Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2019; 7(19): 2995-3011
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.2995
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.2995
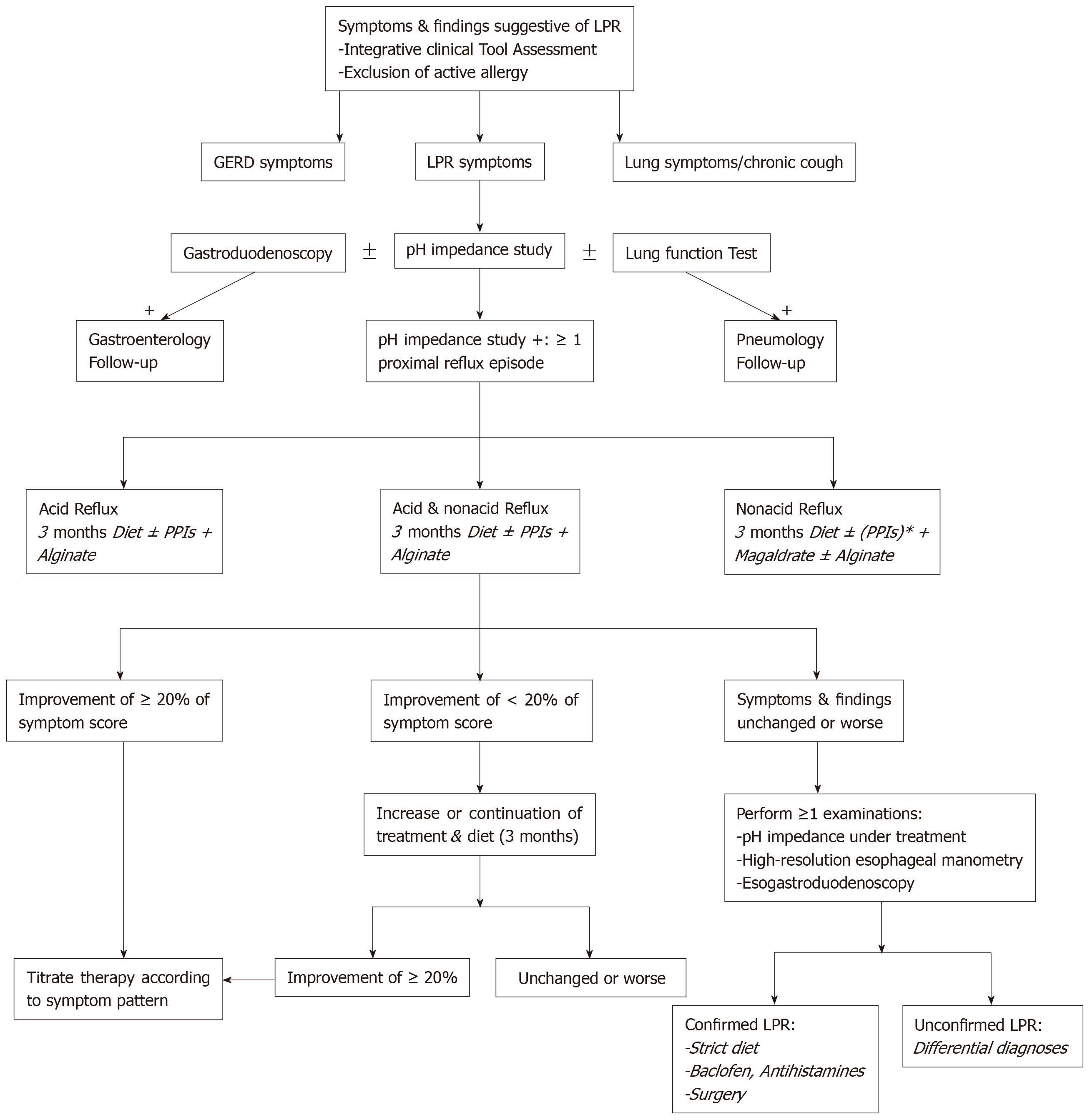
Figure 1 Personalized therapeutic approach for specific laryngopharyngeal reflux disease subtypes.
In this algorithm, proximal reflux event was defined as an episode that reached two impedance sensors in the hypopharynx or proximal esophagus. Acidic event consisted of a gaseous or liquid reflux with a pH ≤ 4.0 while nonacidic event was a gaseous or liquid reflux with a pH > 4.0. The LPR diagnosis was based on the occurrence of ≥ 1 proximal episode. Acid reflux episode consisted of an episode with pH > 4.0. Nonacid reflux episode consisted of an episode with pH ≤ 4.0. Because there are no guidelines in the definition of acid, nonacid and mixed laryngopharyngeal reflux disease (LPRD) disease, LPRD was defined as acid when the ratio of number of acid reflux episodes/number of nonacid reflux episodes was > 2. LPRD was defined as nonacid when the ratio of number of acid reflux episodes/number of nonacid reflux episodes < 0.5. Mixed reflux consisted of a ratio ranged from 0.51 to 2.0. 1For nonacid LPR, PPIs are not necessary regarding their low efficacy.
- Citation: Lechien JR, Mouawad F, Barillari MR, Nacci A, Khoddami SM, Enver N, Raghunandhan SK, Calvo-Henriquez C, Eun YG, Saussez S. Treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: A systematic review. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(19): 2995-3011
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i19/2995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.2995