Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2020; 8(2): 264-275
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i2.264
Published online Jan 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i2.264
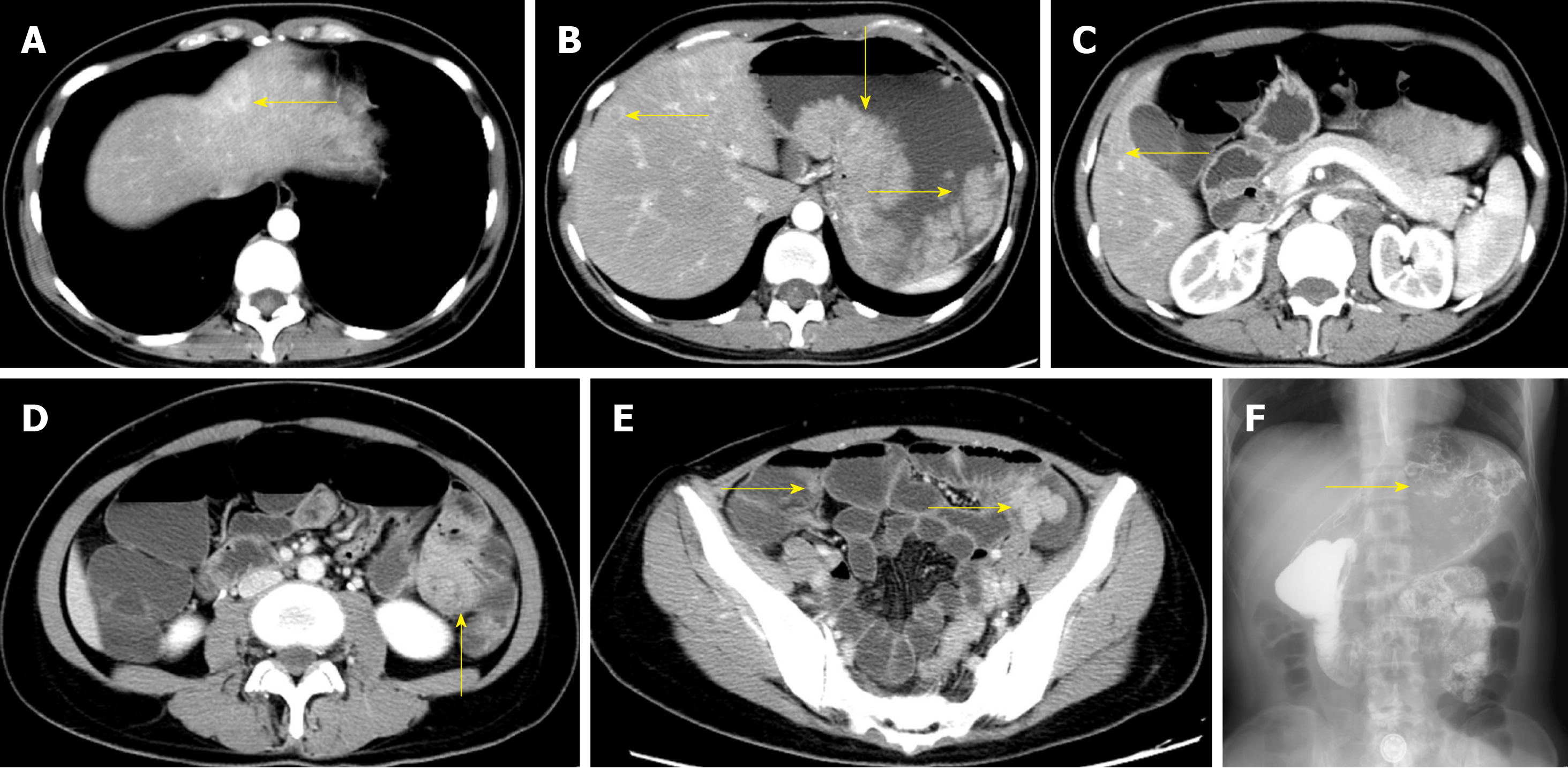
Figure 1 Preoperative imaging and clinical features of case 1.
