Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2020; 8(11): 2374-2379
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2374
Published online Jun 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2374
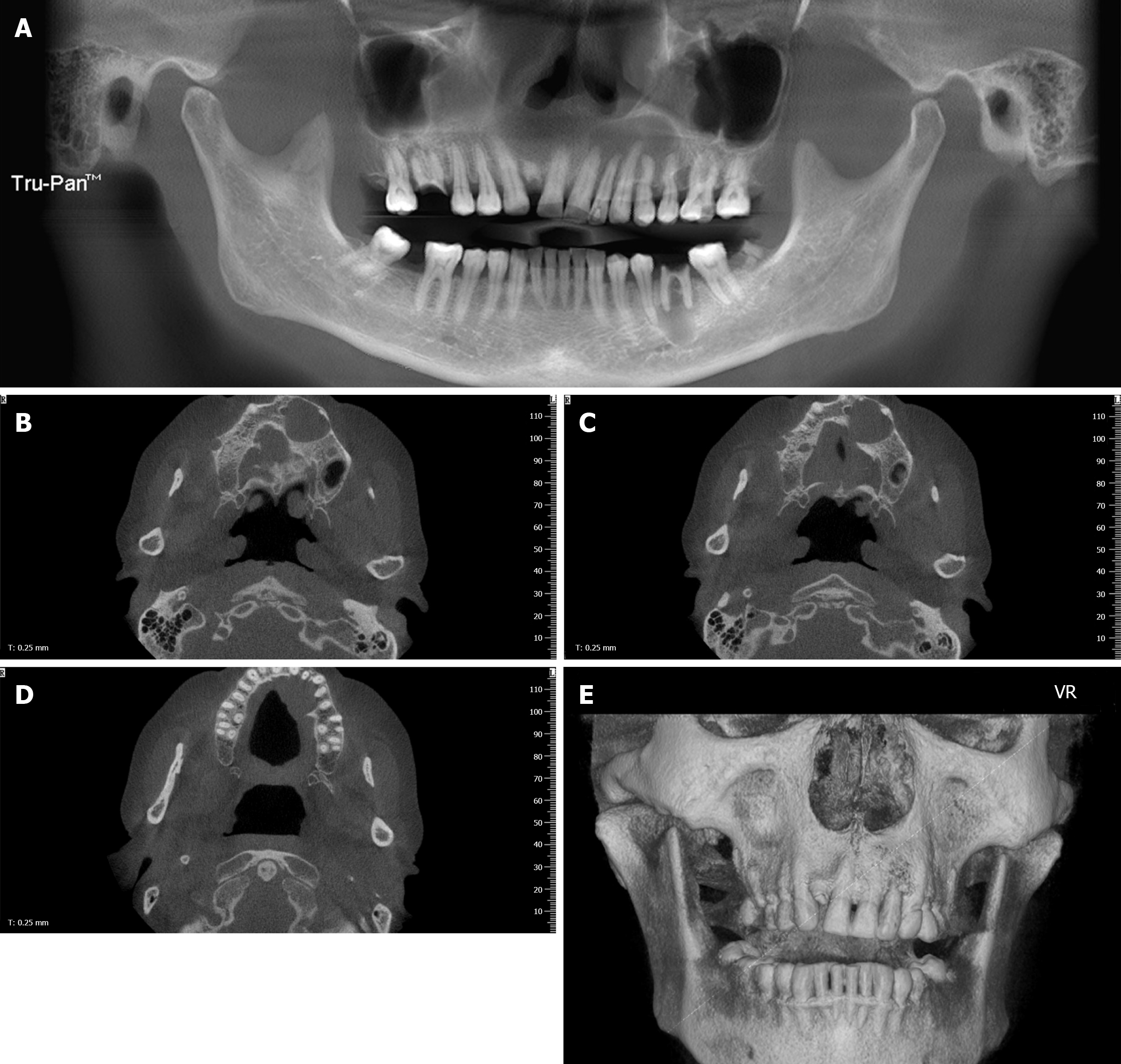
Figure 1 Images of cone beam computed tomography.
A: Panoramic radiograph revealing a cystic lesion in the left maxilla and periapical radiolucency of inflammatory origin in the left first mandibular molar. The left maxillary lesion extended from the left maxillary central incisor to the left secondary maxillary premolar and showed no evident root resorption; B-D: An axial scan revealed buccal and palatal swelling of the cystic lesion with a clear boundary and a palatal cortex defect; E: Three-dimensional imaging revealed an intact labial maxillary bone.
