Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2020; 8(15): 3341-3348
Published online Aug 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3341
Published online Aug 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3341
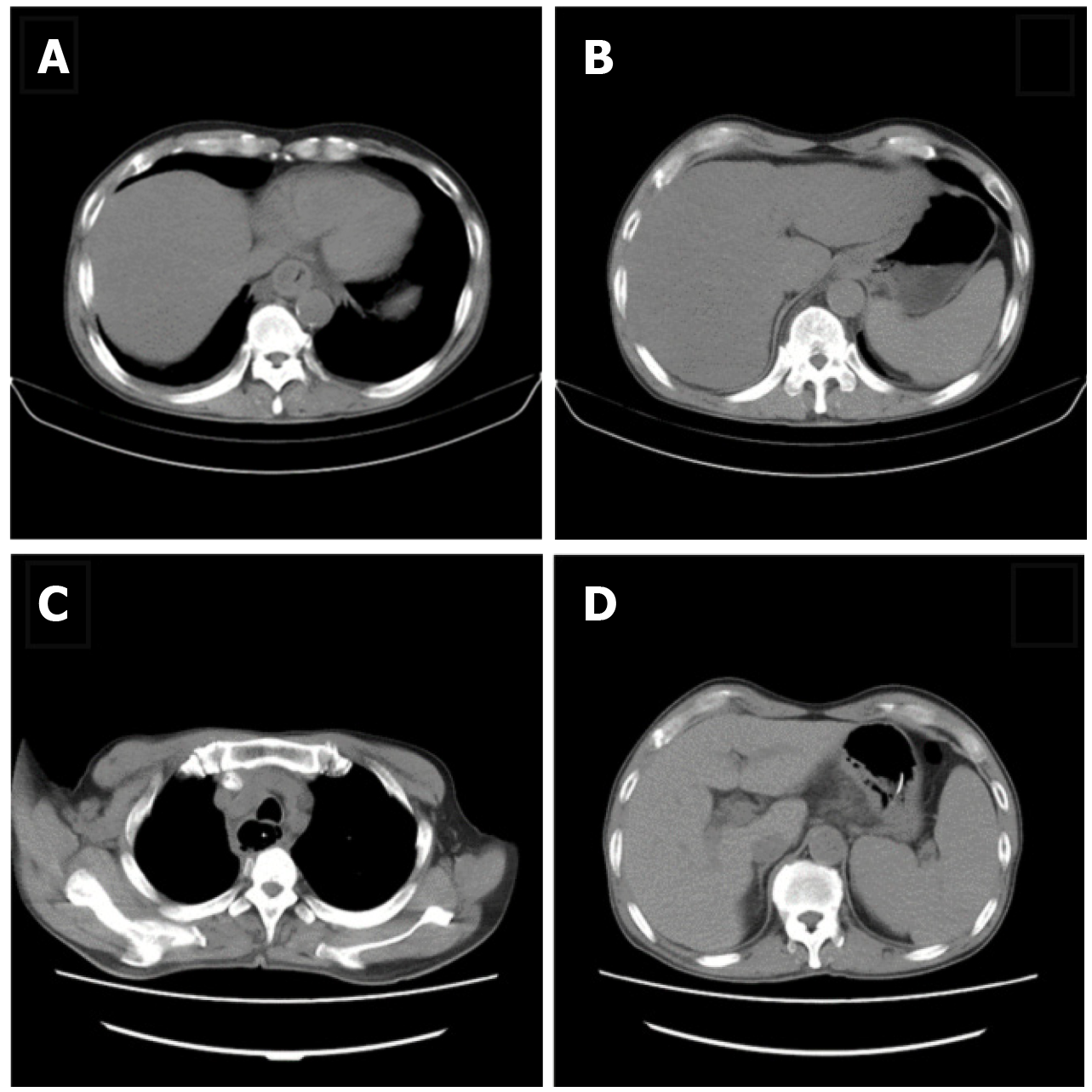
Figure 1 Thoracic computed tomography.
A: Thoracic computed tomography (CT) scan showed oesophageal dilatation and effusion, wall thickening of the lower oesophagus, inflammation of the upper lobe of the right lung, and bilateral pleural effusion; B: Abdominal CT scan showed thickening of the gastric wall of the cardia and adjacent lesser curvature of the stomach, fatty liver, and gallstones; C: Chest CT scan re-examination revealed oesophageal mucosal exfoliation involving the stomach wall. Right upper and middle lobe inflammation had improved since the previous report and oesophageal dilatation and effusion had reduced; D: Abdominal CT scan showed thickening of the gastric wall of the cardia and adjacent lesser curvature of the stomach which was the same as the previous review.
