Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2020; 8(21): 5235-5249
Published online Nov 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5235
Published online Nov 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5235
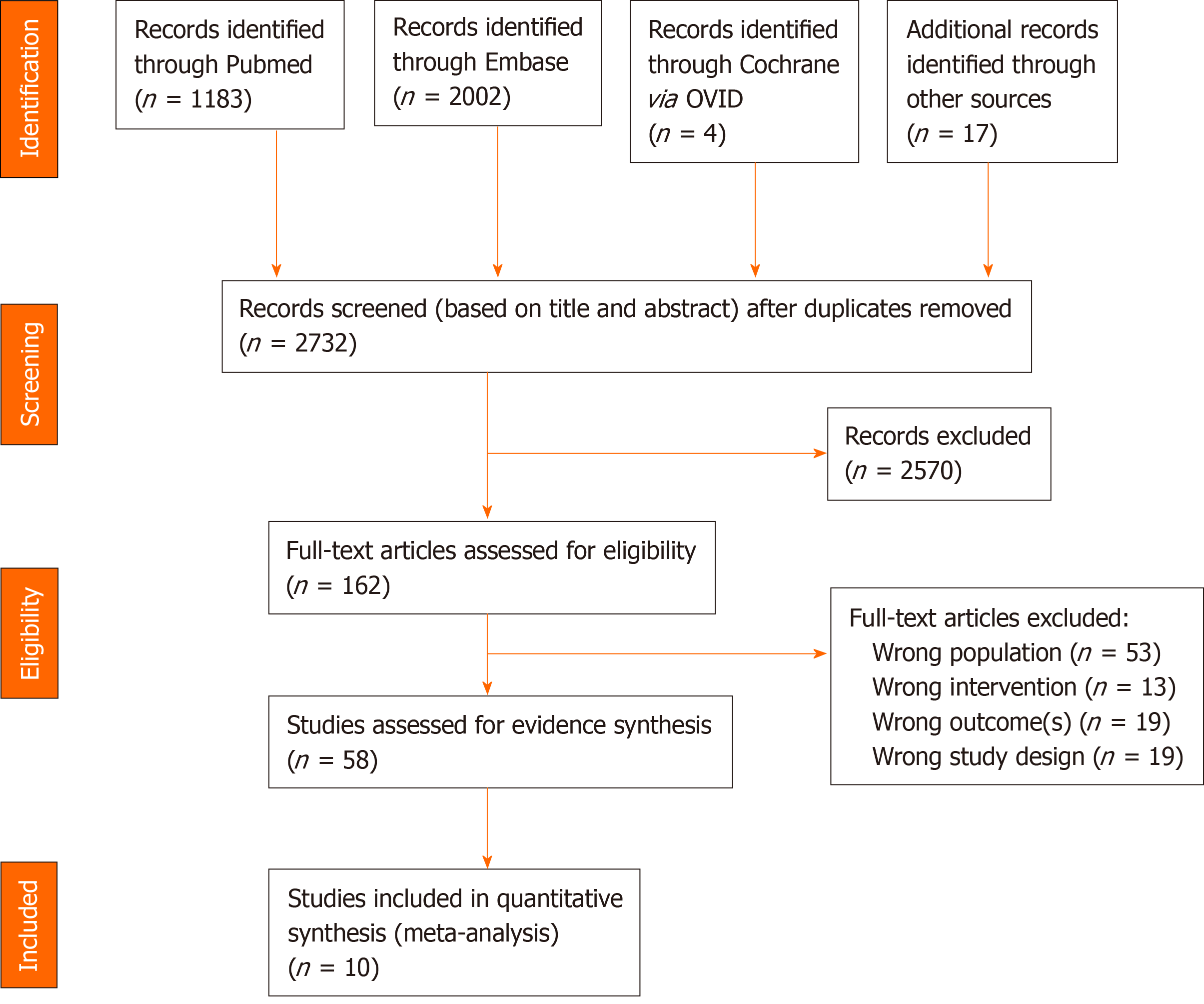
Figure 1 PRISMA diagram of article selection.