A: Liver metastasis in segment II; B: Liver metastasis in segment IV; C: Liver metastasis in segment V; D: Intussusception in the small intestine; E: Multiple polyps in the small intestine; F: Large filling defects in the fundus of the stomach by angiography.
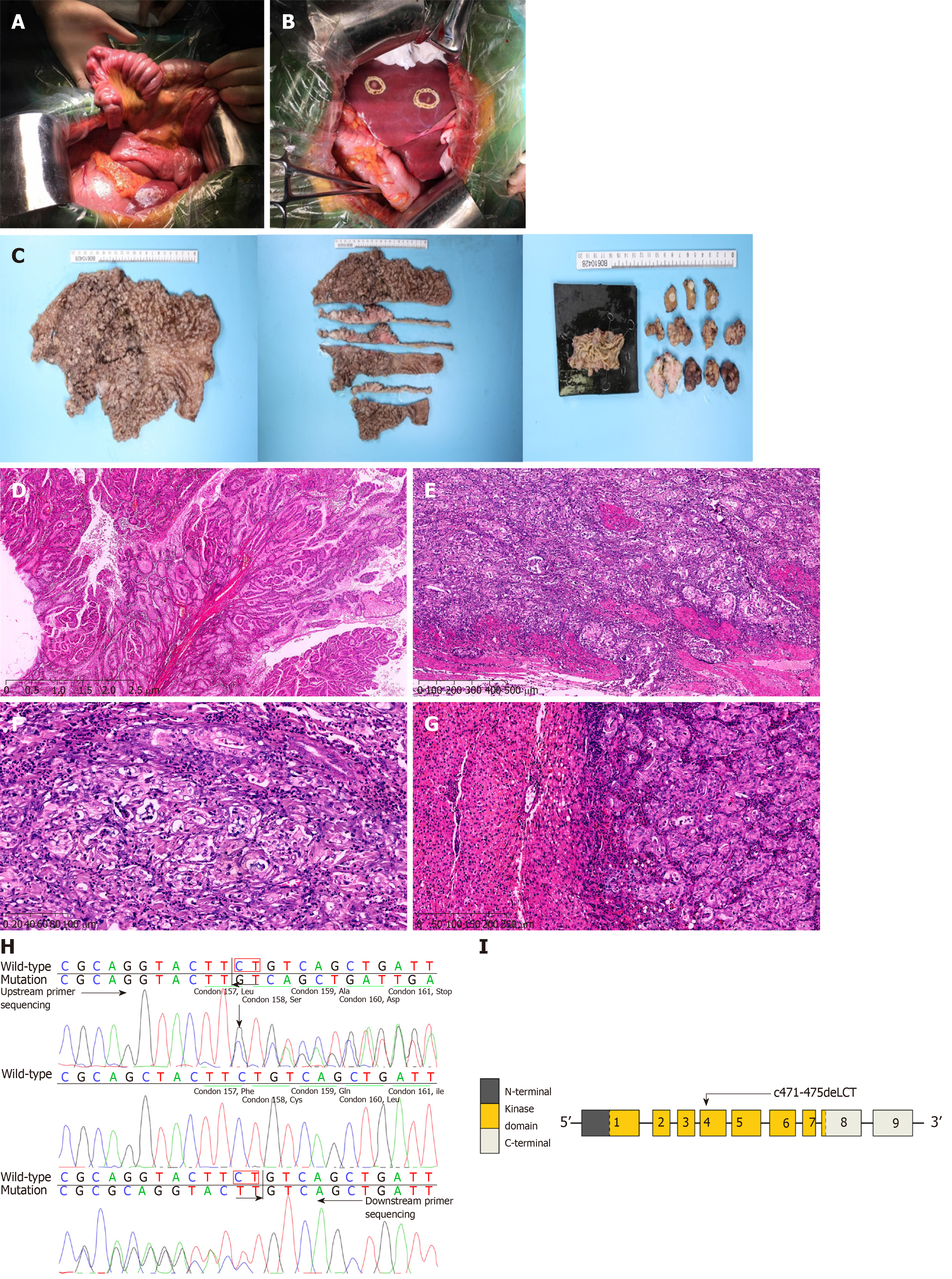
Figure 2 Intraoperative exploration, pathological specimens, and postoperative pathological features of case 1.
