Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2019; 7(24): 4398-4406
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4398
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4398
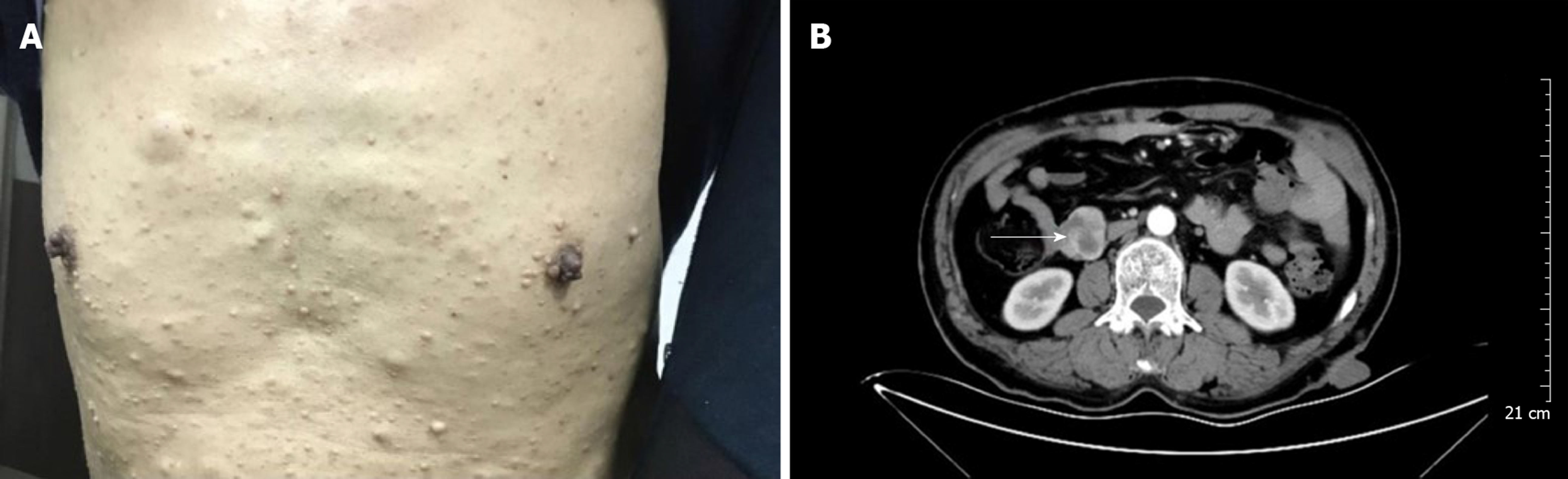
Figure 1 Multiple nodules from the skin and abdomen.
A: Multiple nodules of varying sizes with brown spots are visible on the skin; B: Enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen showed a mass at the junction of the descending and horizontal duodenum (arrow), suggesting a diagnosis of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
