Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2020; 8(23): 5962-5975
Published online Dec 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5962
Published online Dec 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5962
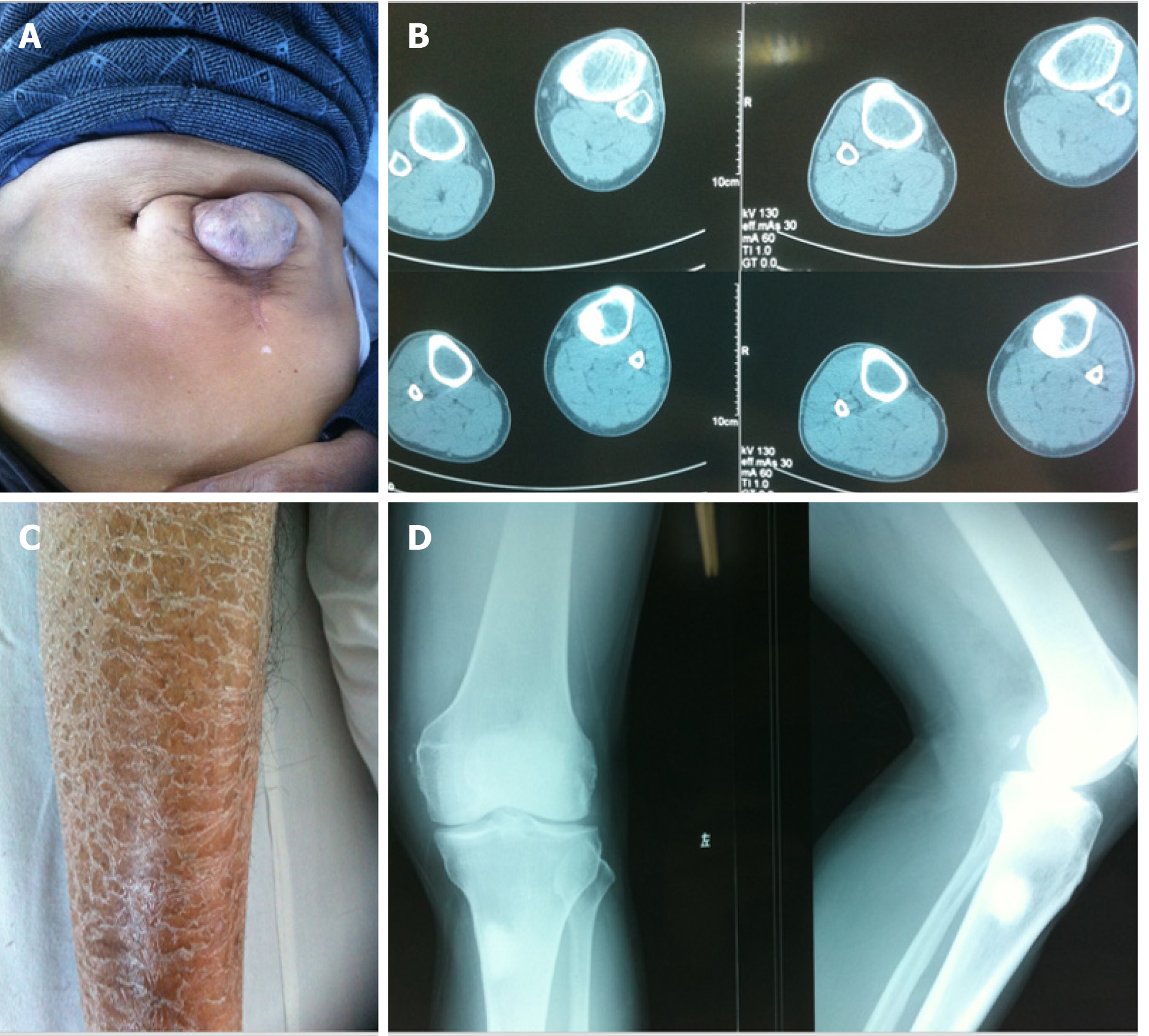
Figure 1 Clinical data of the patient.
A: The patient did not heal after an exploratory laparotomy for acute abdomen at 40 years old and a ventral hernia was formed; B and D: Computed tomography and X-ray of the left knee joint showed a high-density shadow in the upper left tibia, which was considered to be an osteogenic nodule, the medullary cavity of the tibia was enlarged, and cortical bone was thinned; C: The patient suffered from psoriasis on both lower extremities.