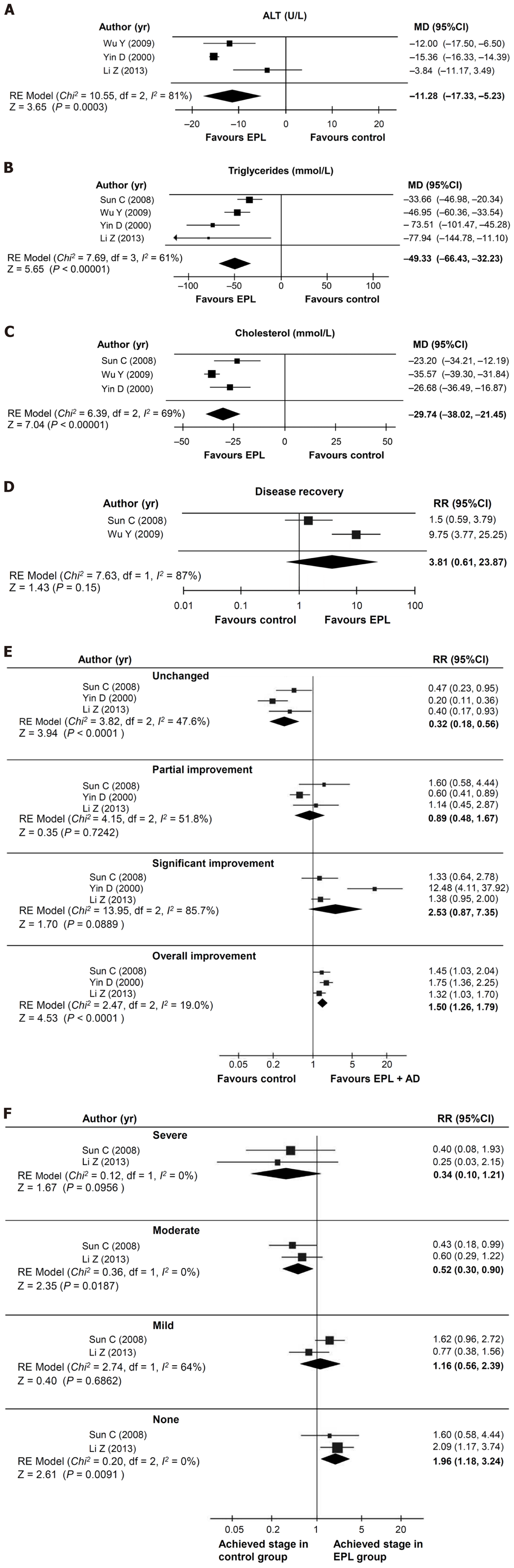
Figure 2 Results of the direct meta-analyses (random effects model) of randomized controlled trials comparing essential phospholipids + antidiabetic therapy with antidiabetic therapy (control).
