Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2019; 7(22): 3792-3799
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3792
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3792
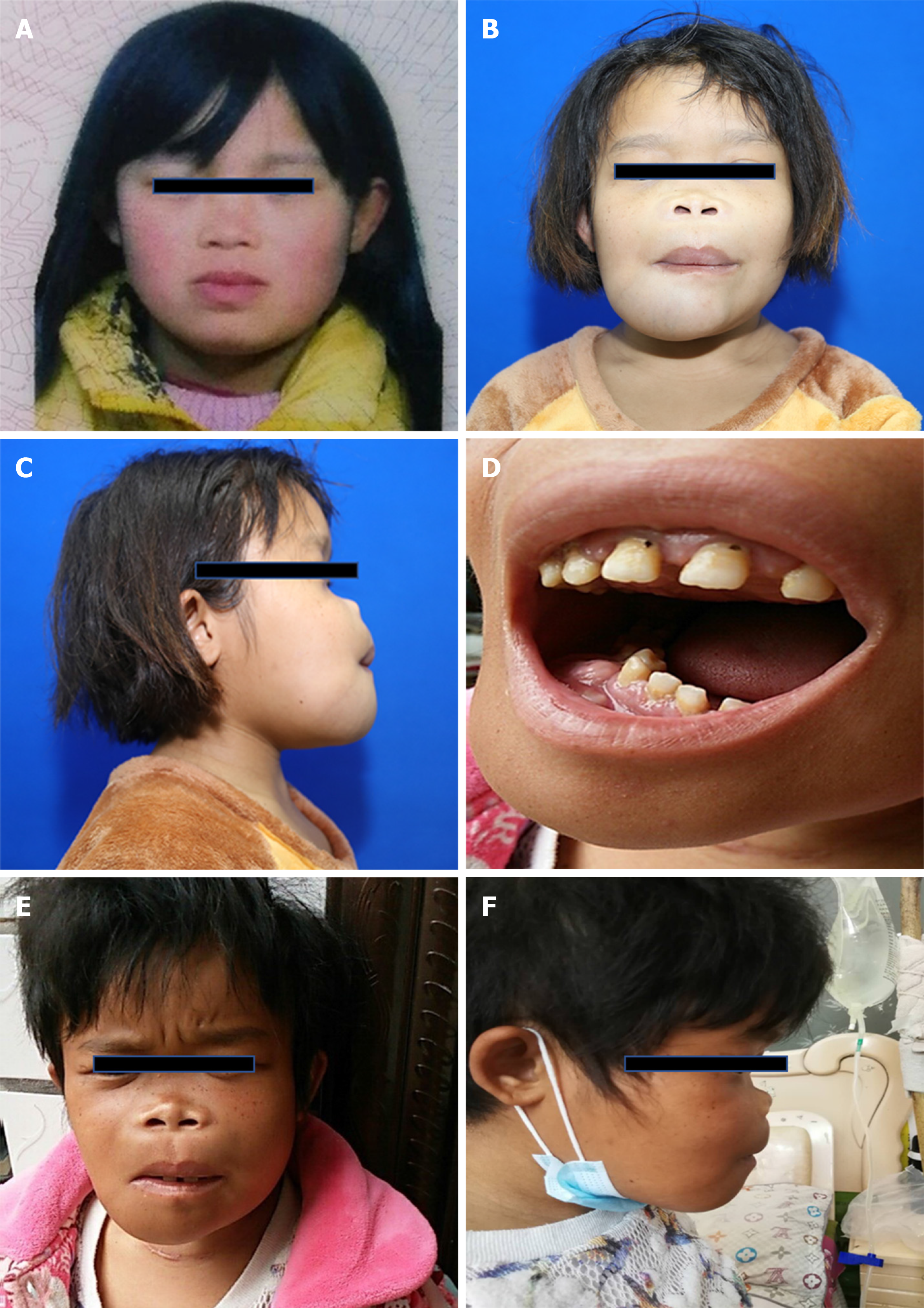
Figure 1 A 24-year-old woman had obvious facial deformity with difficultly chewing and swallowing.
A: Normal appearance four years prior; B and C: Frontal and side photos, respectively, of the craniofacial deformity before parathyroidectomy; D: Increasing width of dentition with alveolar bone neoplasia; E and F: Frontal and side photos of craniofacial deformity with partial relief 4 mo after parathyroidectomy.
