Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2020; 8(14): 3057-3063
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3057
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3057
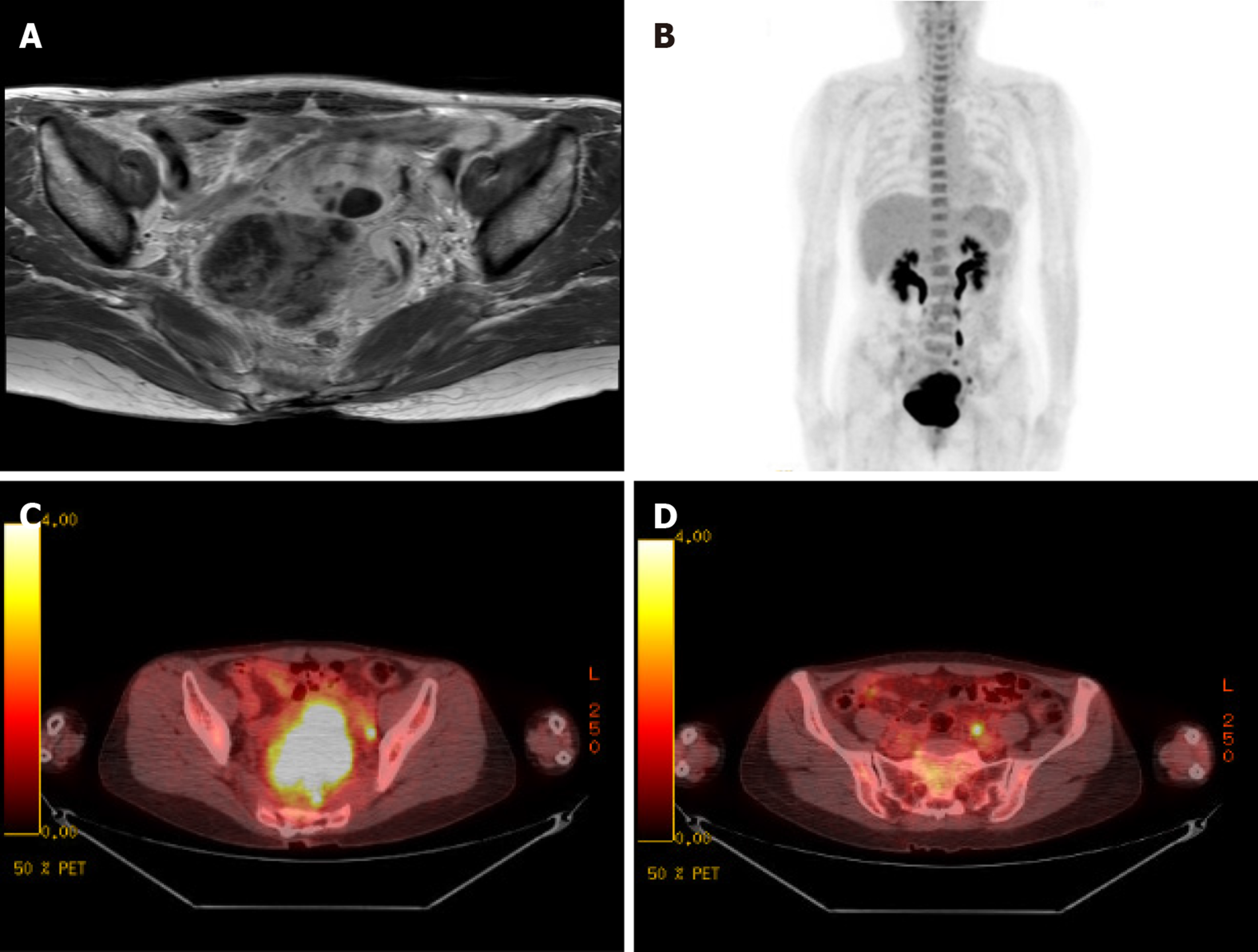
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography image.
A: T1 weighted axial image showing a low intensity mutiseptated cystic lesion on the pelvic cavity and uterus; B: Positron emission tomography-computer tomography image (PET-CT) shows multiple hypermetabolic foci at the pelvis; C: PET-CT showing high 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in the rectum and uterus; D: FDG uptakes are noted in the left internal iliac lymph node.
