Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2019; 7(8): 917-927
Published online Apr 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.917
Published online Apr 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.917
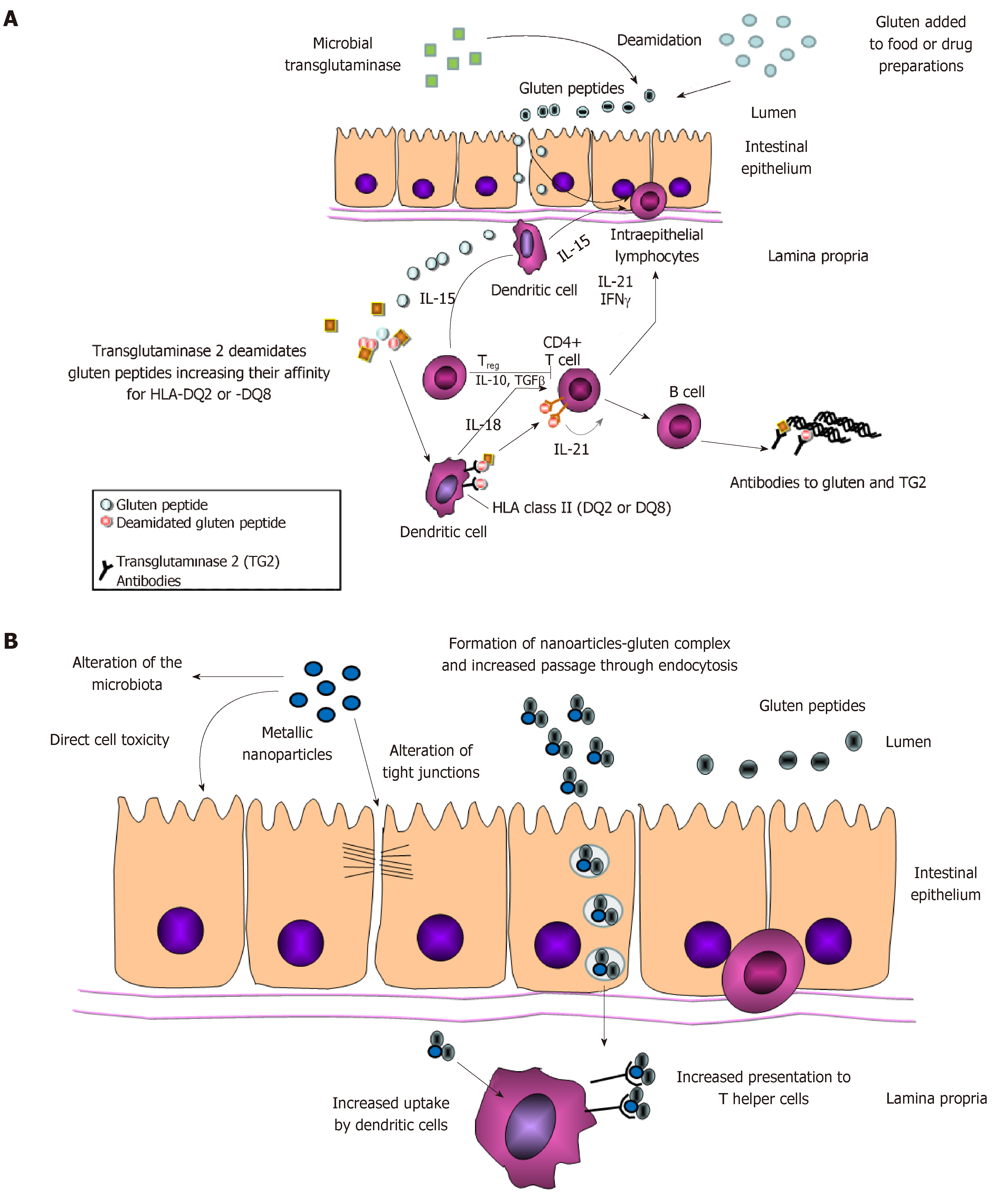
Figure 1 Role of Food additives in the pathogenesis of celiac disease.
A: The pathogenesis of celiac disease involves the digestion of gluten in the gut lumen, the increased passage of gluten peptides through the intestinal epithelium, the deamination by the tissue transglutaminase 2 and the uptake by antigen-presenting cells. Once the gluten peptides are presented within the HLA class II molecule they activate CD4+ T cells, which in turn trigger the destruction of the tissue by CD8+ T cells and the production of autoantibodies by B cells. The increase amount of gluten or bacterial transglutaminase used as additive could increase this process; B: Metallic nanoparticles could affect both gluten passage through the epithelium (paracellularly or intracellularly) or the presentation of the antigen by dendritic bells. Moreover they can alter the microbiota, influencing gluten processing and/or immune response.
- Citation: Mancuso C, Barisani D. Food additives can act as triggering factors in celiac disease: Current knowledge based on a critical review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(8): 917-927
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i8/917.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i8.917