Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2020; 8(1): 133-139
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.133
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.133
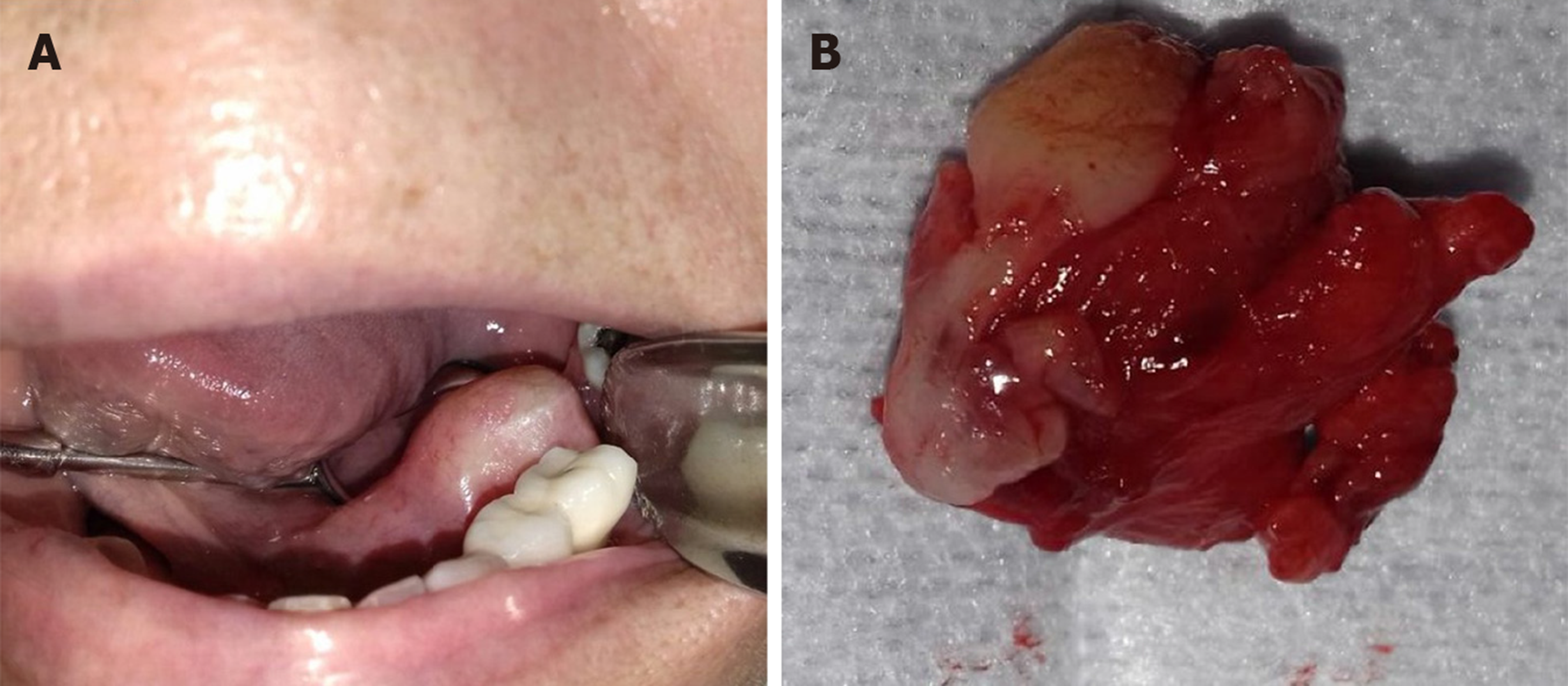
Figure 1 Clinical and macroscopic aspects of the lesion.
A: Volume increase in floor of mouth on the left side, measuring approximately 5 cm × 4 cm × 4 cm, with smooth, flat surface on palpation, not adherent to deep planes; B: Macroscopic appearance of the specimen by excisional biopsy.