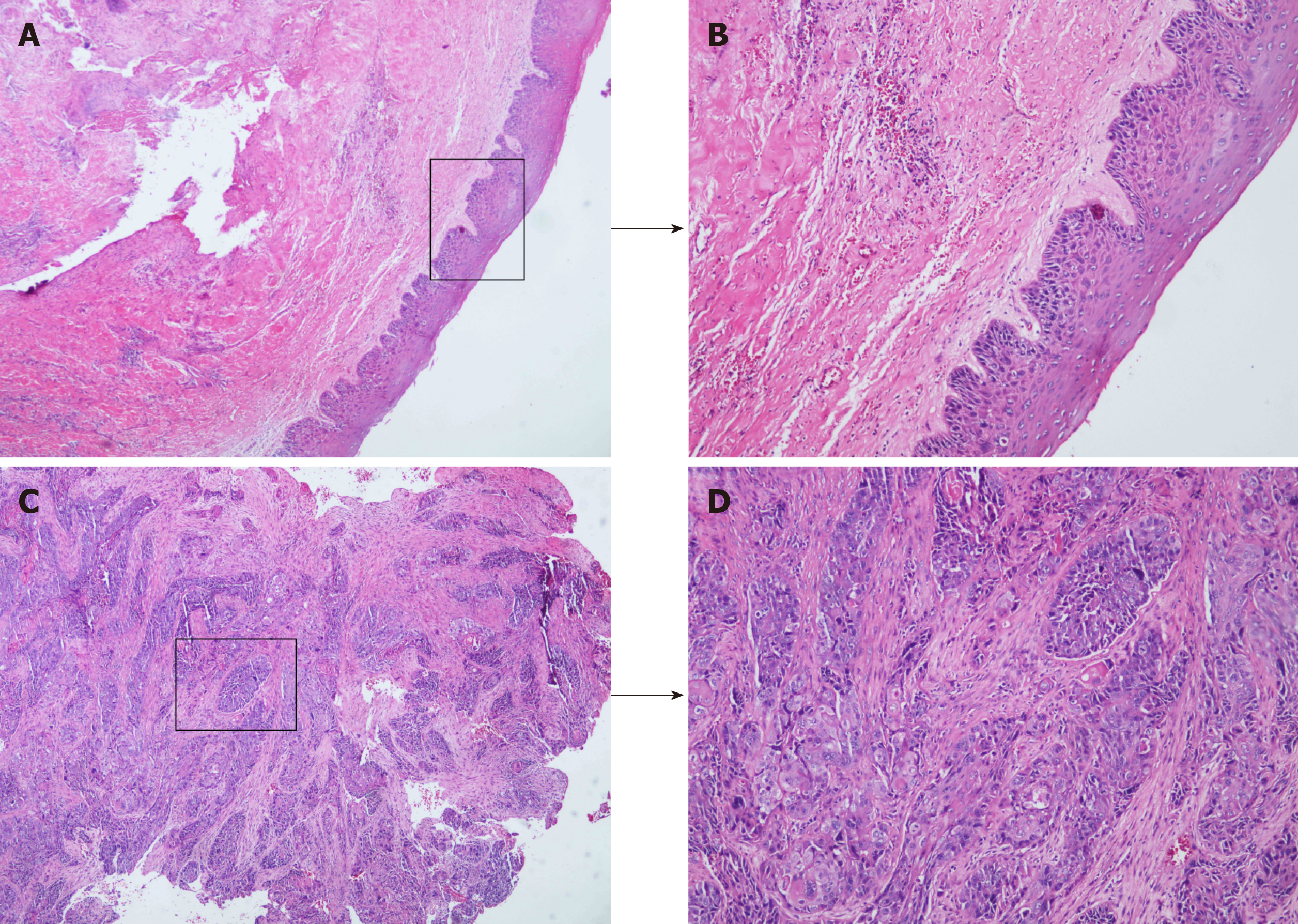
Figure 2 Malignant transformation of odontogenic keratocysts.
A: Histopathological examination revealed an intact structure of cyst lining (× 40) B: Inflammatory cell infiltration in the submucosa (× 100); C: Destruction of cyst lining and invasion of massive squamous cell carcinoma (× 40); D: Moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (distinct foci of squamous cell carcinoma, × 100).
- Citation: Luo XJ, Cheng ML, Huang CM, Zhao XP. Reduced delay in diagnosis of odontogenic keratocysts with malignant transformation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(11): 2374-2379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i11/2374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2374