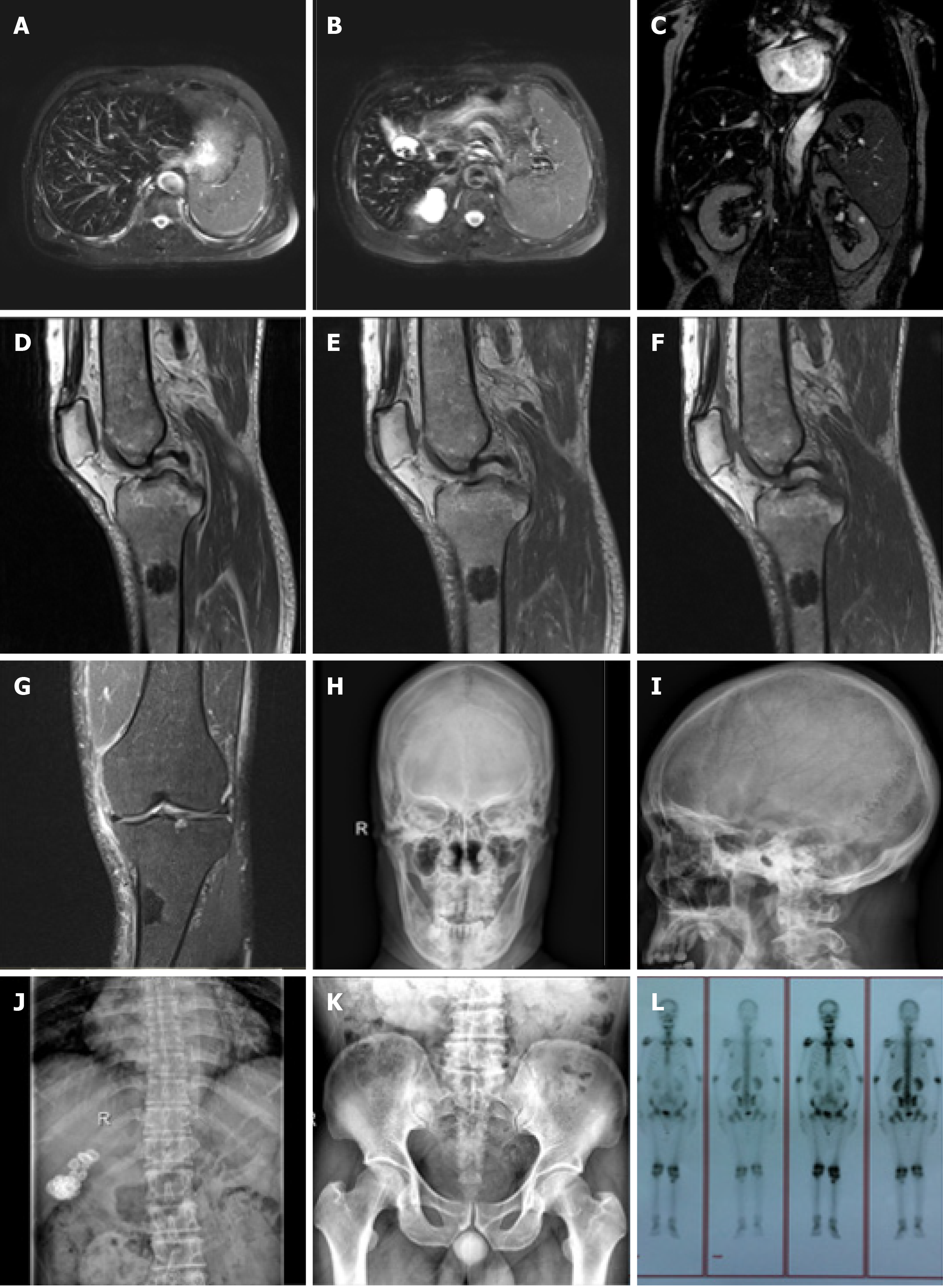
Figure 2 Imaging examination of the patient.
A-C: Hepatic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a decreased hepatic diffuse signal, which was considered to be due to hemochromatosis, spleen enlargement, multiple gallstones and a renal cyst; D-G: MRI of the left knee joint showed wide abnormal mixed concentrations in the marrow cavity of the left femur, tibia, fibula and patella. Nodular lesions were noted in the marrow cavity of the proximal lateral left tibia. Left knee degenerative osteoarthrosis, degeneration and a tear in the anterior horn of the lateral knee joint meniscus, secondary degeneration in the medial meniscus anterior and posterior horn and the lateral meniscus posterior horn were also seen. A small amount of joint effusion was found in the left knee joint capsule, with soft tissue swelling around the knee joint; H-K: X-Ray showed thinned external and internal plates of the frontal bone and occipital bone, widened diploe, a high density striped shadow in the low end of the occipital bone which was considered ligament calcification. Hyperosteogeny of the vertebral body and bilateral acetabular, and slightly rare bone trabecula were observed. A high density shadow on the right upper abdomen which was considered biliary calculi, and increased density in a massive shadow in the right medioventral region were noted; L: The full-body single photon emission computed tomography showed an abnormal spotted radiated concentration on the upper end of the left tibia, abnormal radiated symmetry concentration in extremity joints, and an inflammatory lesion was considered.
