Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2020; 8(24): 6358-6363
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6358
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6358
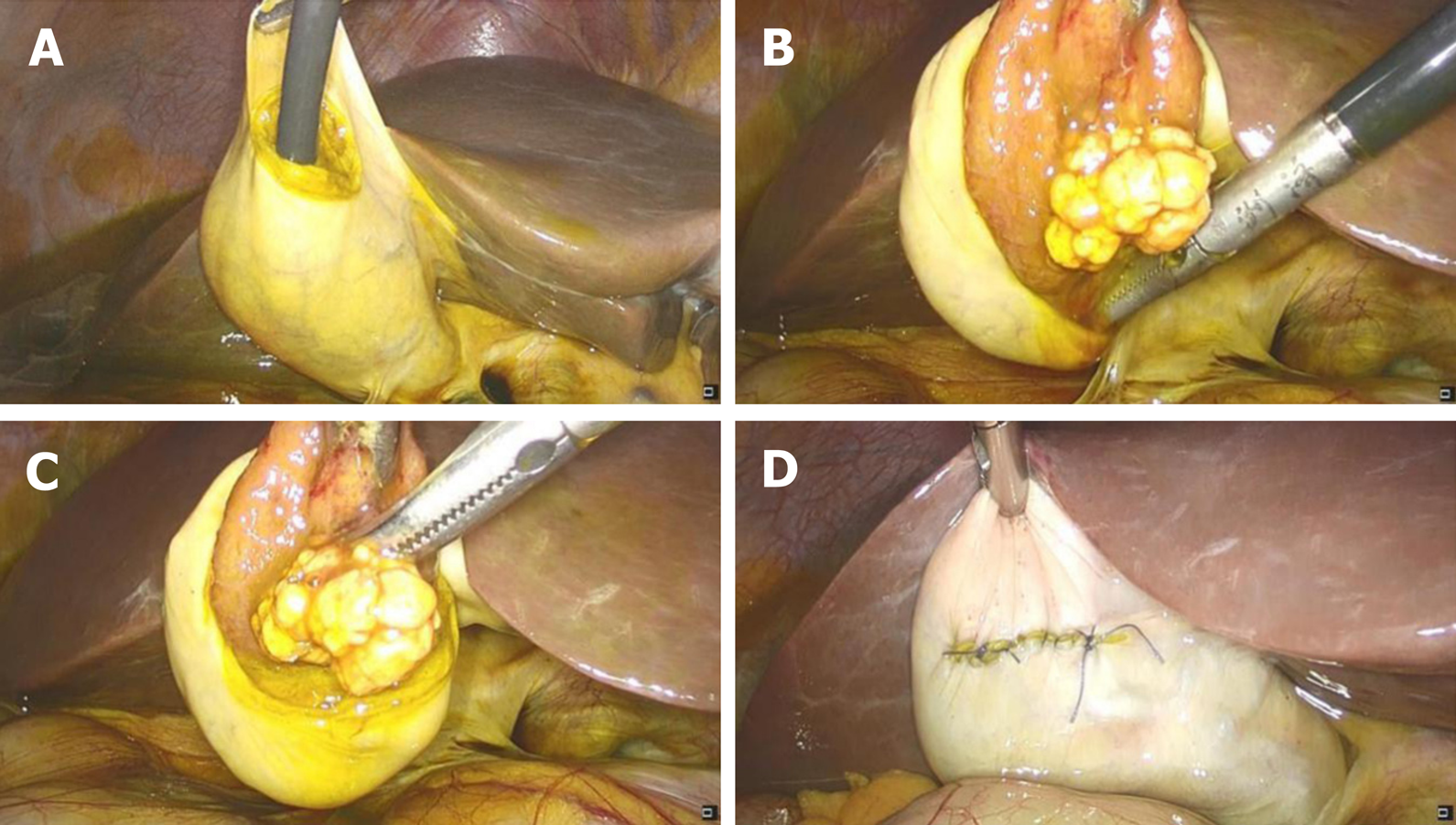
Figure 1 Laparoscopic images.
