Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2020; 8(21): 5104-5115
Published online Nov 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5104
Published online Nov 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5104
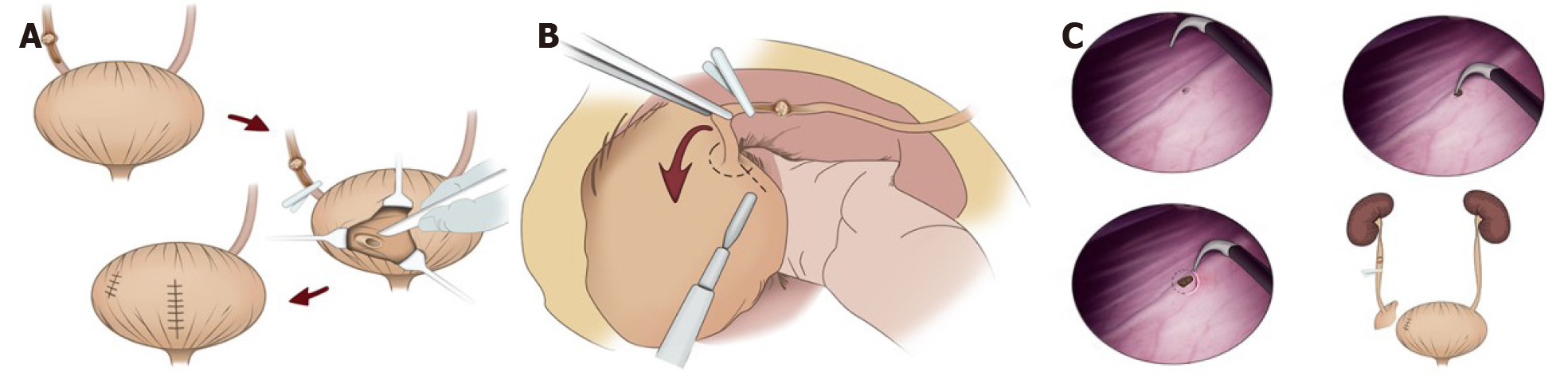
Figure 1 Surgical procedure.
A: An overview of the surgical procedure of intrasvesical incision of the bladder cuff; B: An overview of the surgical procedure of extravesical incision of the bladder cuff; C: An overview of the surgical procedure of transurethral incision of the bladder cuff.
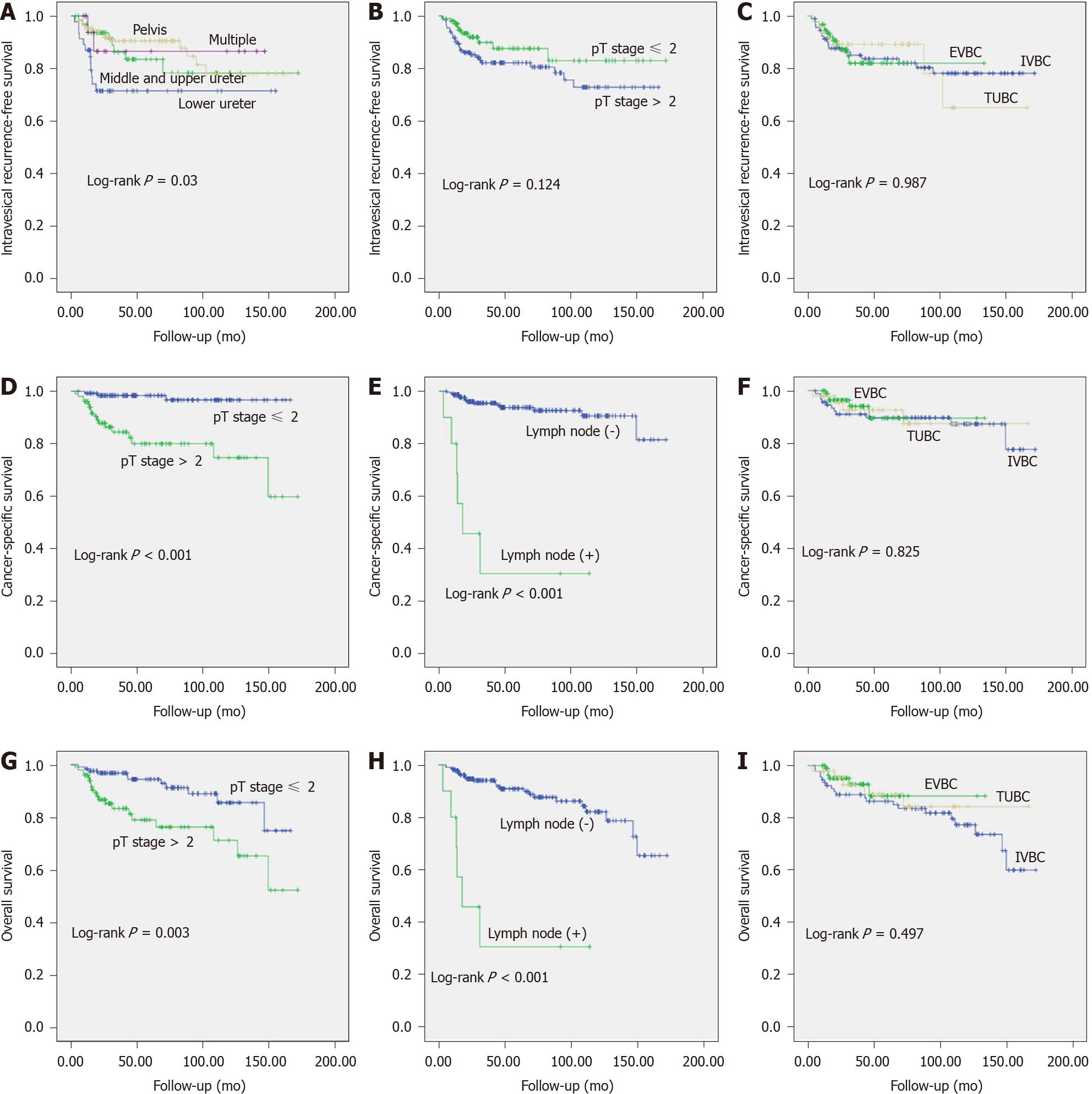
Figure 2 Survival curves for 248 primary urinary tract urothelial carcinoma patients.
A: Intravesical recurrence-free survival (IRFS) by tumor location; B: IRFS by pathological tumor (pT) stage; C: IRFS by different bladder cuff excision (BCE) techniques; D: Cancer-specific survival (CSS) by pT stage; E: CSS by lymph node status; F: CSS by different BCE techniques; G: Overall survival (OS) by pT stage; H: OS by lymph node status; I: OS by different BCE techniques. EVBC: Extravesical incision of the bladder cuff; IVBC: Intrasvesical incision of the bladder cuff; TUBC: Transurethral incision of the bladder cuff.
- Citation: Lai SC, Wu PJ, Liu JY, Seery S, Liu SJ, Long XB, Liu M, Wang JY. Oncological impact of different distal ureter managements during radical nephroureterectomy for primary upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(21): 5104-5115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i21/5104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5104