A: Change in alanine aminotransferase levels; B: Change in triglyceride levels; C: Change in total cholesterol levels; D: Relative risk of recovery; E: Relative risk of change in disease; F: Relative risk of final disease severity. EPL: Essential phospholipids; MD: Mean difference; CI: Confidence interval; RE: Random effects; RR: Relative risk; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
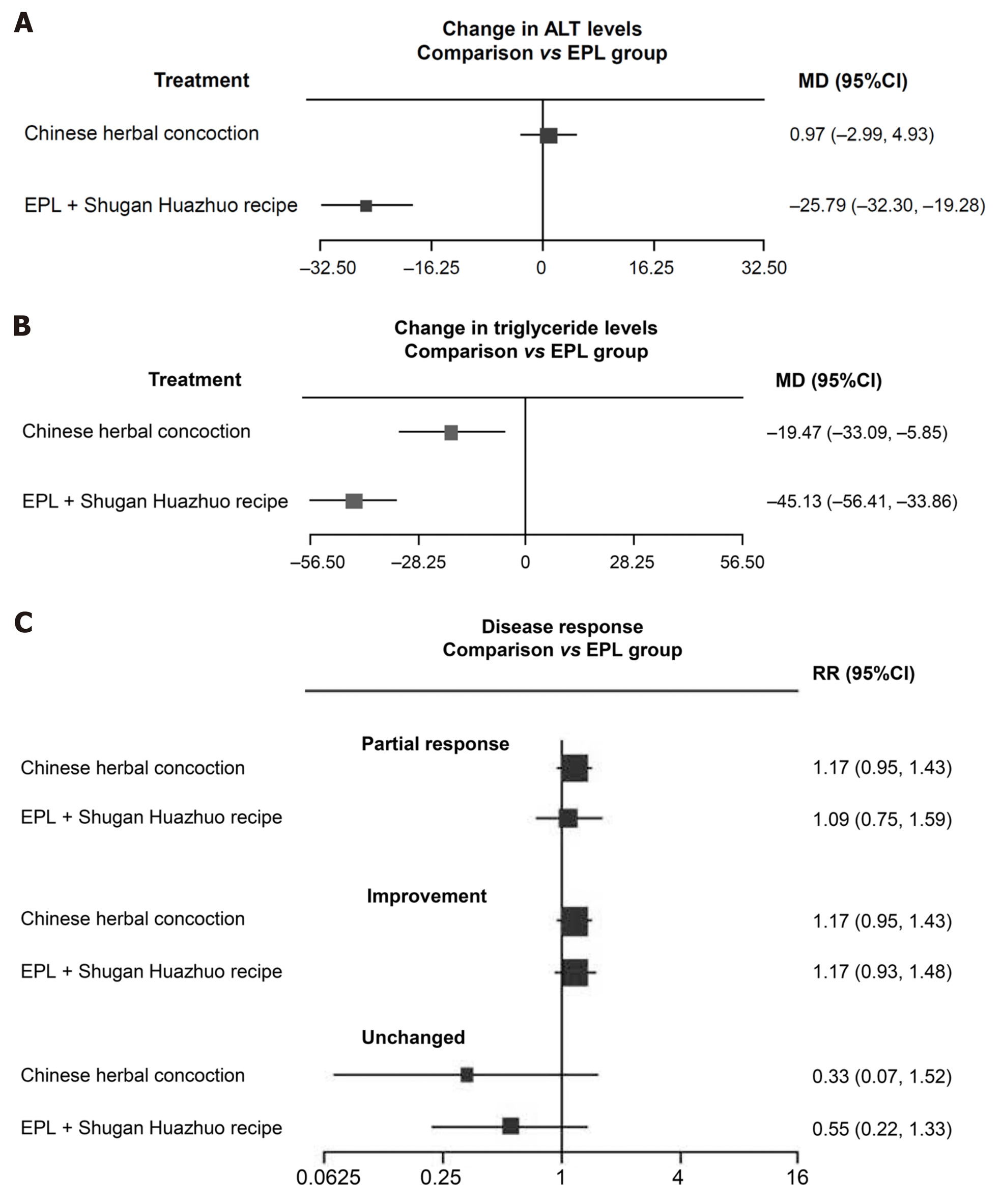
Figure 3 Results of the indirect meta-analyses (random effects model) comparing essential phospholipids with Chinese herbal medicines in combination with essential phospholipids.