A: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, placing choledochoscope in the gallbladder to observe the gallbladder polyp; B: Placing the polyp into the abdominal cavity; C: Electrocoagulation resection of the gallbladder polyp; D: Suturing the gallbladder layer by layer.
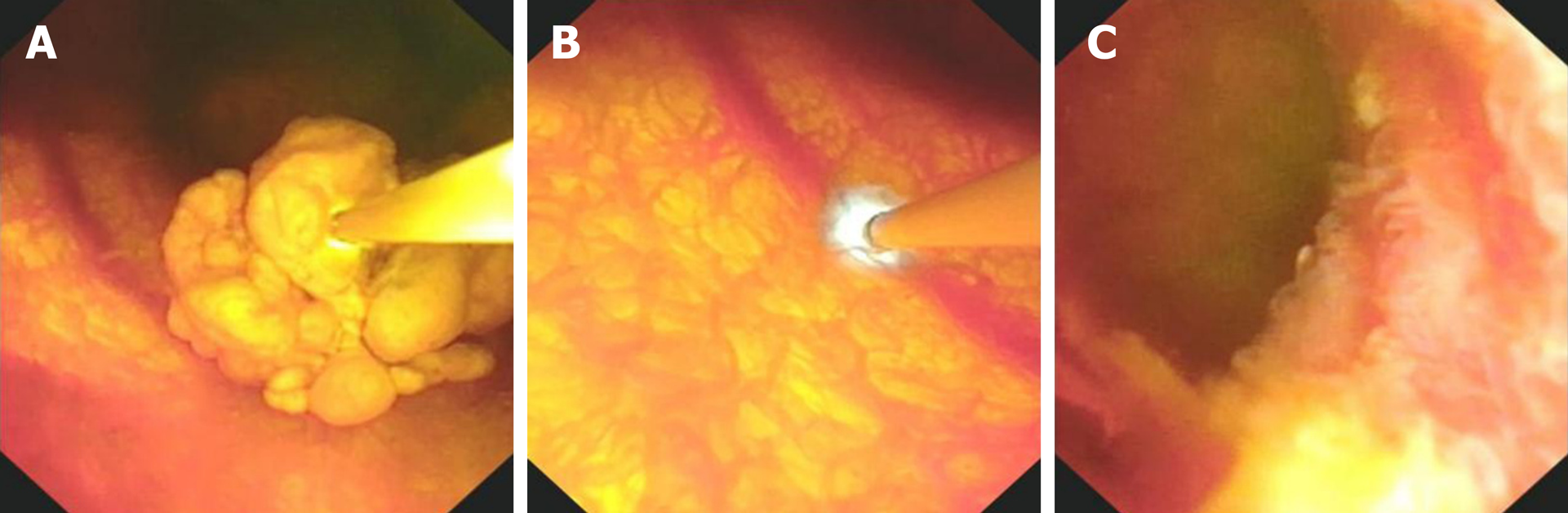
Figure 2 Images under choledochoscopy.
A: Observation of the surface of the polyp of the gallbladder; B: Using probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy to examine the normal gallbladder wall; C: The edge of gallbladder polypectomy.
