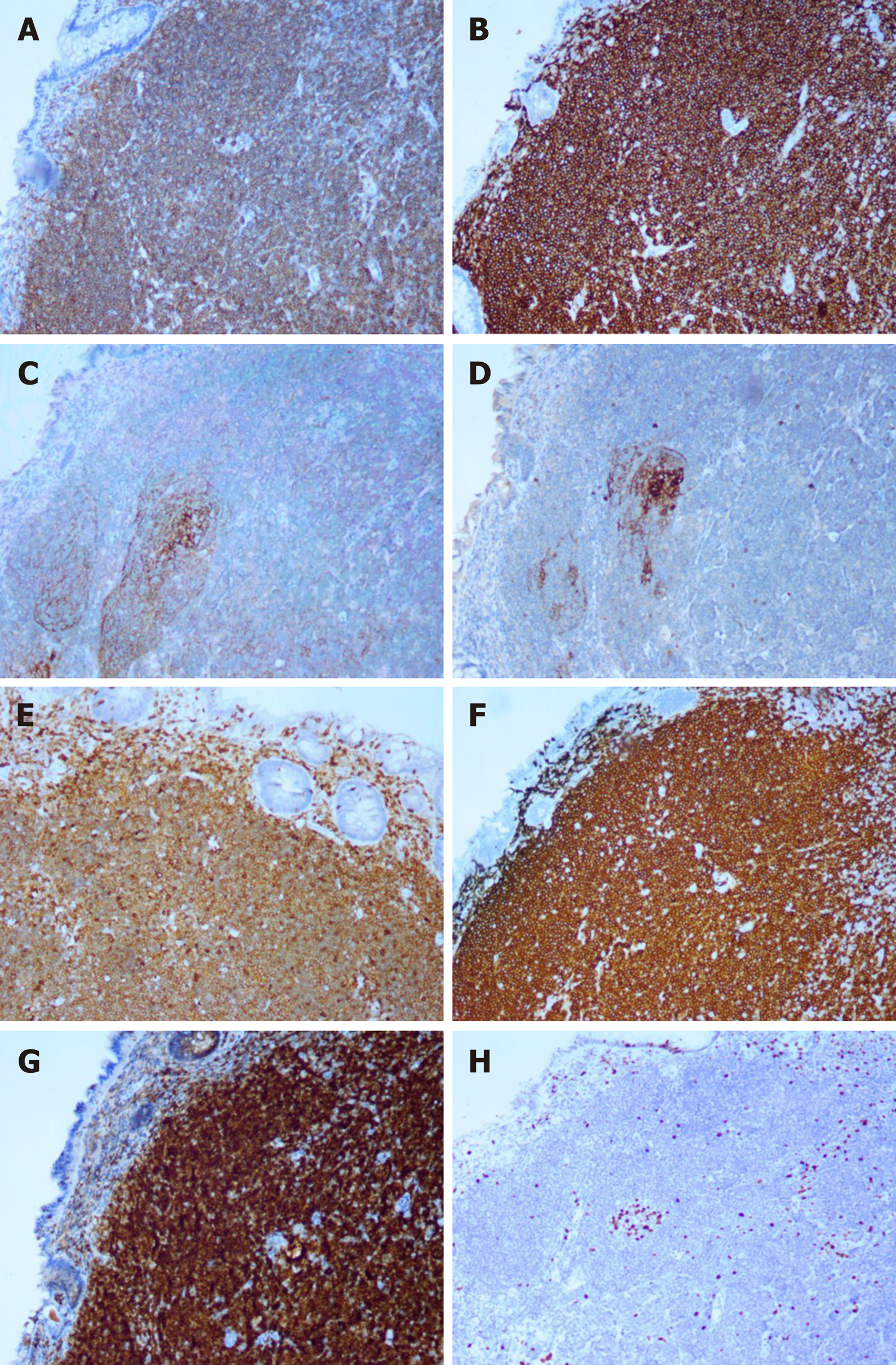
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining (× 100).
A: Immunostaining for CD19; B: Immunostaining for CD20; C: Immunostaining for CD21 (dendritic cells); D: Immunostaining for CD23 (dendritic cells); E: Immunostaining for CD43; F: Immunostaining for CD79a; G: Immunostaining for BCL-2; H: Immunostaining for Ki67 (10% positive).