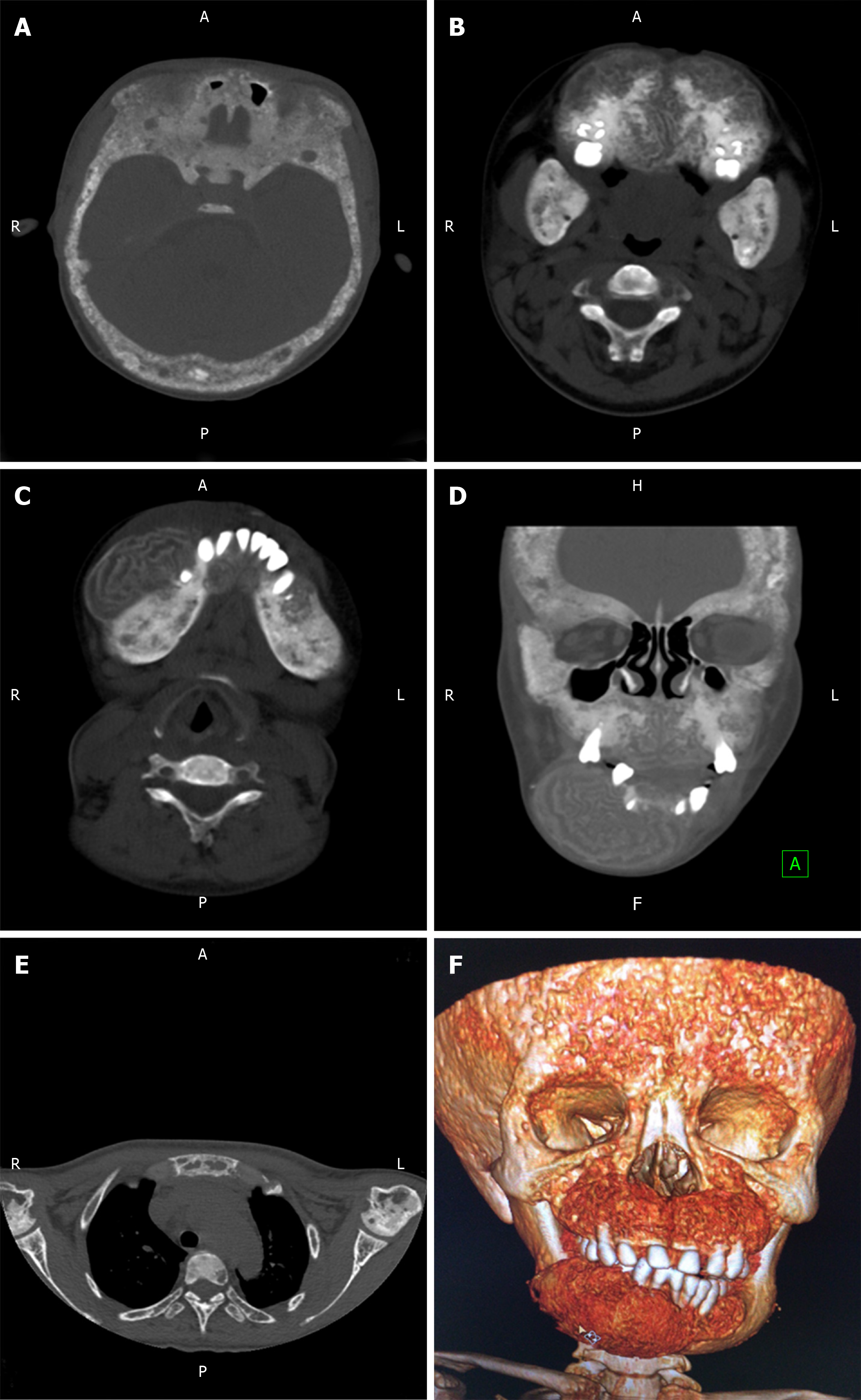
Figure 2 Non-contrast computed tomography showed skull and maxillofacial bone changes.