A: Small intestinal intussusceptions during intraoperative exploration; B: Liver metastasis observed during intraoperative exploration; C: Total stomach tissue, multiple polyps in the small intestine, intra-hepatic metastatic nodules, and pathological materials; D: P-J polyps (H&E staining; magnification, × 10); E: Carcinomas invading the intrinsic myometrium (H&E staining; magnification, × 50); F: Highly differentiated adenocarcinoma (H&E staining; magnification, × 200); G: Adenocarcinoma infiltration in the liver tissue (H&E staining; magnification, × 100); H: Sanger sequencing (forward and backward) revealed a heterozygous deletion, c.471_472delCT; I: Gene structure of STK11 with a mutation in exon 4.
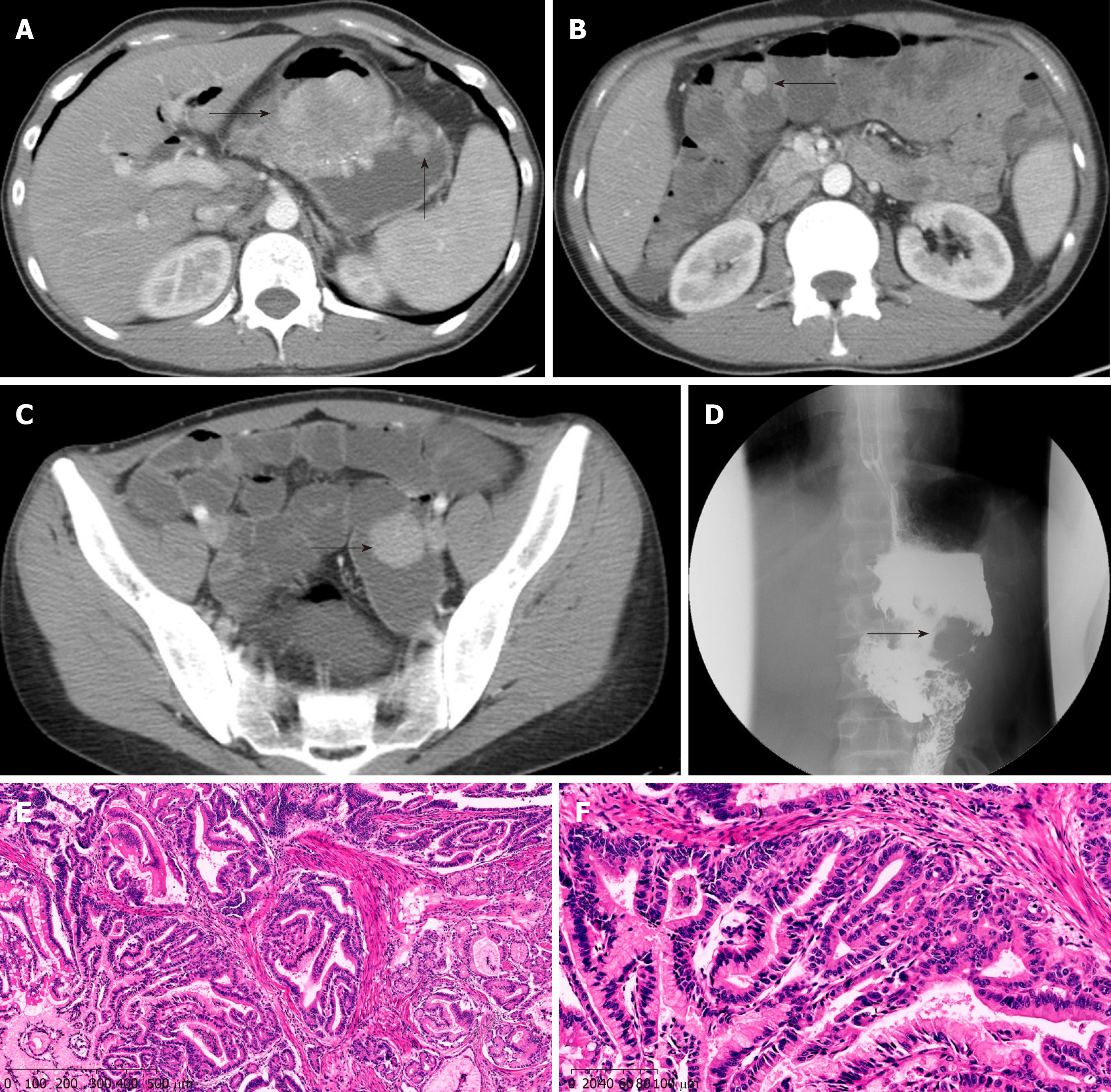
Figure 3 Preoperative imaging and clinical pathological features of case 2.