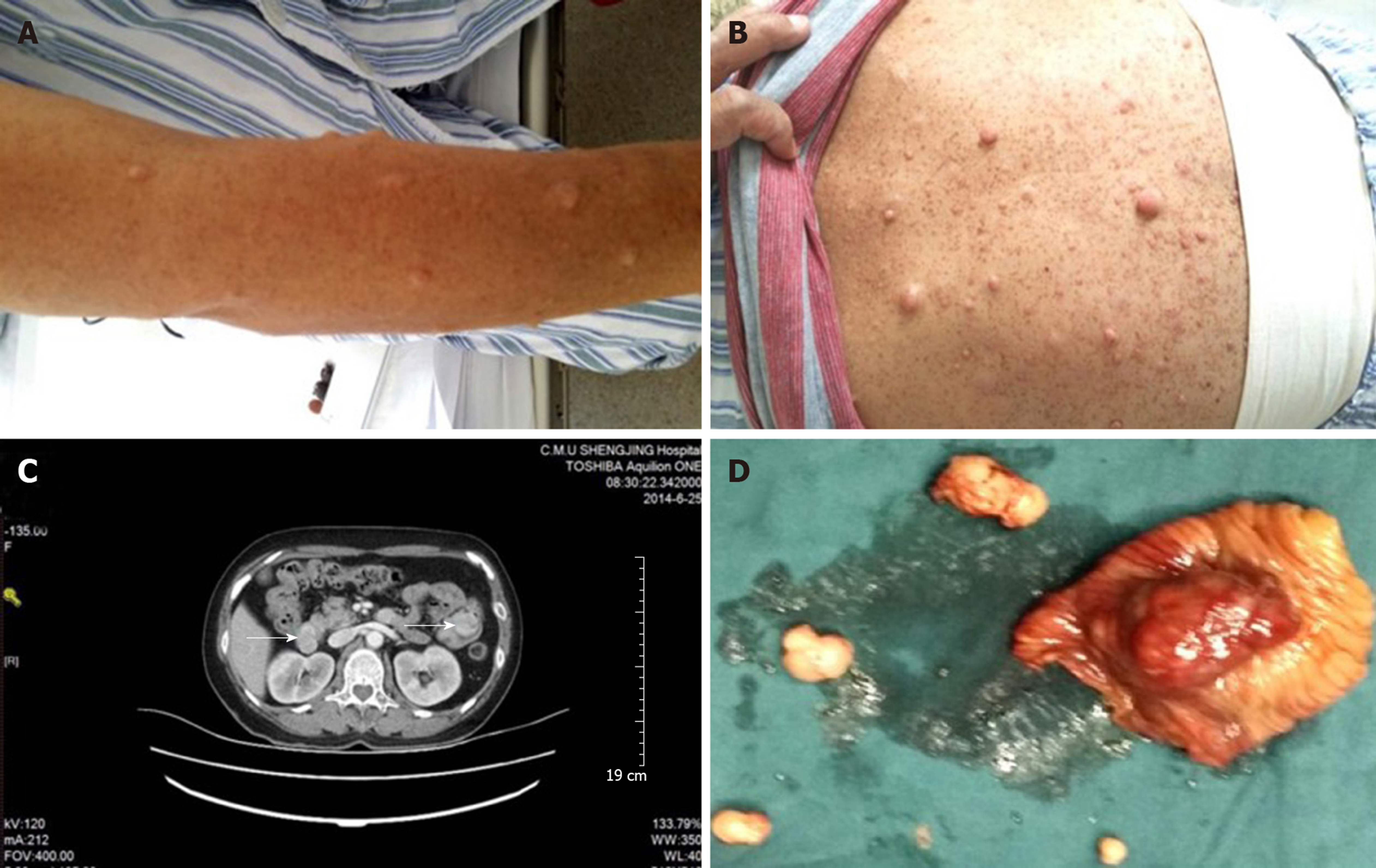
Figure 2 Multiple nodules from the skin and abdomen.
A, B: Multiple nodules of varying sizes with brown spots are visible on the skin; C: Enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen showed multiple tumors in the initial segment of the duodenum and jejunum (arrows), suggesting a diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors; D: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor specimen.
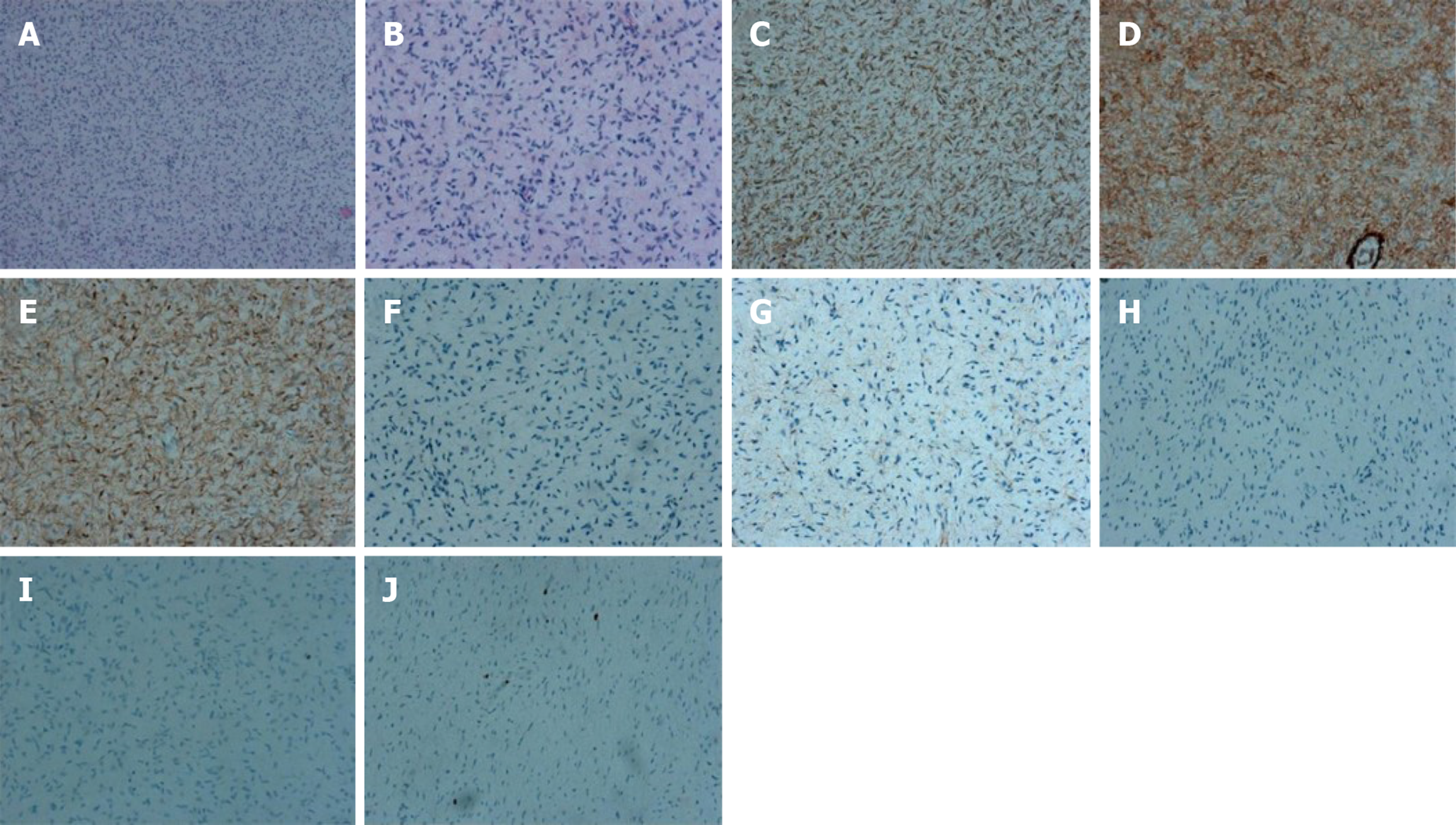
Figure 3 Microscopic and immunohistochemical features of multiple nodules from the skin.
A, B: Tumor composed of spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (A: × 100; B: × 200, hematoxylin-eosin staining); C: Positive for CD34 [3,3’-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining]; D: Positive for S-100 (DAB staining); E: Positive for VIM (DAB staining); F: Negative for CK (DAB staining); G: Negative for EMA (DAB staining); H: Negative for SMA (DAB staining); I: Negative for desmin (DAB staining); J: The percentage of Ki67 positive cells was approximately 2% (DAB staining).