A: There was a marked heterogeneous widening of the skull with sclerotic and lytic changes; B, C, and D: The distinct overgrowth of the maxilla and mandible bone was profoundly affected by diffuse bone abnormalities; E: Osteolysis, osteofibrosis, osteoporosis, and sclerosis coexisted in the scapula, humerus, sternum, and vertebra; F: A volume rendering 3D reconstruction of the craniomaxillofacial structures.
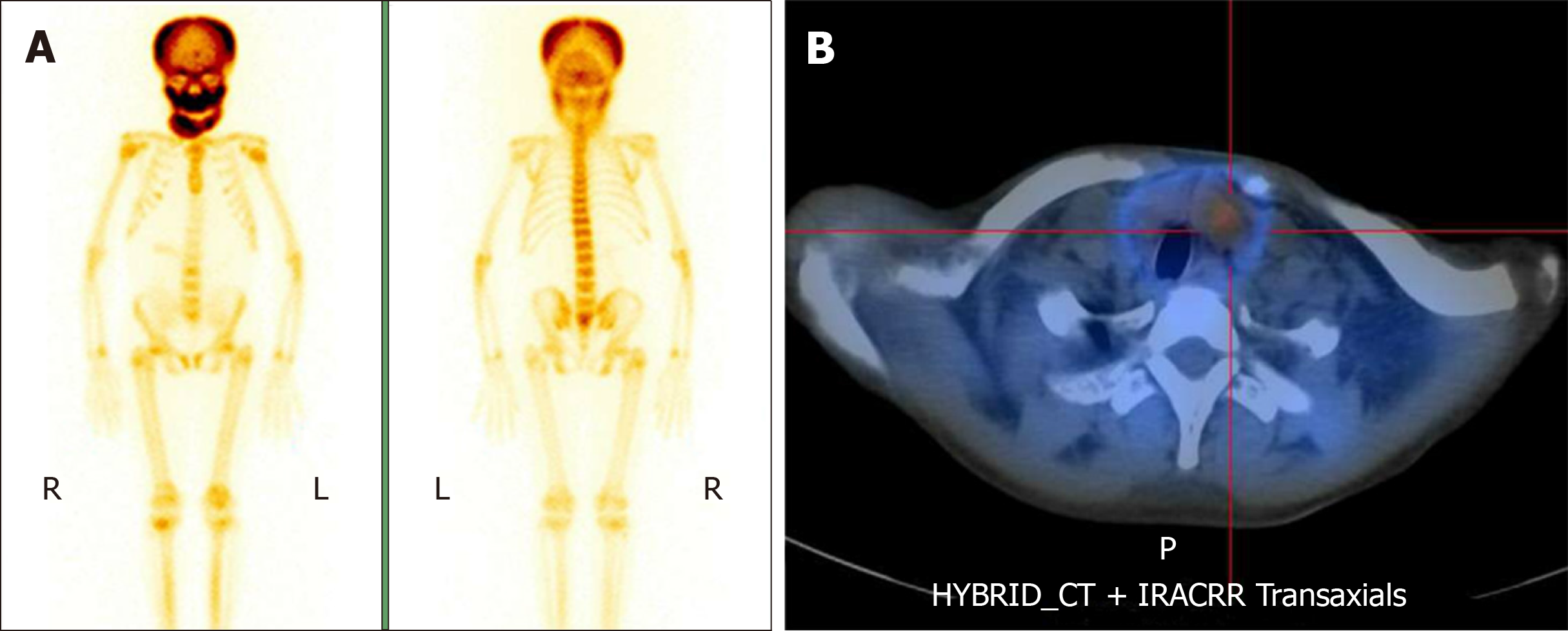
Figure 3 Nuclear examinations before the operation.
A: 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate bone scintigraphy indicated increased radiotracer in the bilateral parietal, maxilla, and mandible. The signal was strongest on the right side of the mandible area; B: 99mTc-sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography showed only one hyperplastic parathyroid gland on the left side.