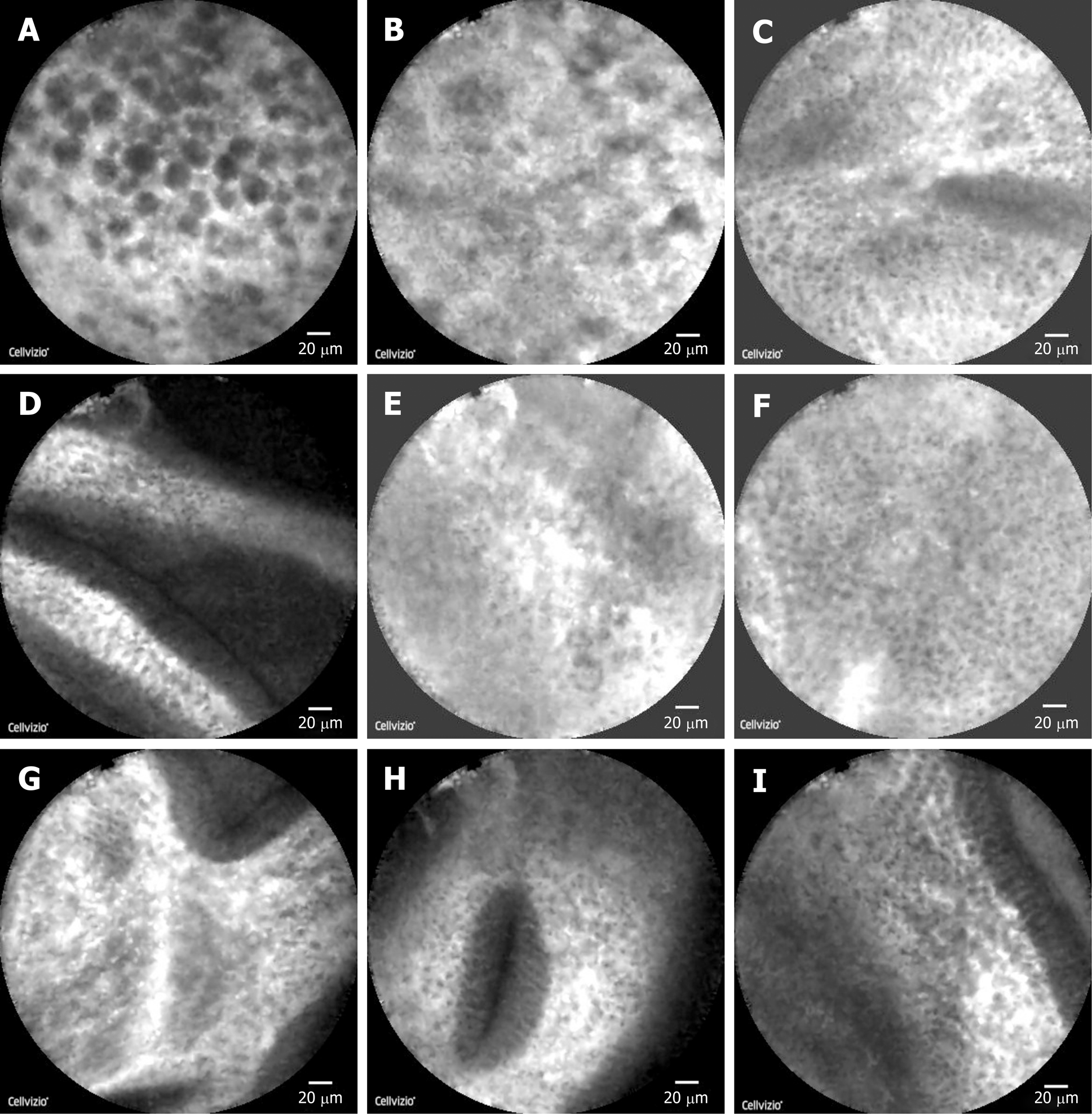
Figure 3 Images under probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy.
A: Gallbladder polyp cells were closely arranged and round with a maximum diameter of about 20 μm and black in color; B: Surface of the polyp showed a lack of blood supply, and vascular diameter of about 10 μm was considered; C: The remaining normal gallbladder mucosal cells were round, with nuclei located in the center of the cells, about 5-10 μm in diameter, arranged neatly; D: Normal gallbladder wall microvessel ran in a straight line; E: Mucosa at the fundus of the gallbladder showed sparse cells and fewer microvessels; F and G: Cells of mucous membrane of the gallbladder body were tighter, and microvessels were abundant; H: Oval glandular structure in the mucosa on the neck of the gallbladder, with a size of about 25 μm × 120 μm, with black in the center and a highlighted brush/dot contour at the edges; I: Basal cells were relatively dense, with a diameter of about 5-10 μm.