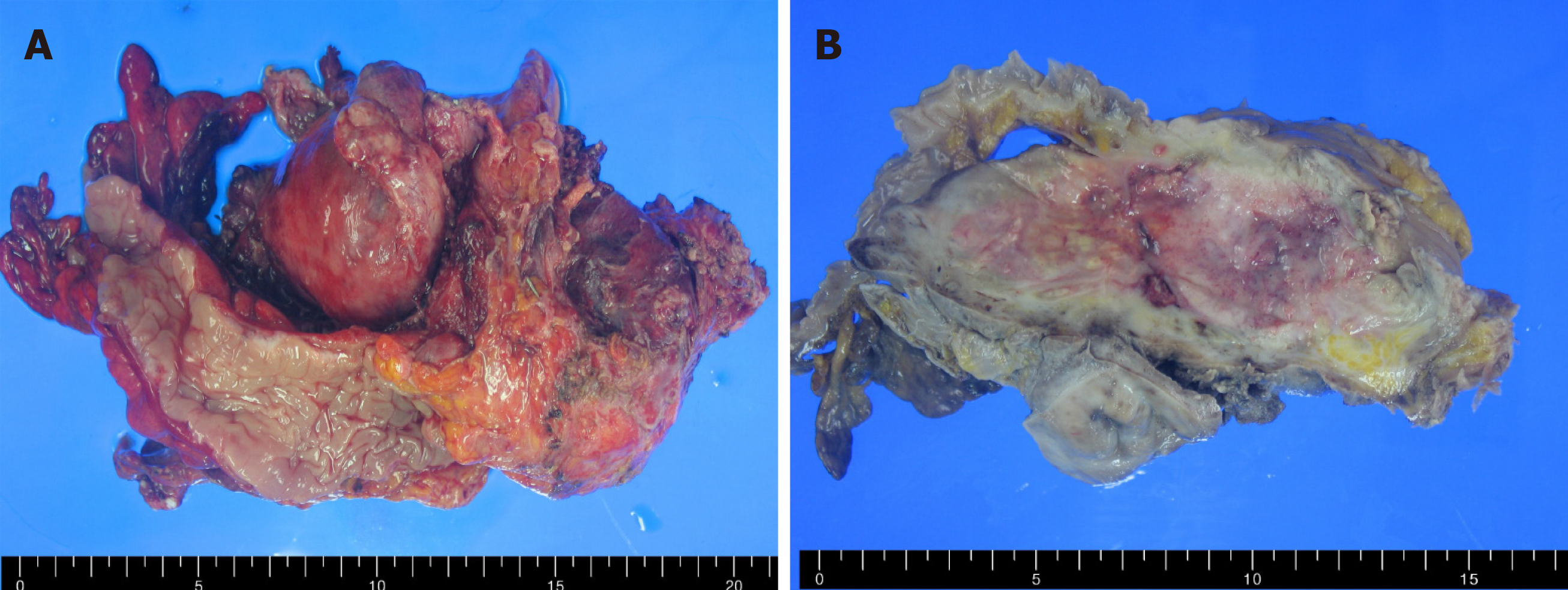
Figure 2 En bloc resected tumor.
A: Fresh specimen; B: Formalin fixed specimen.
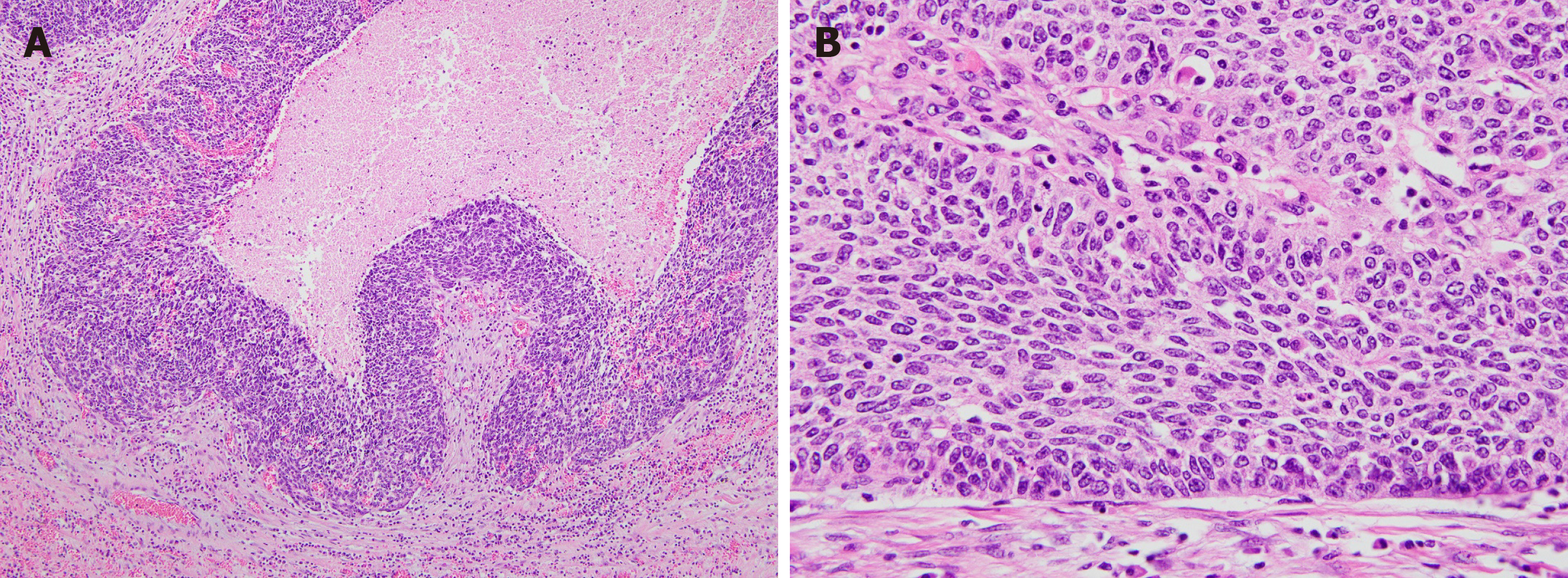
Figure 3 Pathological findings of the tumor.
A: At a lower power view, the tumor shows a poorly differentiated carcinoma with solid growth pattern and foci of intratumoral necrosis (× 200); B: At a high power view, tumor cells are pleomorphic and shows scant cytoplasm. Tumor cells are arranged perpendicularly to the boundary between the tumor and adjacent normal tissue (× 400).
- Citation: Lee TG, Yoon SM, Kim MJ. Successful treatment of basaloid squamous cell carcinoma in the rectosigmoid colon: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(14): 3057-3063
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i14/3057.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3057