A: Multiple polyps in the gastric cavity; B: Multiple polyps in the small intestine; C: Polyps in the small intestine; D: Filling defects in the gastric cavity by angiography; E: Carcinomas invading the intrinsic myometrium (H&E staining; magnification, × 100); F: Area of highly differentiated adenocarcinoma (H&E staining; magnification × 400).
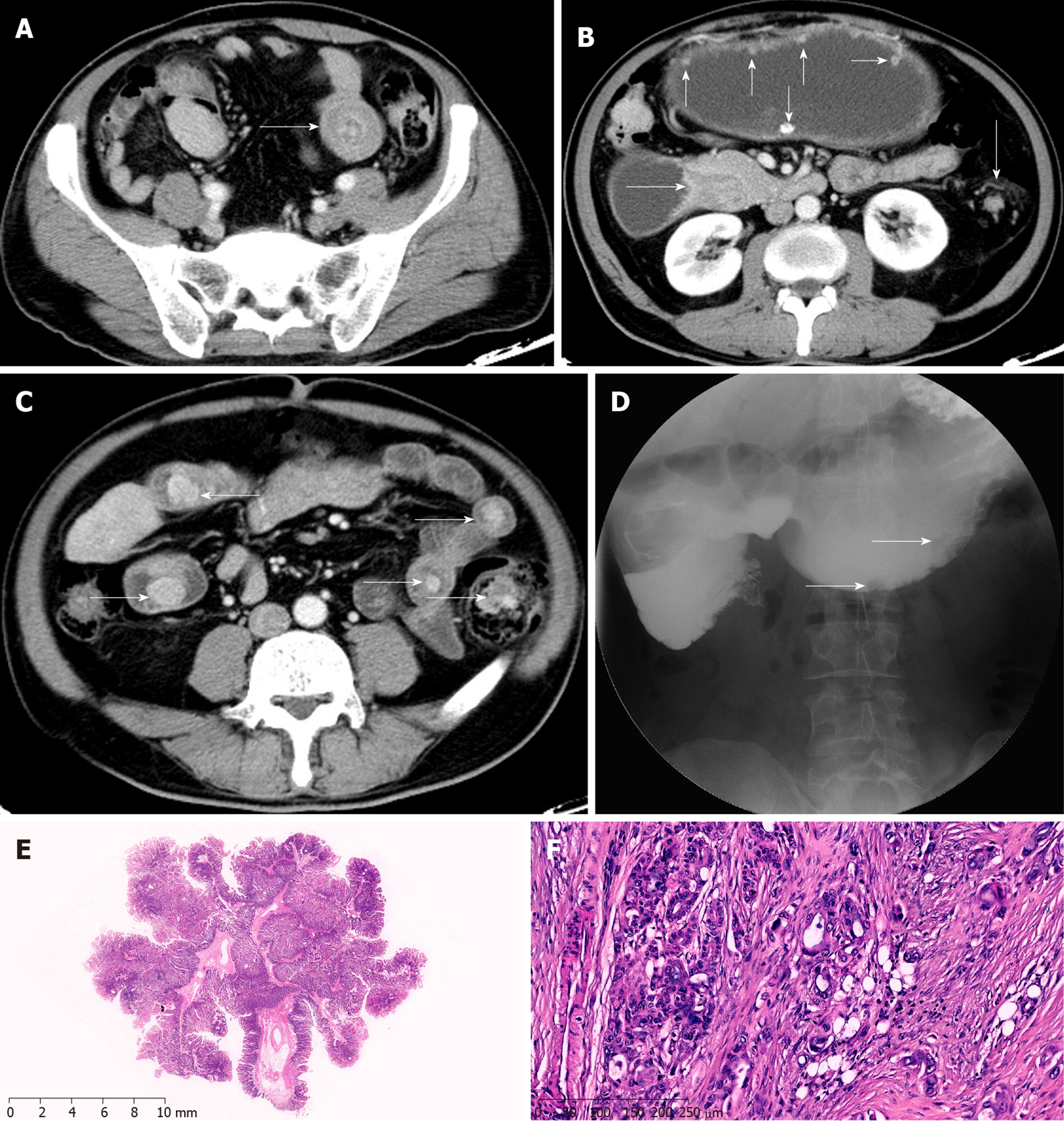
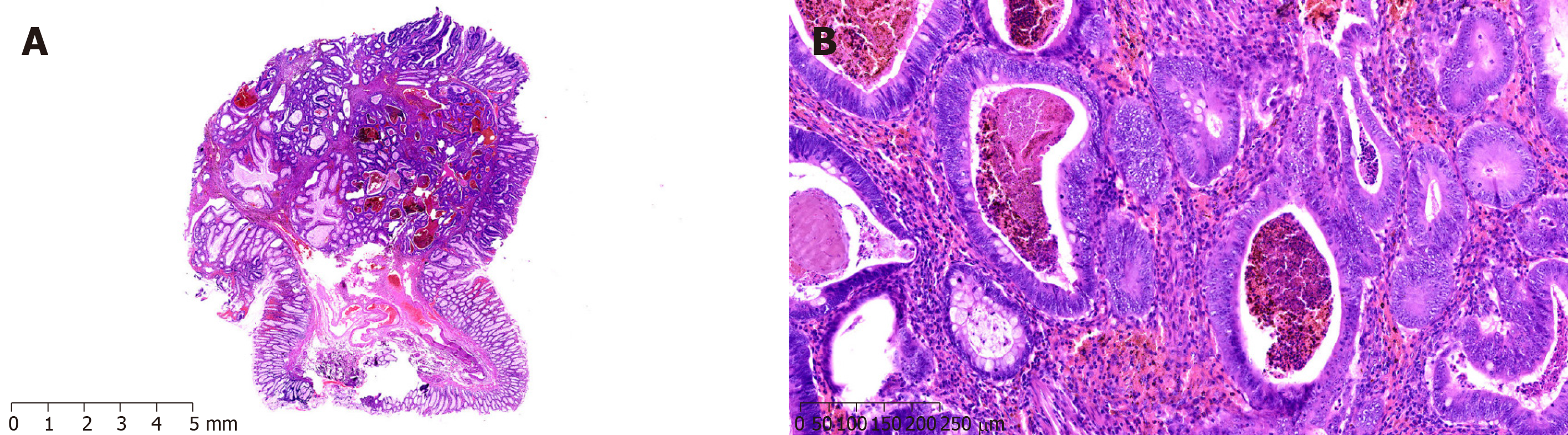
Figure 4 Preoperative imaging and clinical pathological features of case 3.
A: Intussusception in the small intestine; B: Multiple polyps in the abdominal cavity; C: Multiple polyps in the small intestine; D: Small filling defects in the abdominal cavity observed by angiography; E: P-J polyps (H&E staining; magnification, × 10); F: Adenocarcinoma infiltration in the fibrous tissue (H&E staining; magnification, × 100).