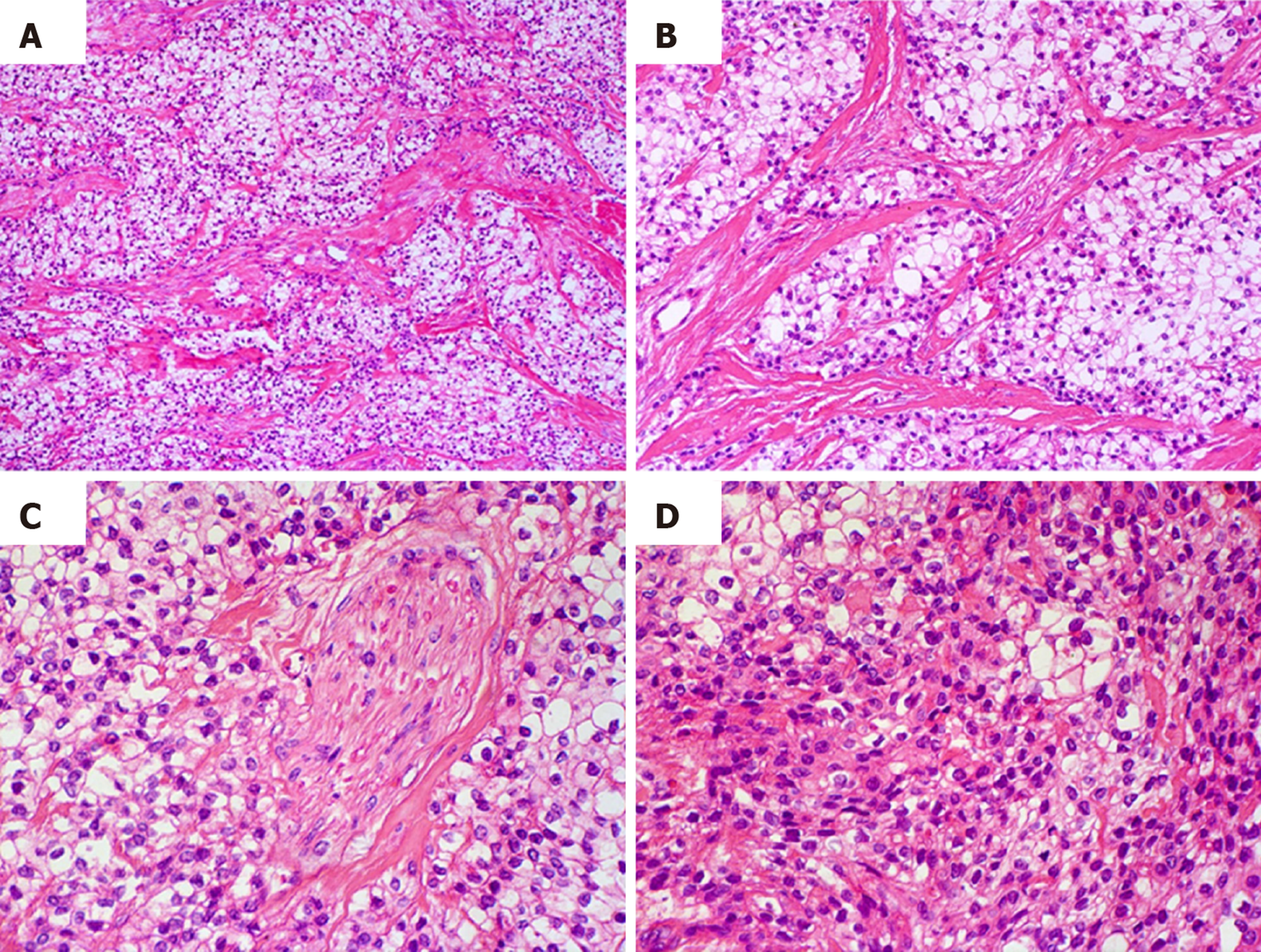
Figure 2 Histological characteristics of the tumor.