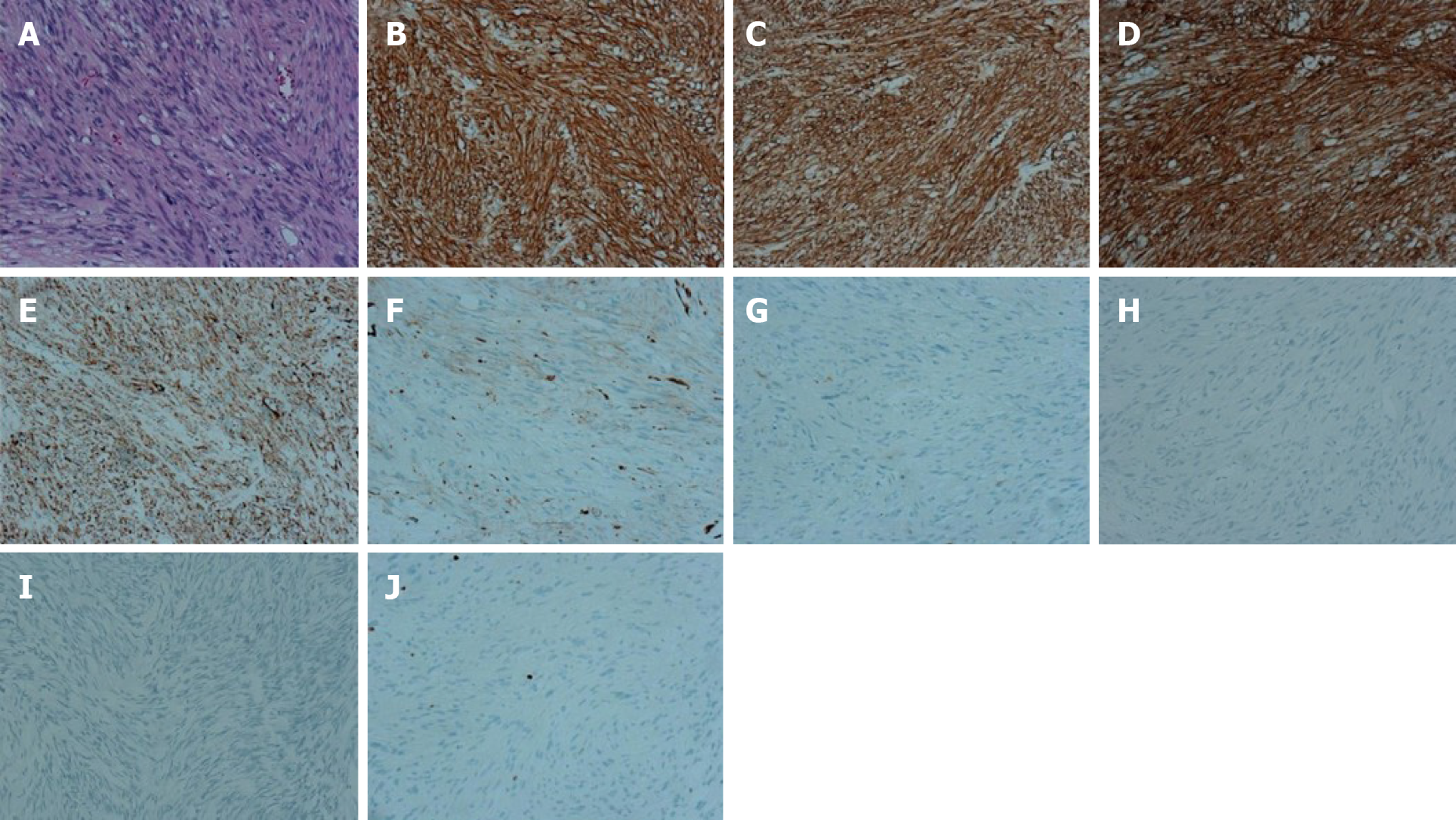
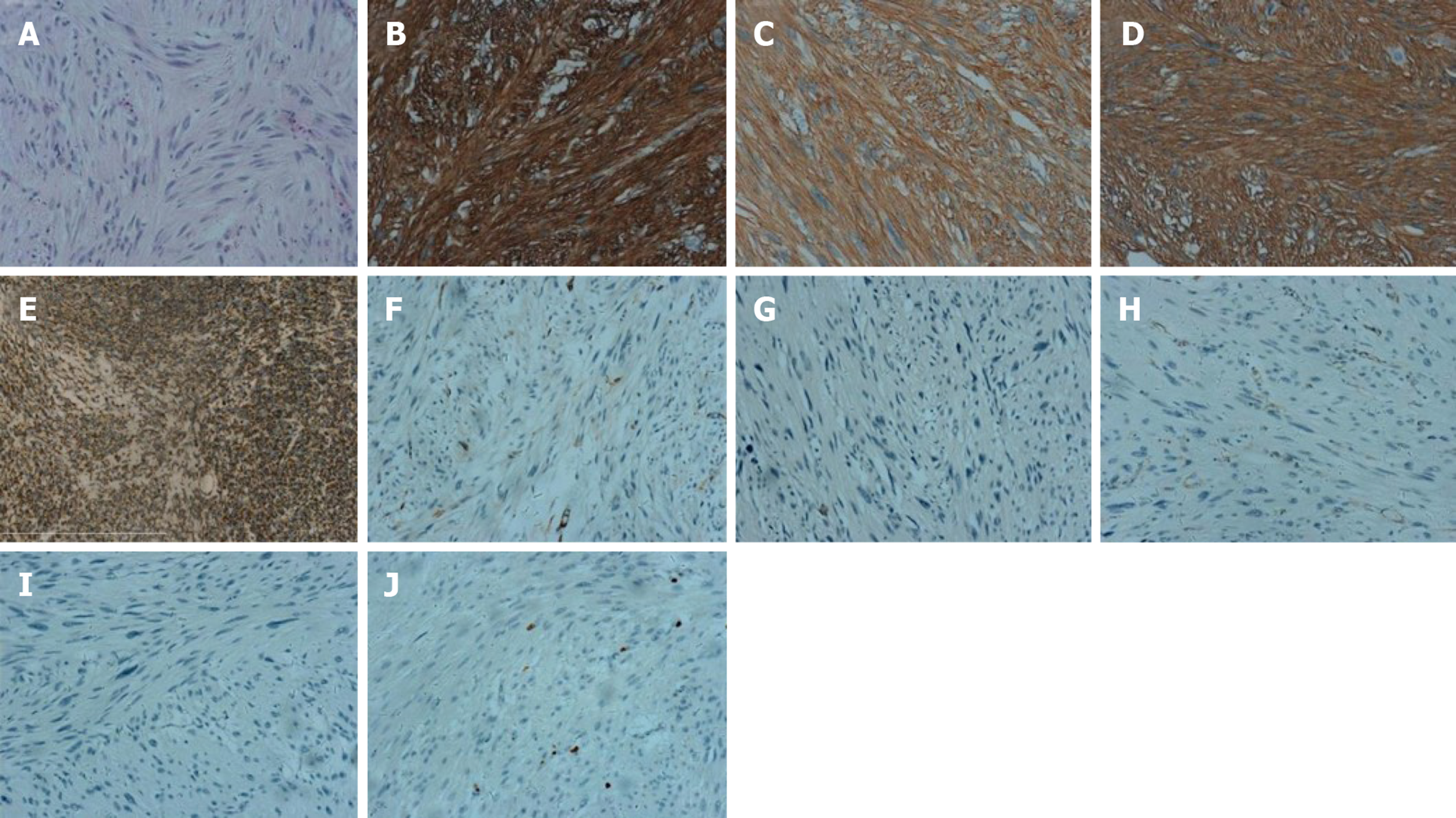
Figure 4 Microscopic and immunohistochemical features (× 200).
A: Tumor composed of spindle or polygonal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (Hematoxylin-eosin staining); B: Positive for CD117 [3,3’-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining]; C: Positive for DOG-1 (DAB staining); D: Positive for CD34 (DAB staining); E: Positive for SDHB (DAB staining); F: Negative for SMA (DAB staining); G: Negative for S-100 (DAB staining); H: Negative for desmin (DAB staining); I: Negative for β-catenin (DAB staining); J: The percentage of Ki67 positive cells was approximately 2% (DAB staining).
