Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2020; 8(13): 2749-2757
Published online Jul 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i13.2749
Published online Jul 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i13.2749
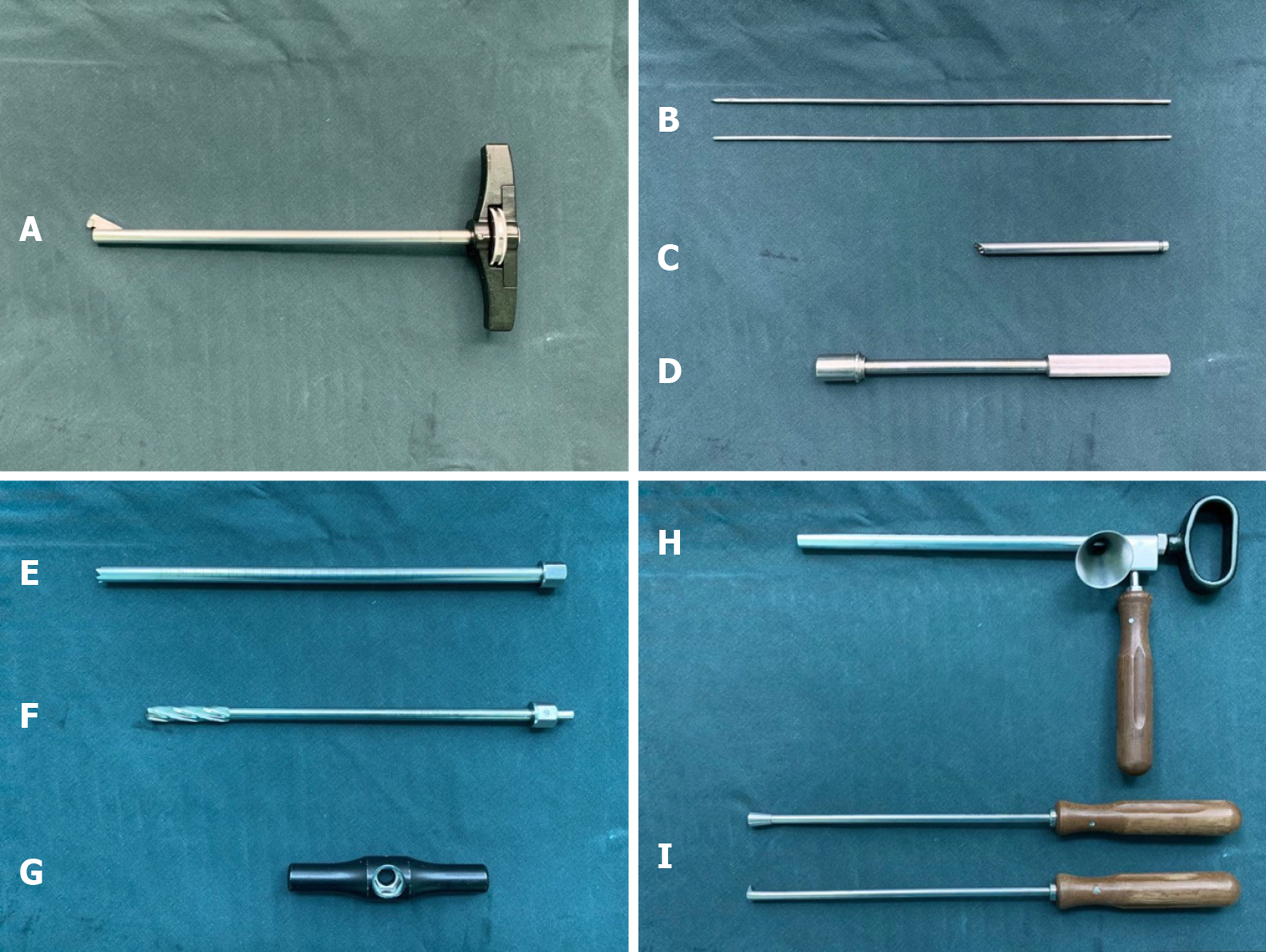
Figure 1 The tool for the surgery (Yierkang Technology Development Co.
, Ltd, Beijing, China). A: Single blade expandable reamer; B: 2.5 mm guide wire; C: The guiding device with a convex tip (introducer) for fixing it on the lateral cortical bone of femur; D: Retainer of the introducer; E: Trephine; F: Cannulated drill; G: Handle of the trephine and cannulated drill; H: Bone graft funnel; I: Pestles.