A and B: Groups of clear cells separated by thick bundles of eosinophilic collagen fibers with hyaline appearance; C: Neural invasion area; D: Diffuse proliferation of tumor cells forming solid areas or tumor sheets. A population of tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm was also observed (Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification A: ×100, B: ×200, C, D: ×400).
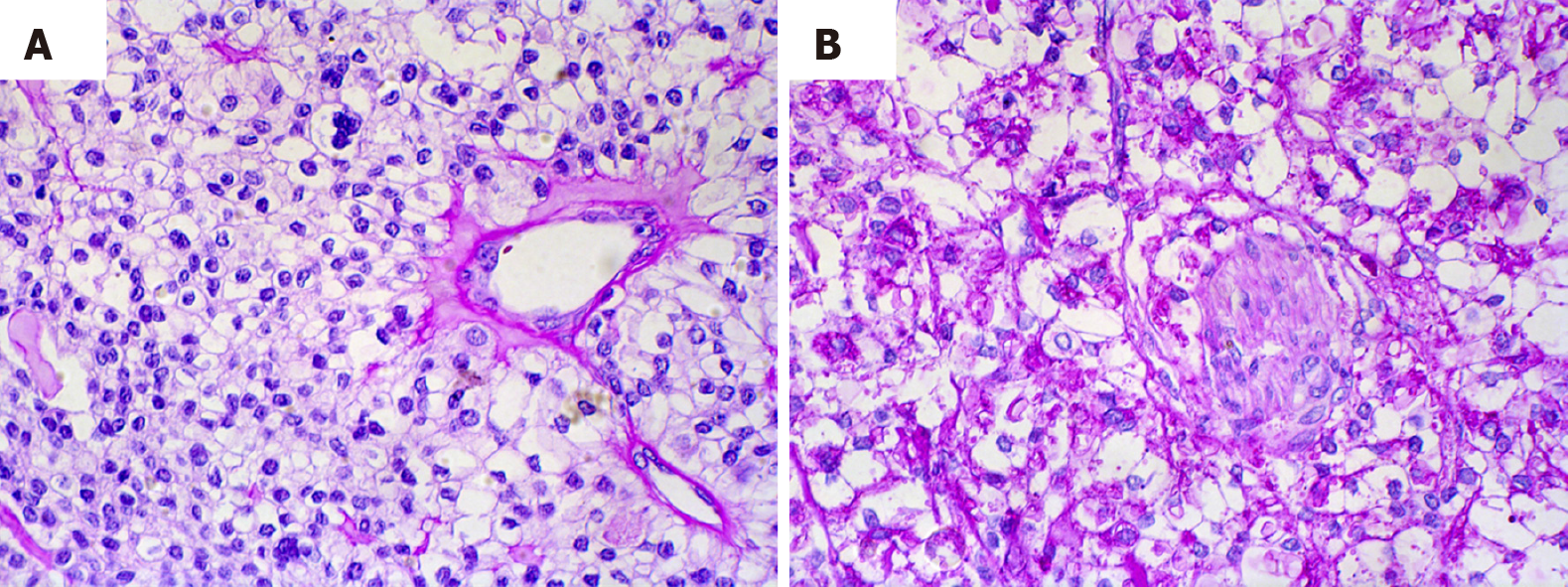
Figure 3 Negative tumor cells staining and histochemistry periodic acid-Schiff positive without diastase.
A: Negative tumor cells staining by periodic acid-Schiff with diastase; B: Histochemistry periodic acid-Schiff positive without diastase (original magnification, ×400).