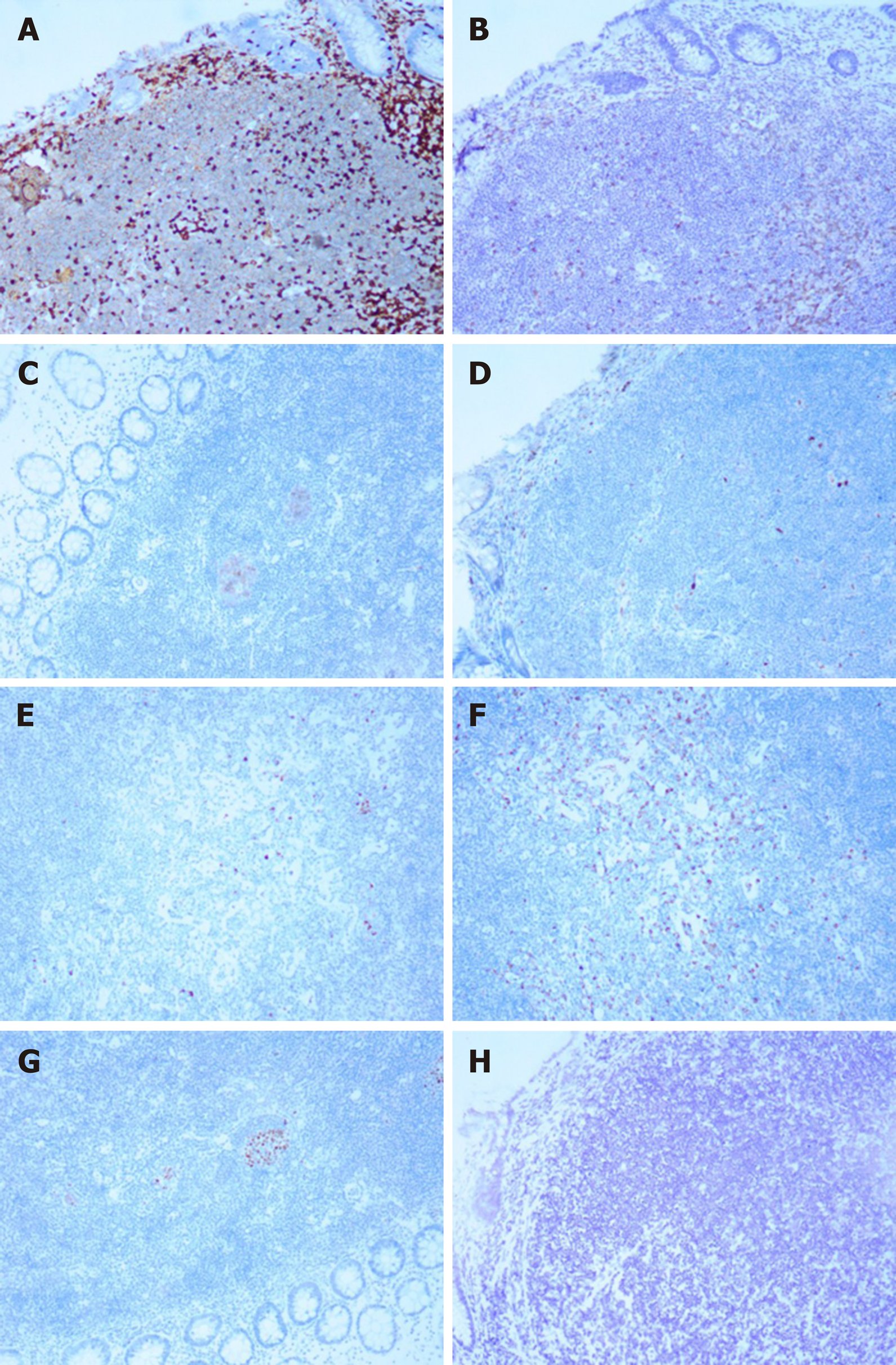
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining (× 100).
A: Immunostaining for CD3; B: Immunostaining for CD5; C: Immunostaining for CD10; D: Immunostaining for Cyclin D1; E: Immunostaining for kappa; F: Immunostaining for lambda; G: Immunostaining for BCL-6; H: Immunostaining for EBER.