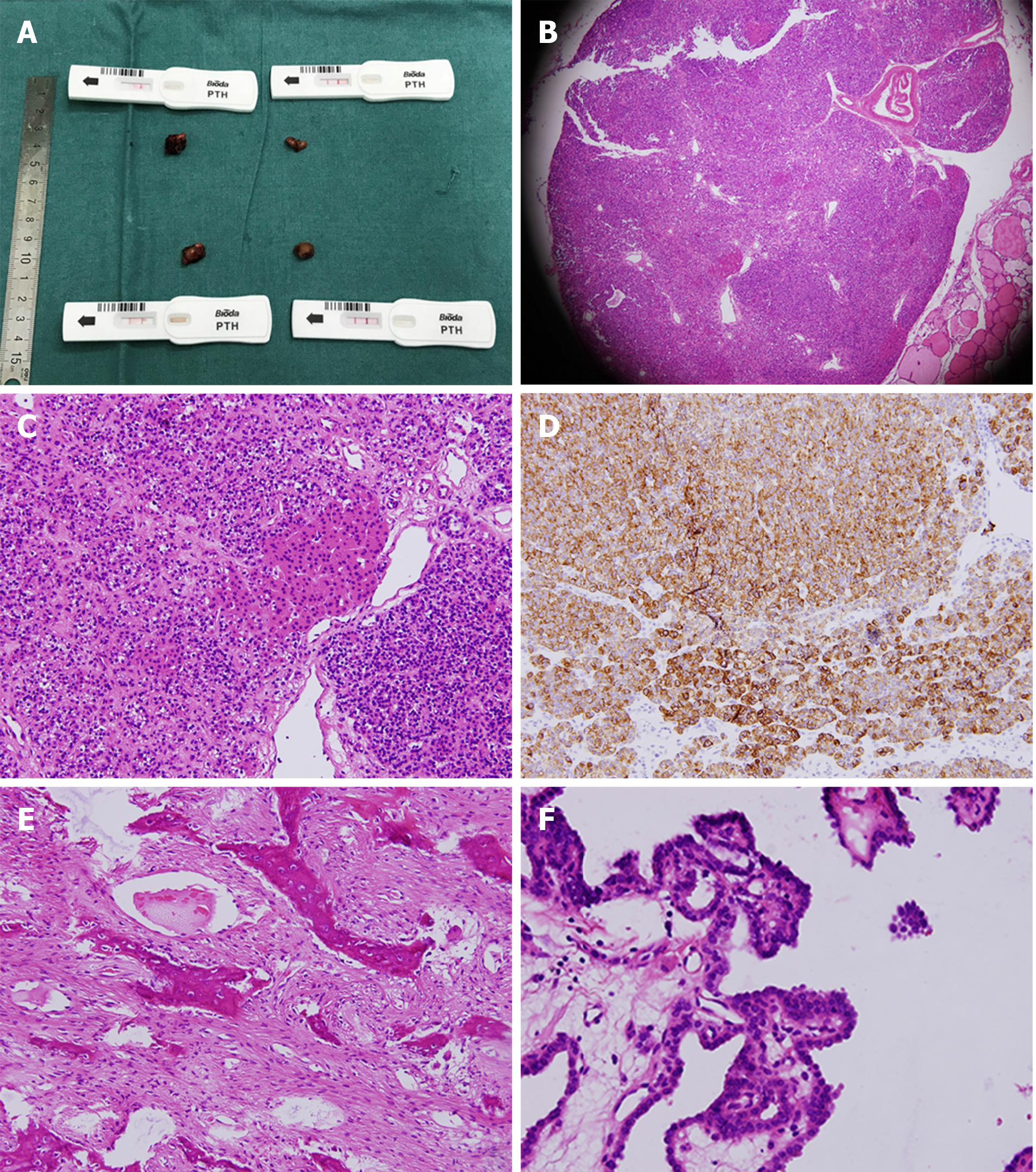
Figure 4 Histopathological examination of secondary hyperparathyroidism, mandibular biopsy, and papillary thyroid cancer.
A: Four parathyroid glands were confirmed by colloidal gold-based immunoassays during the operation; B and C: Histochemistry of the hyperplastic parathyroid gland by microscopy at 200× and 400×; D: Immunohistochemistry of the hyperplastic parathyroid gland by microscopy at 400×; E: Bone trabeculae could be seen in the fibroblast background with multinucleated megakaryocytes; F: Histochemistry of the papillary thyroid carcinoma by microscopy at 400×.
- Citation: Yu Y, Zhu CF, Fu X, Xu H. Sagliker syndrome: A case report of a rare manifestation of uncontrolled secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(22): 3792-3799
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i22/3792.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3792