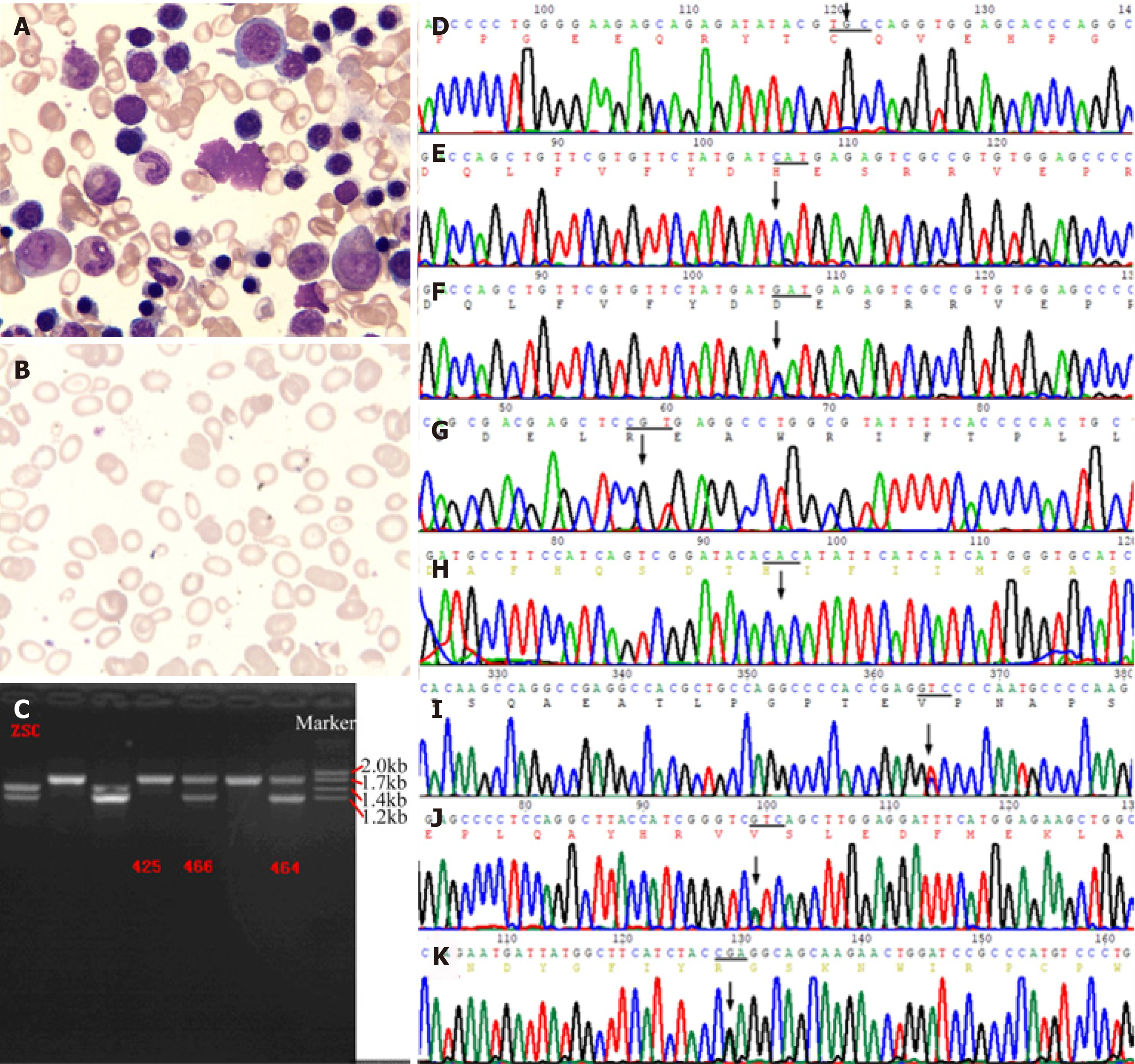
Figure 3 Bone marrow smear and genetic analysis.
A: Bone marrow smear showed erythroid cell hyperplasia, with polychromatic normoblasts. Nucleocytoplasmic development was imbalanced, with visible binuclear and mitotic types. Mature erythrocytes differed in size, which included partially large spherocytes 3%, teardrop 4%, irregular 5%, and fragmented 3% cells. Visible polychromatic erythrocytes and corpuscles were observed. Extracellular iron ++, intracellular iron -19%, +45%, ++28%, +++6%, ringed sideroblasts 2%; B: Blood smear showed obvious erythrocyte hyperplasia, possibly due to hemolytic anemia; C: Two heterozygous deletion mutants of the -α4.2, --SEA carrying globin gene were finally detected; D-H: The patient had p.C282Y and p.H63D of HFE gene, p.R459H and p.H32R of G6PD gene which were wild-type; F: His daughter carried a heterozygous p.H63D mutation of HFE gene; I-K: The patient showed p.A1583V mutation of PIEZO1 gene, p.I103V mutation of POFUT1 gene, and p.Q170R mutation of TGM5 gene.
- Citation: Ruan DD, Gan YM, Lu T, Yang X, Zhu YB, Yu QH, Liao LS, Lin N, Qian X, Luo JW, Tang FQ. Genetic diagnosis history and osteoarticular phenotype of a non-transfusion secondary hemochromatosis. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(23): 5962-5975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i23/5962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5962