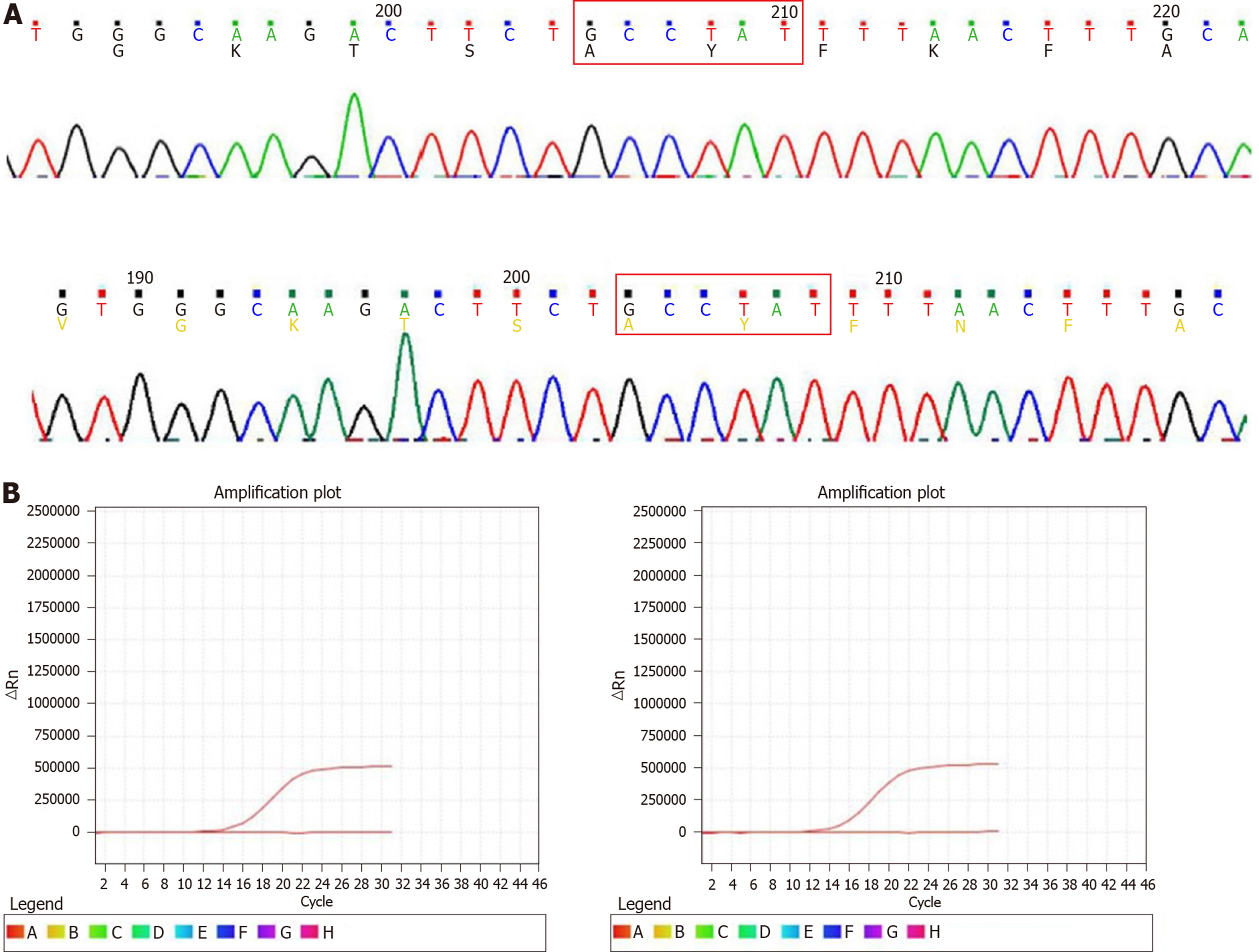
Figure 5 Molecular analysis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
A: Detection of KIT/platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRA) mutations by Sanger sequencing. None of the six tumors from two patients had a KIT/PDGFRA mutation; B: Detection of BRAFV600E mutation by real-time polymerase chain reaction. None of the six tumors from two patients had a BRAFV600E mutation.
Figure 6 Microscopic and immunohistochemical features (× 200) of a mass located approximately 40 cm away from the Treitz ligament.
A: Tumor composed of spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (Hematoxylin-eosin staining); B: Positive for CD117 [3,3’-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining]; C: Positive for DOG-1 (DAB staining); D: Positive for CD34 (DAB staining); E: Positive for SDHB (DAB staining); F: Negative for SMA (DAB staining); G: Negative for S-100P (DAB staining); H: Negative for desmin (DAB staining); I: Negative for β-catenin (DAB staining); J: The percentage of Ki67 positive cells was approximately 2% (DAB staining).
- Citation: Kou YW, Zhang Y, Fu YP, Wang Z. KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor α wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumor associated with neurofibromatosis type 1: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(24): 4398-4406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i24/4398.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4398