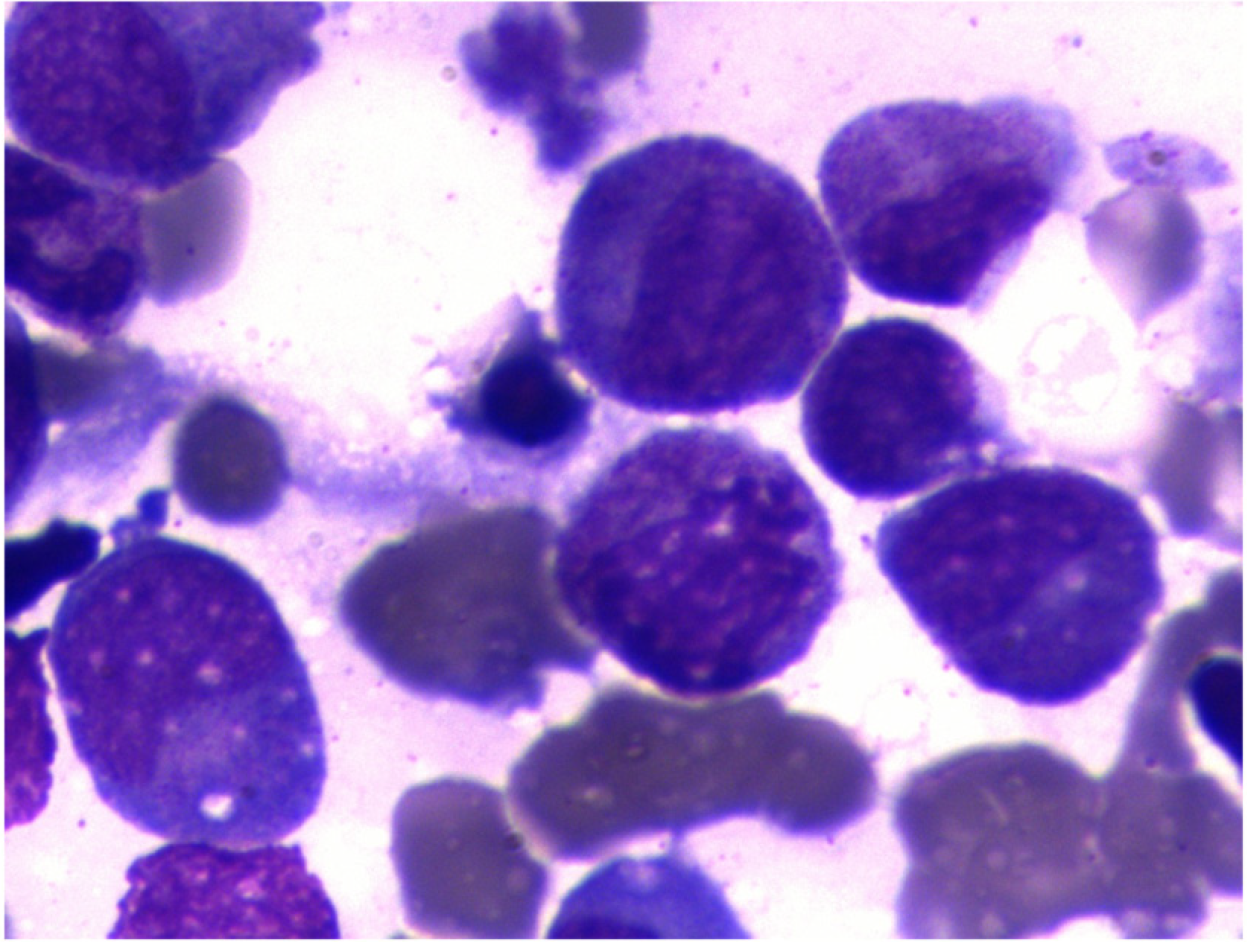
Figure 2 Bone marrow aspiration biopsy indicated erythroid hyperplasia due to thrombocytopenia.