A: Change in alanine aminotransferase levels; B: Change in triglyceride levels; C: Relative risk of disease response. EPL: Essential phospholipids; MD: Mean difference; CI: Confidence interval; RR: Relative risk; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
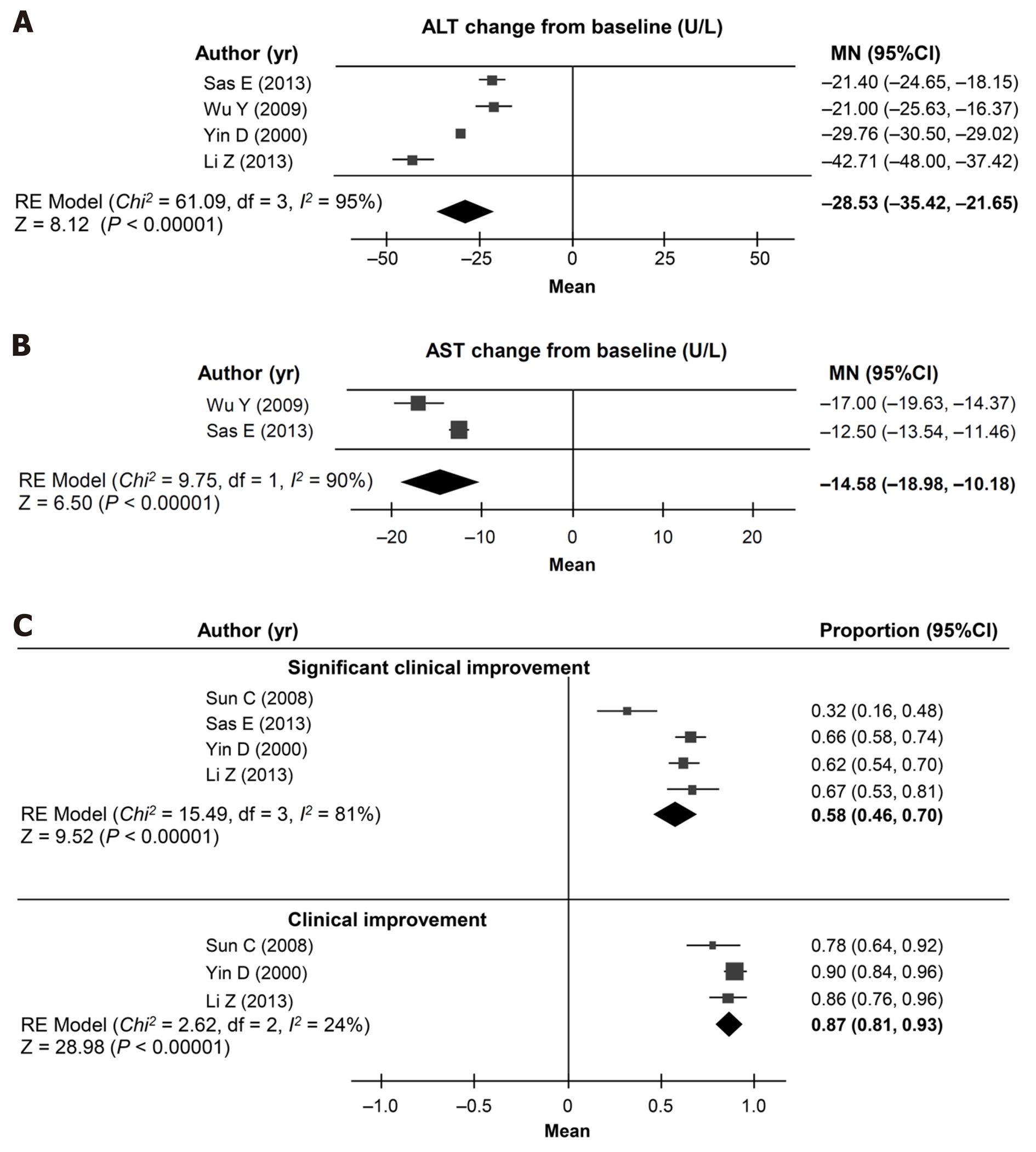
Figure 4 Cohort meta-analysis (random effects model) of outcomes in the non-randomized controlled trials.
A: Change in alanine aminotransferase levels; B: Change in aspartate aminotransferase levels; C: Proportion of patients with an improvement in disease. CI: Confidence interval; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; MN: Mean change from baseline; RE: Random effects.