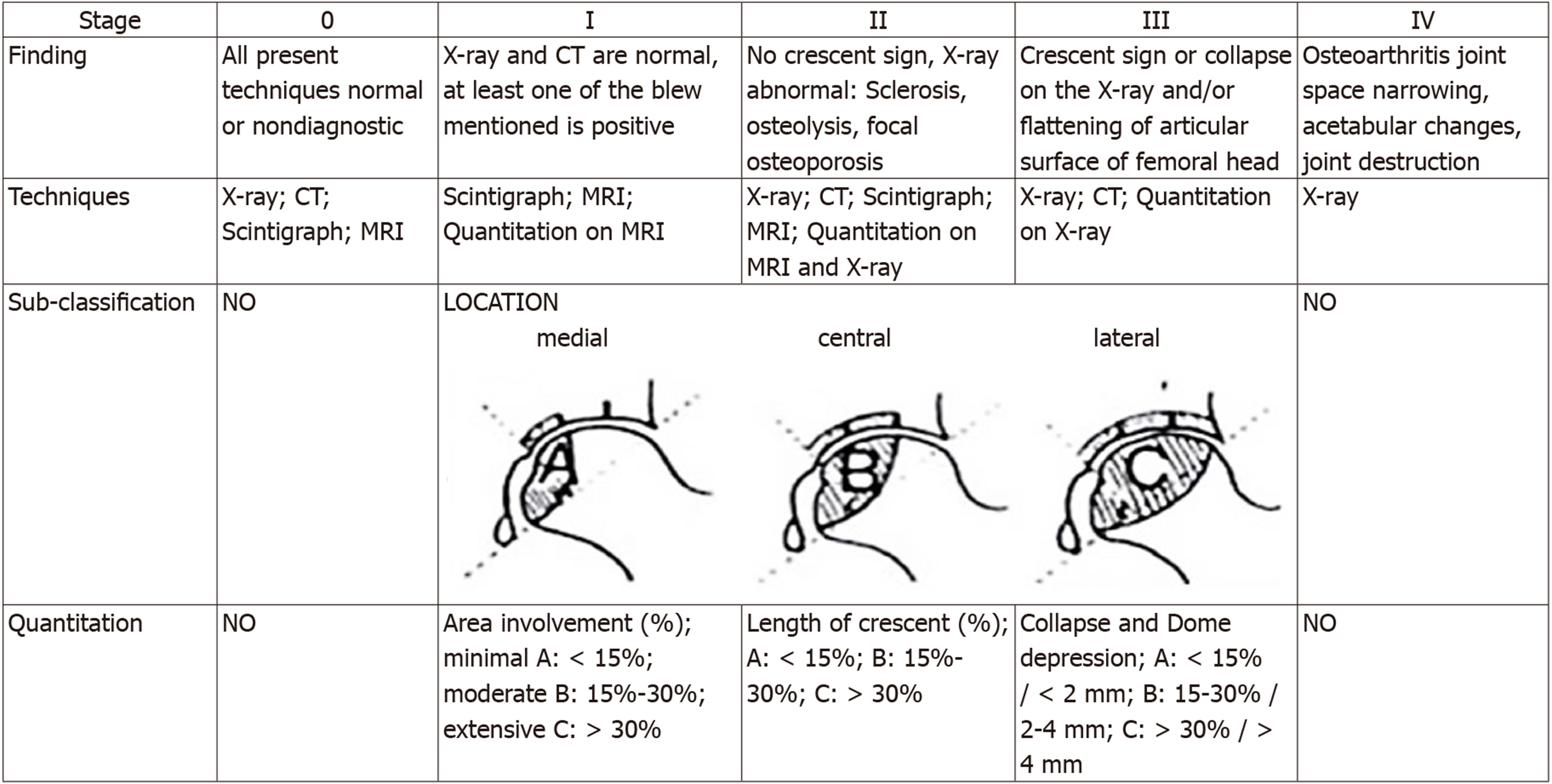
Figure 2 Association Research Circulation Osseous classification system.
CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
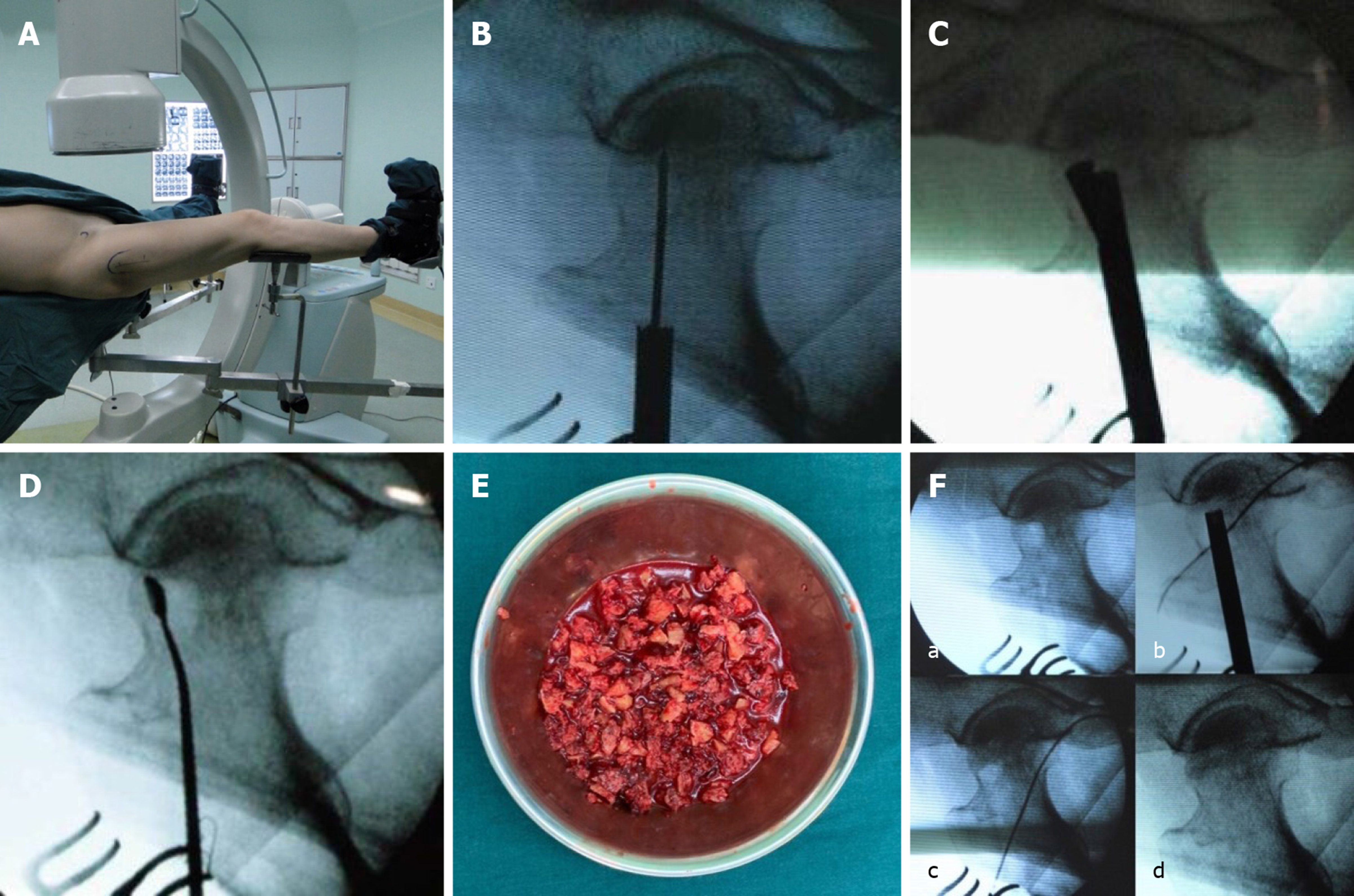
Figure 3 The main steps of the percutaneous expanded decompression and mixed bone graft technique under C-arm fluoroscopy.
A: Intraoperative posture of the patient; B: A 12 mm trephine into the lesion area under guidance of the introducer; C: Turning the handle and the blade control knob on it. The reamer can be rotated and the blades expanded; D: The residual necrotic lesions are removed by cleaning with a sharp spoon; E: Autologous bone from the ipsilateral ilium mixing allogeneic bone pieces with bone marrow aspirate; F: a: Before bone grafting; b: Introduce the bone graft funnel into the drilling channel; c: Tamp the mixture with a pestle; d: Bone graft completed.