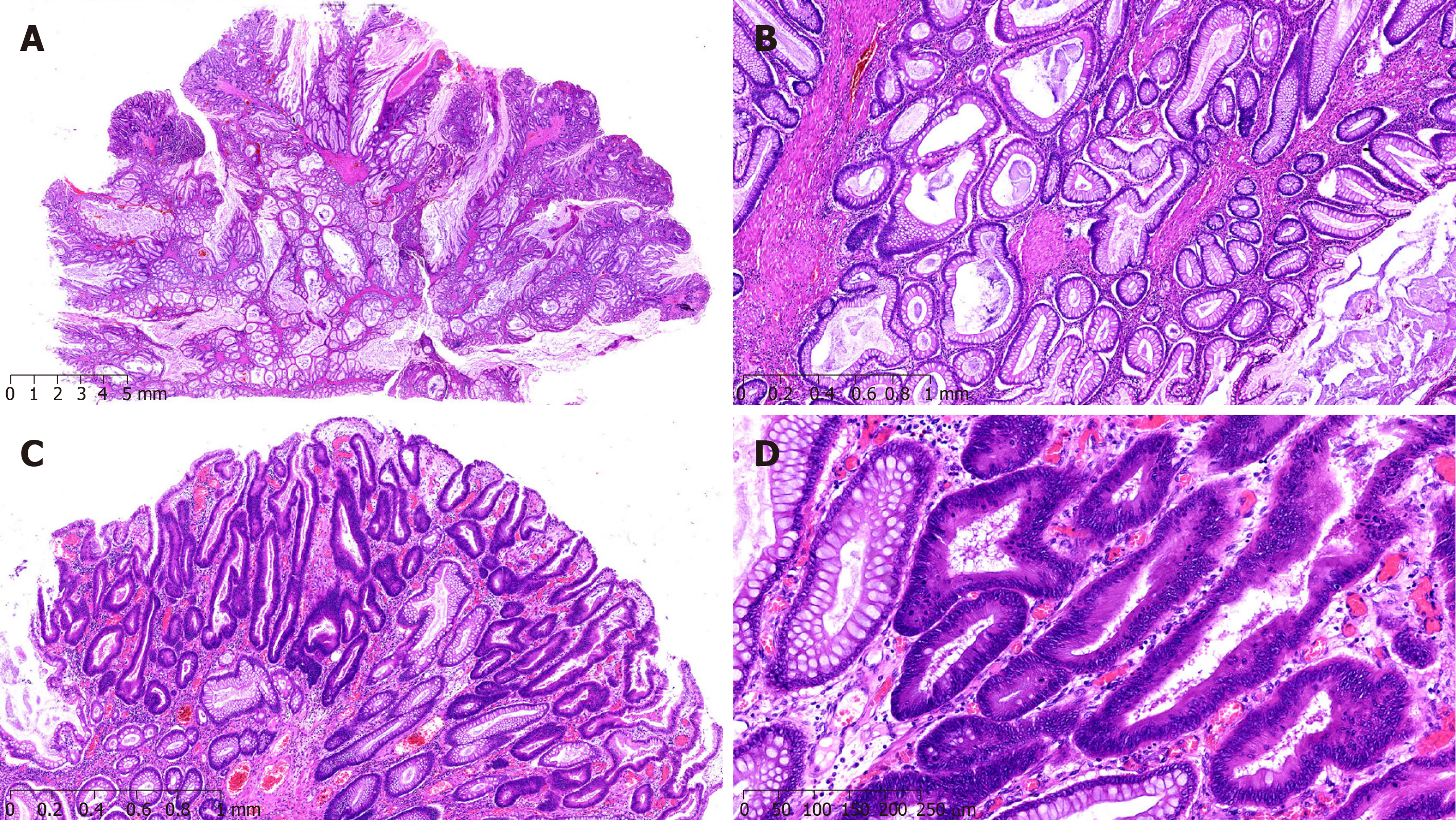
Figure 5 Clinical pathological features of case 4.
A: P-J polyps (H&E staining; magnification, × 10); B: P-J polyps (H&E staining; magnification, × 100); C: The epithelium of polyps showed highly heterogeneous hyperplasia (H&E staining; magnification, × 50); D: The epithelium of polyps showed highly heterogeneous hyperplasia (H&E staining; magnification, × 100).
Figure 6 Clinical pathological features of case 5.
A: P-J polyps (H&E staining; magnification, × 10); B: The epithelium partly showed high grade intraepithelial neoplasia (H&E staining; magnification, × 200).
- Citation: Zheng Z, Xu R, Yin J, Cai J, Chen GY, Zhang J, Zhang ZT. Malignant tumors associated with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: Five cases from a single surgical unit. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(2): 264-275
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i2/264.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i2.264