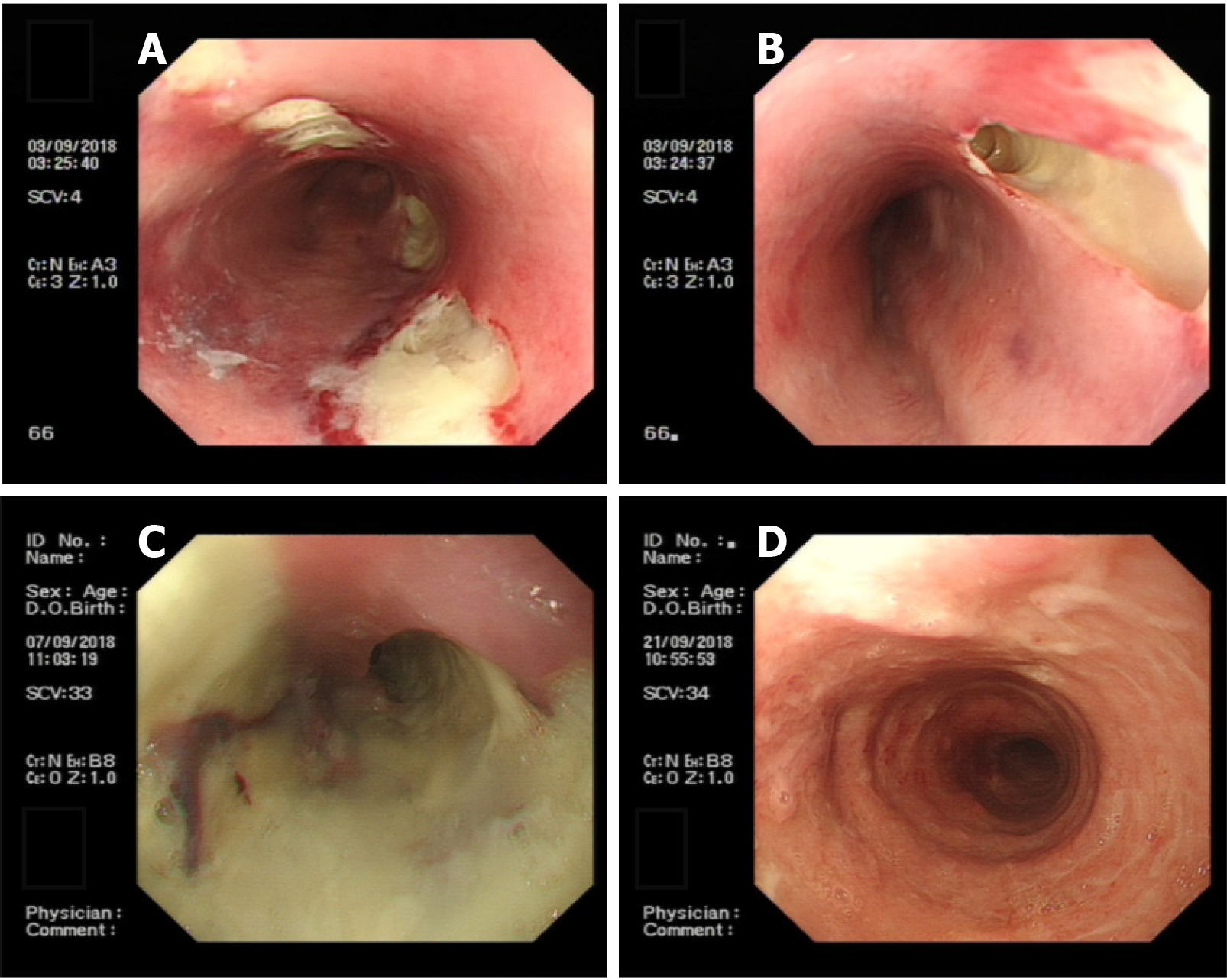
Figure 3 Endoscopic oesophageal mucosal lesions.
A: Endoscopic view showing there were 4 deep ulcers in the oesophagus 30 cm from the incisor teeth, which appeared to be fistulae, ranging in size from 0.5 cm to 3 cm × 1 cm to 3 cm, the mucosa and sub-mucosa were completely destroyed and the surface was covered with necrotic tissue and pus; B: Endoscopic view showing a deep ulcer, 3 cm × 3 cm in size, in the oesophagus 30 cm from the incisor teeth, which appeared to be fistula, the mucosa and sub-mucosa were completely destroyed, and the surface was covered with necrotic tissue and pus; C: Endoscopic view showing 4 deep ulcers merged with each other 30 cm from the incisor teeth, necrotic substances and pus covered the entire circumference of the oesophagus; D: Endoscopic view showing visible granulation tissue on the surface of the entire circumference of the oesophageal mucosal lesion 21 to 38 cm from the incisor teeth.
- Citation: Men CJ, Singh SK, Zhang GL, Wang Y, Liu CW. Acute suppurative oesophagitis with fever and cough: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(15): 3341-3348
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i15/3341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3341