Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2019; 7(8): 928-939
Published online Apr 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.928
Published online Apr 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.928
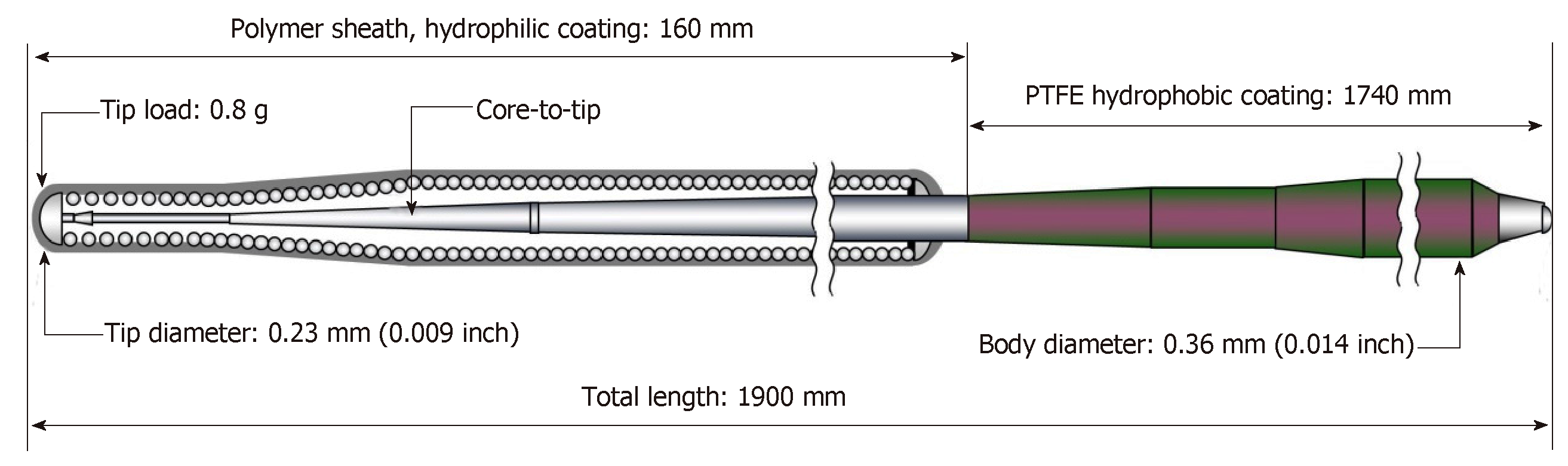
Figure 1 An illustrative image of the Fielder XT guidewire.
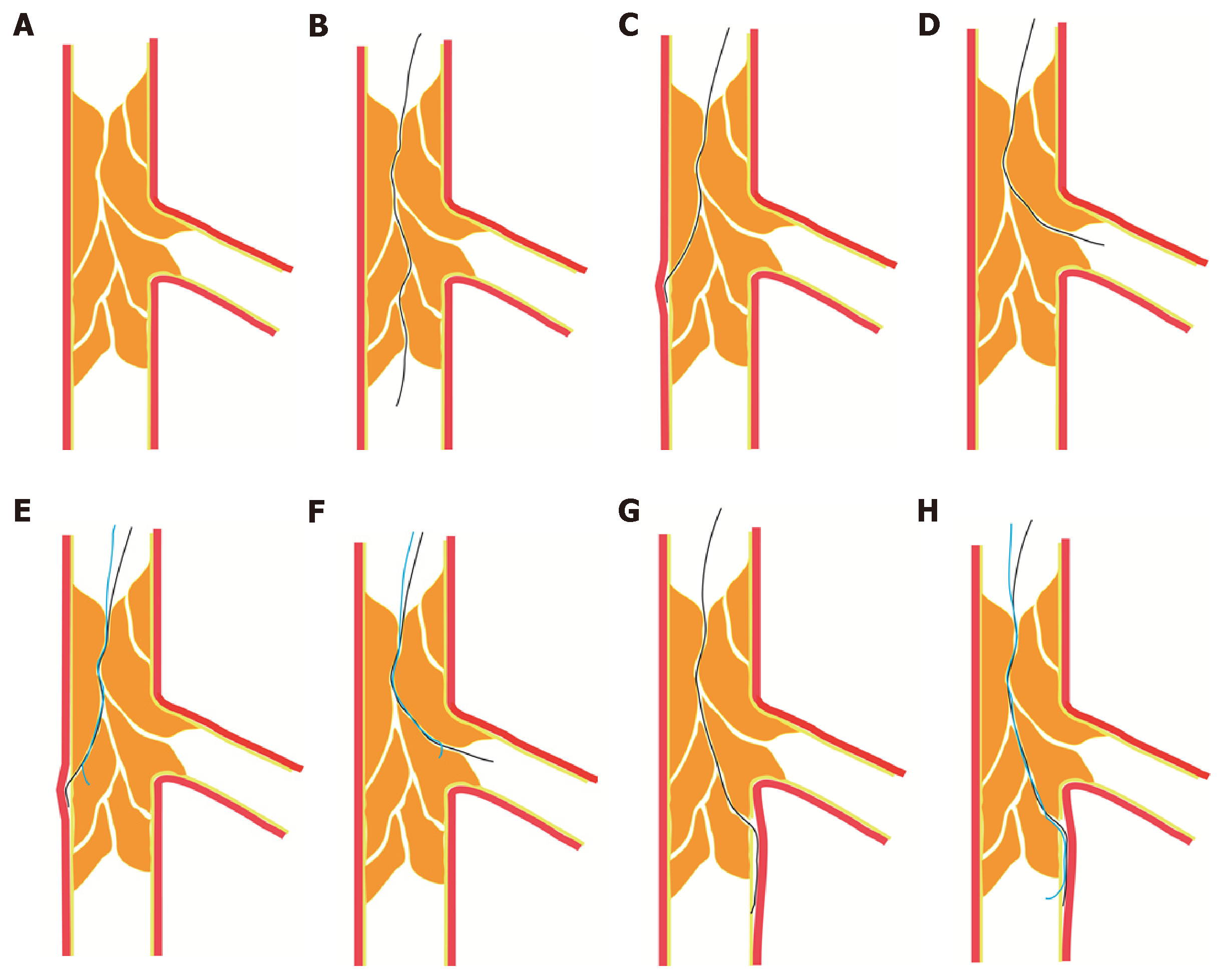
Figure 2 Fielder XT guidewires enter the chronic total occlusion lesions along the microchannels with different anatomical features.
A: Microchannels partly or completely connecting from the proximal cap to the distal end of chronic total occlusion (CTO) lesion; B: A Fielder XT guidewire crossing the CTO lesion through microchannels; C: A Fielder XT guidewire entering the sidewall of the coronary artery and resulting in forming intimal dissection; D: A Fielder XT guidewire entering the side branch of the occlusion segment; E-F: After leaving the Fielder XT guidewire in the false lumen, tracing of a second tapered guidewire along the same pathway into the true lumen; G: A Fielder XT guidewire crossing the occlusion segment into the subintimal of the distal cap; H: A stiff guidewire with a tapered tip entering the distal true lumen after the distal cap.
- Citation: Wang QC, Lin HR, Han Y, Dong H, Xu K, Guan SY, Chen ZH, Hao HX, Bin JP, Liao YL, Jing QM. Optimal use of fielder XT guidewire enhances the success rate of chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(8): 928-939
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i8/928.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.928