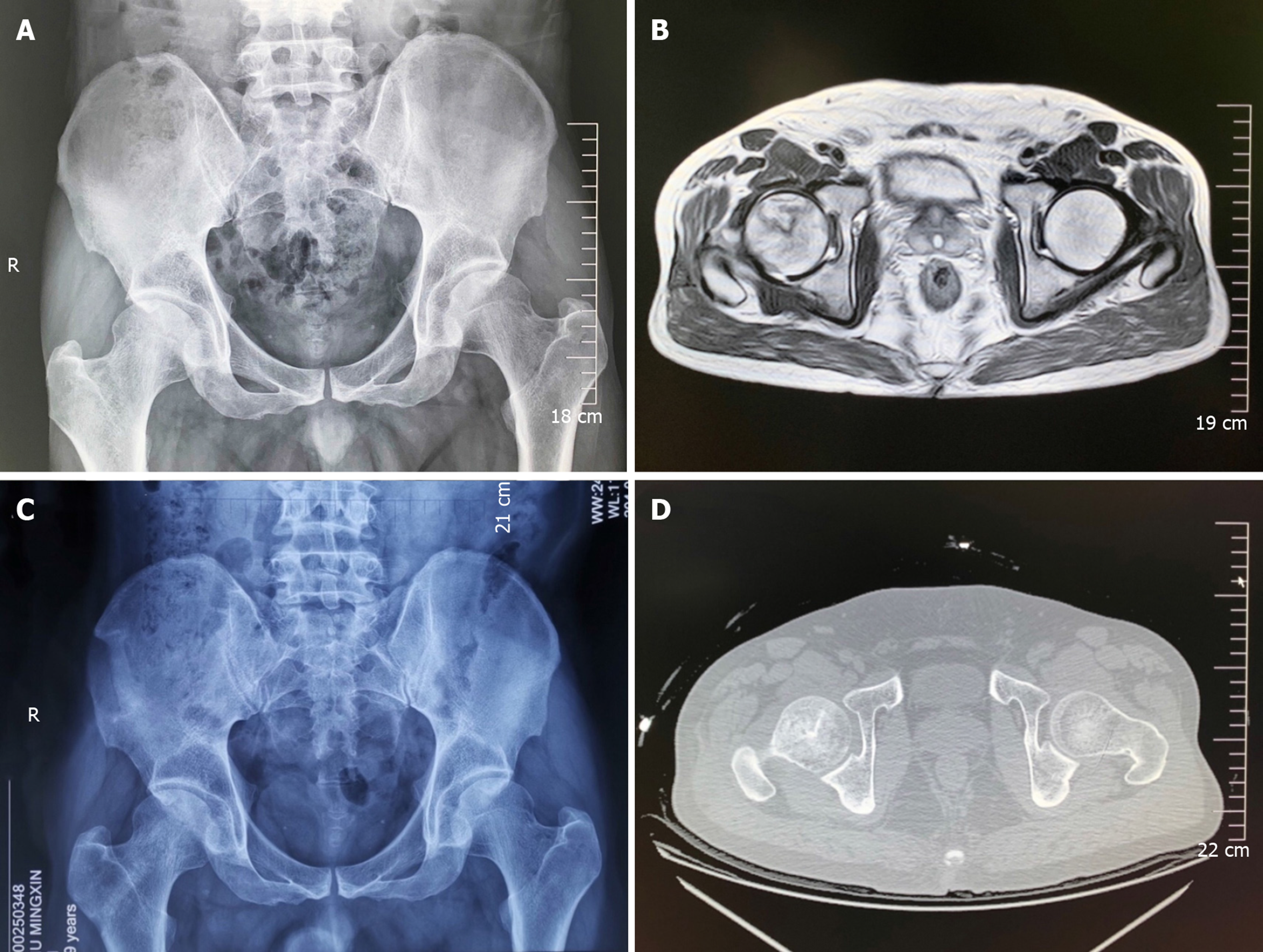
Figure 4 Radiography and computed tomography of the implanted bone.
A: Preoperative radiograph; B: Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging; C: Postoperative radiograph; D: Postoperative computed tomography.
- Citation: Lin L, Jiao Y, Luo XG, Zhang JZ, Yin HL, Ma L, Chen BR, Kelly DM, Gu WK, Chen H. Modified technique of advanced core decompression for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(13): 2749-2757
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i13/2749.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i13.2749