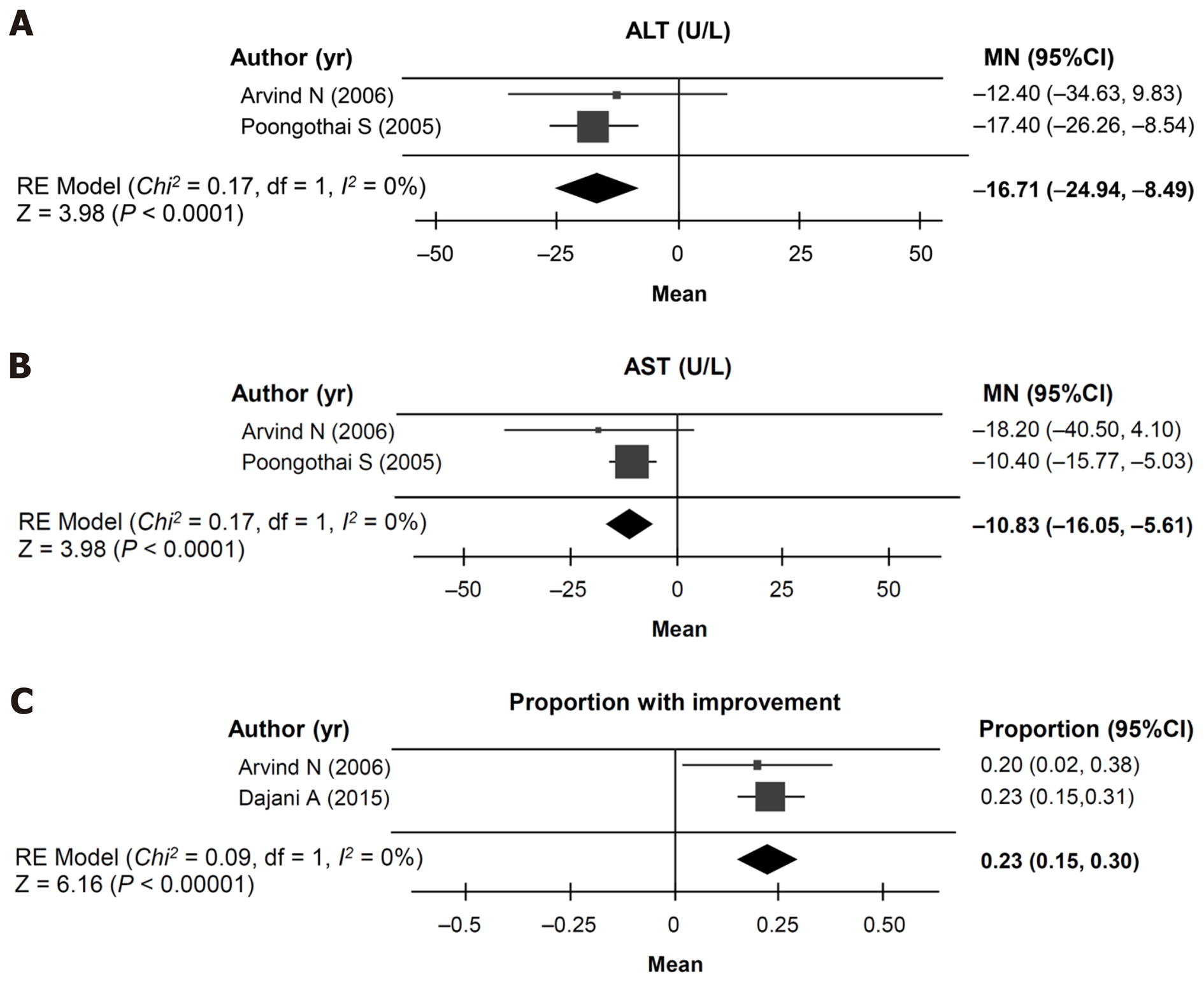
Figure 5 Cohort meta-analysis (random effects model) of outcomes in the randomized controlled trials.
A: Change in alanine aminotransferase levels; B: Change in aspartate aminotransferase levels; C: Proportion of patients with disease improvement. CI: Confidence interval; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; MN: Mean change from baseline; RE: Random effects.
- Citation: Dajani AI, Popovic B. Essential phospholipids for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(21): 5235-5249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i21/5235.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5235