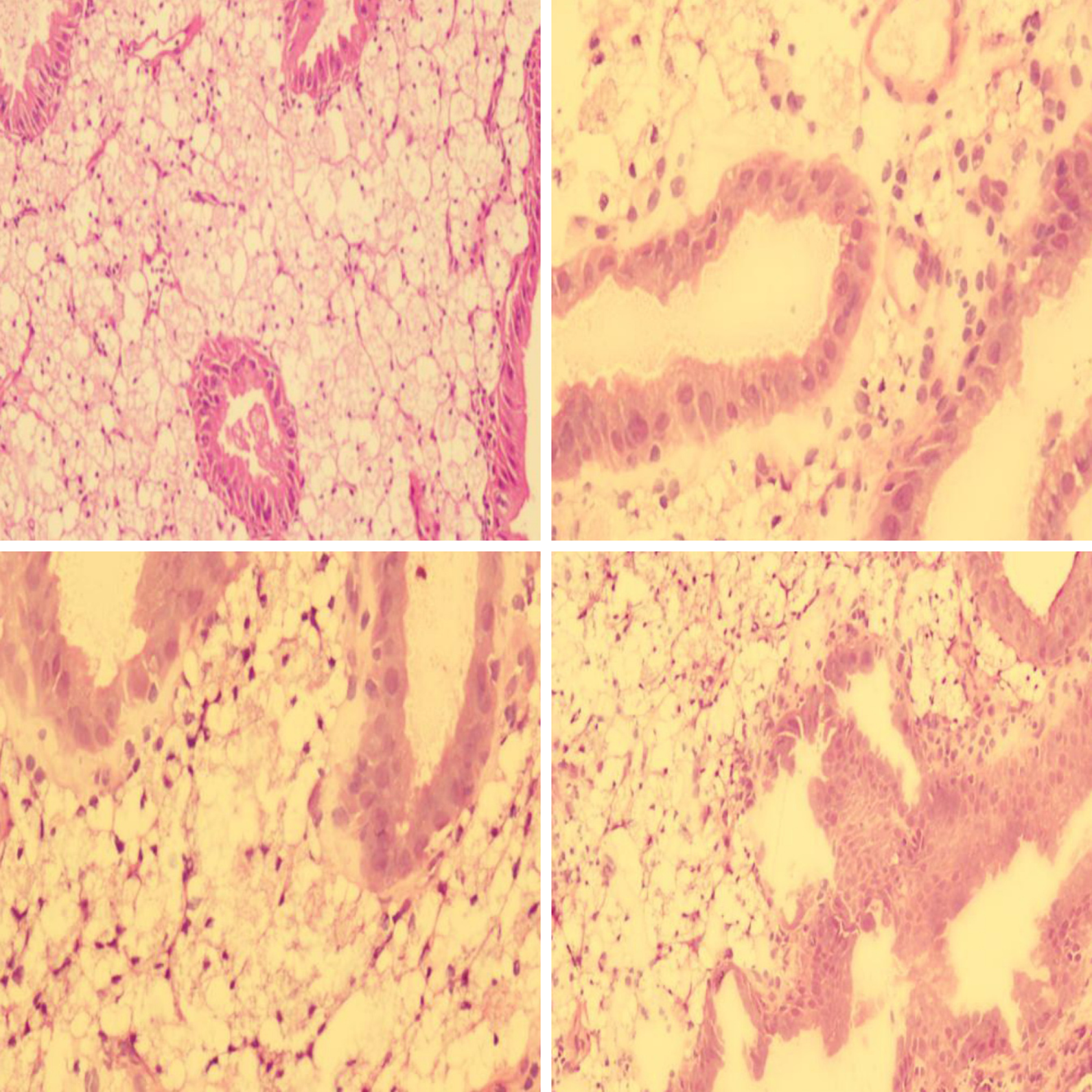
Figure 4 Histological examinations by hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed the pathology of the gallbladder polyp.
A large amount of sterols was shown to be deposited in the gallbladder polyp cells.
- Citation: Tang BF, Dang T, Wang QH, Chang ZH, Han WJ. Confocal laser endomicroscopy distinguishing benign and malignant gallbladder polyps during choledochoscopic gallbladder-preserving polypectomy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(24): 6358-6363
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i24/6358.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6358