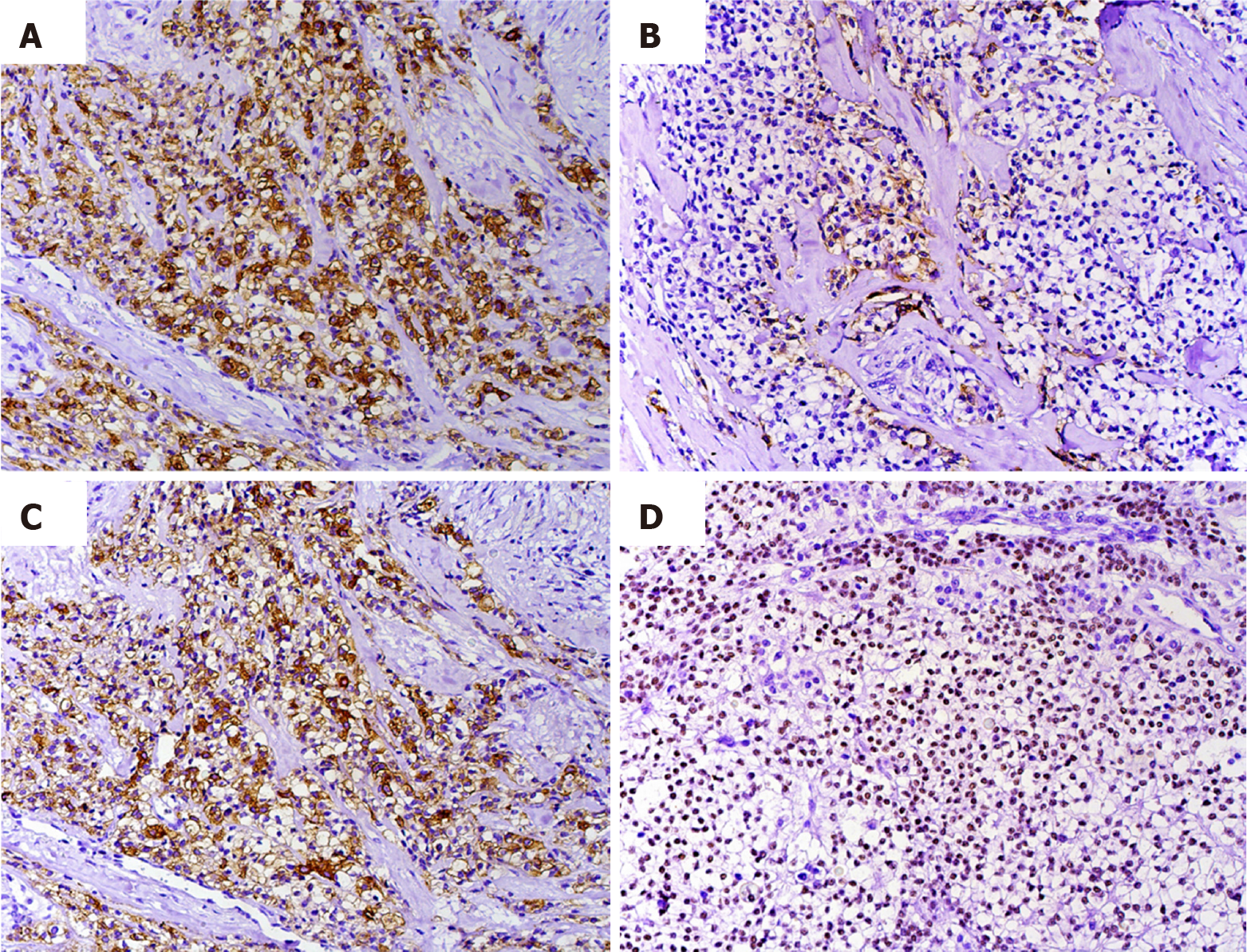
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical profile of the tumor.
An intense and diffuse positive reaction was observed in most tumor cells for AE1-AE3 (A), CK7 (C), and p63 (D), whereas CK5 (B) showed focal positivity (original magnification A, B, C, D. ×200).
- Citation: Donohue-Cornejo A, Paes de Almeida O, Sánchez-Romero C, Espinosa-Cristóbal LF, Reyes-López SY, Cuevas-González JC. Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma-a rare entity in the oral cavity: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(1): 133-139
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i1/133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.133