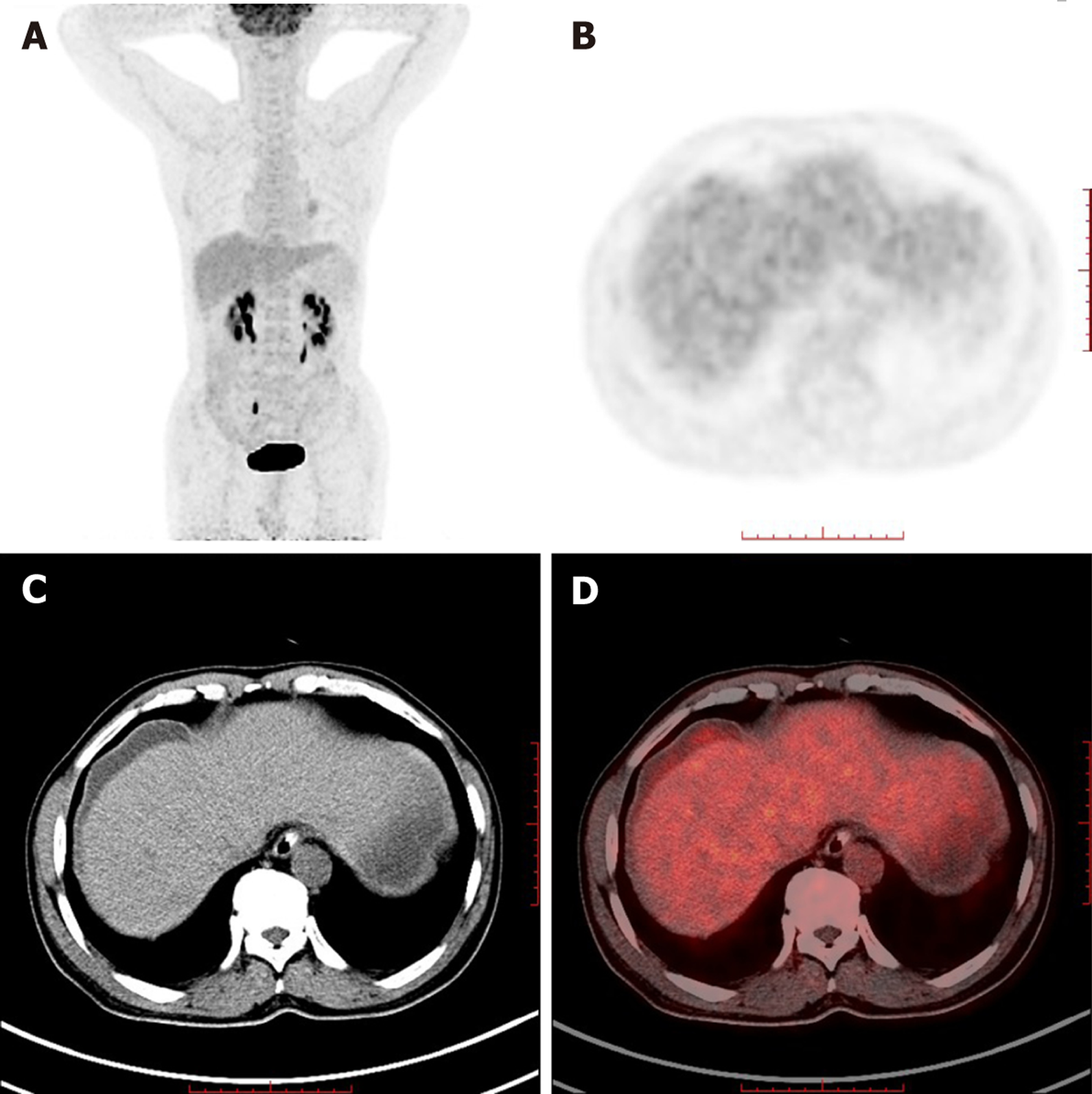
Figure 5 Whole-body maximum intensity projection 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography.
A: Slightly increased fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism in the subcapsular effusion of the liver, as well as in the right upper area of the peritoneum; B: Positron emission tomography; C: Computed tomography; D: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography in axial projection showing lesions in the subcapsular effusion of the liver.
- Citation: Li JJ, Chen BC, Dong J, Chen Y, Chen YW. Synchronous colonic mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma found after surgery for adenocarcinoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(24): 6456-6464
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i24/6456.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6456