Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2019; 7(15): 1908-1925
Published online Aug 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i15.1908
Published online Aug 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i15.1908
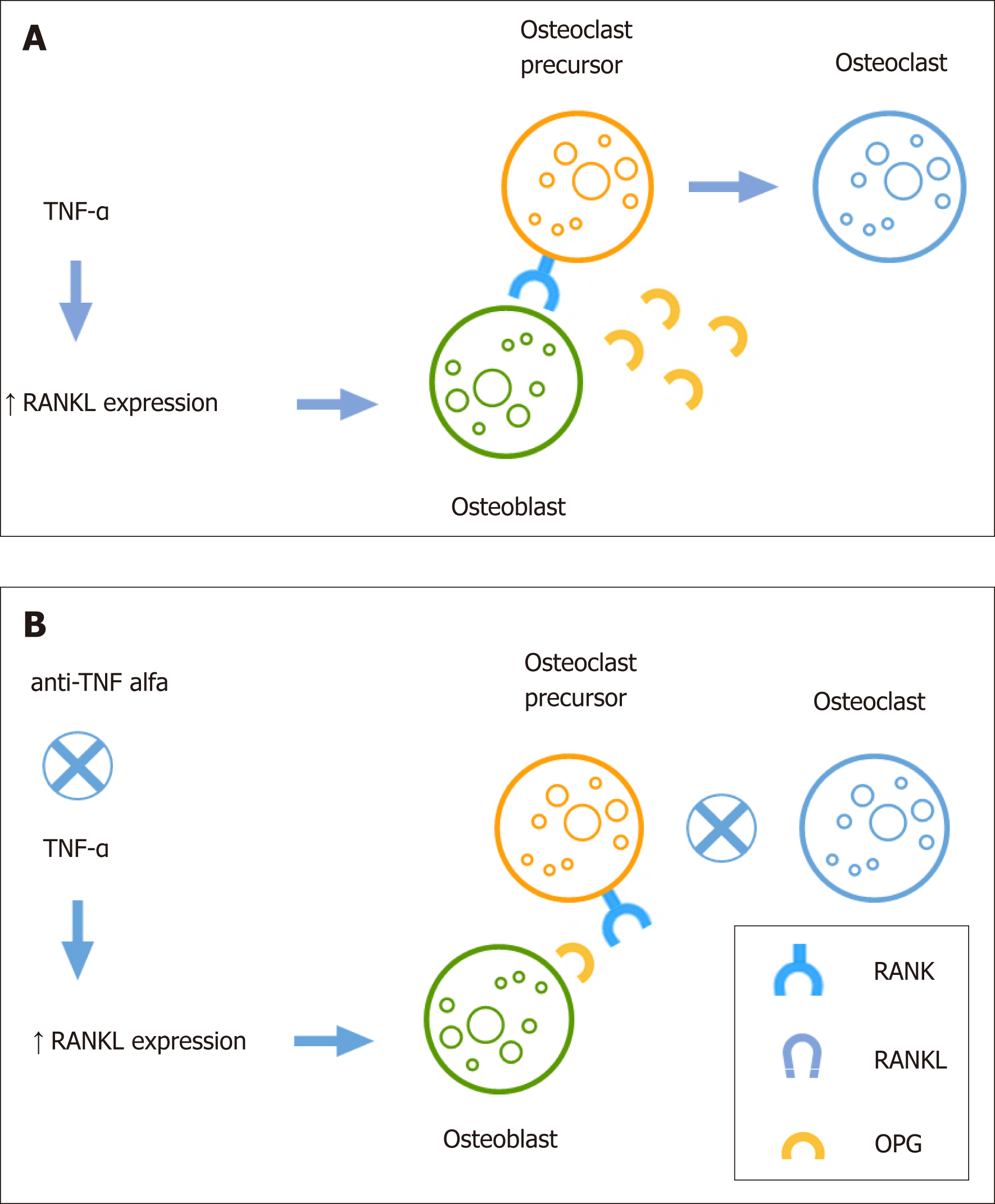
Figure 1 Modulation of osteoclast differentiation by serum TNF-α and anti-TNF-α treatment.
A: TNF-α influences osteoclast precursor differentiation and bone resorption activity inducing RANKL expression on osteoblast cells and preventing the binding of OPG; B: Anti-TNF-α treatment reduces RANKL expression resulting in decrease of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption.
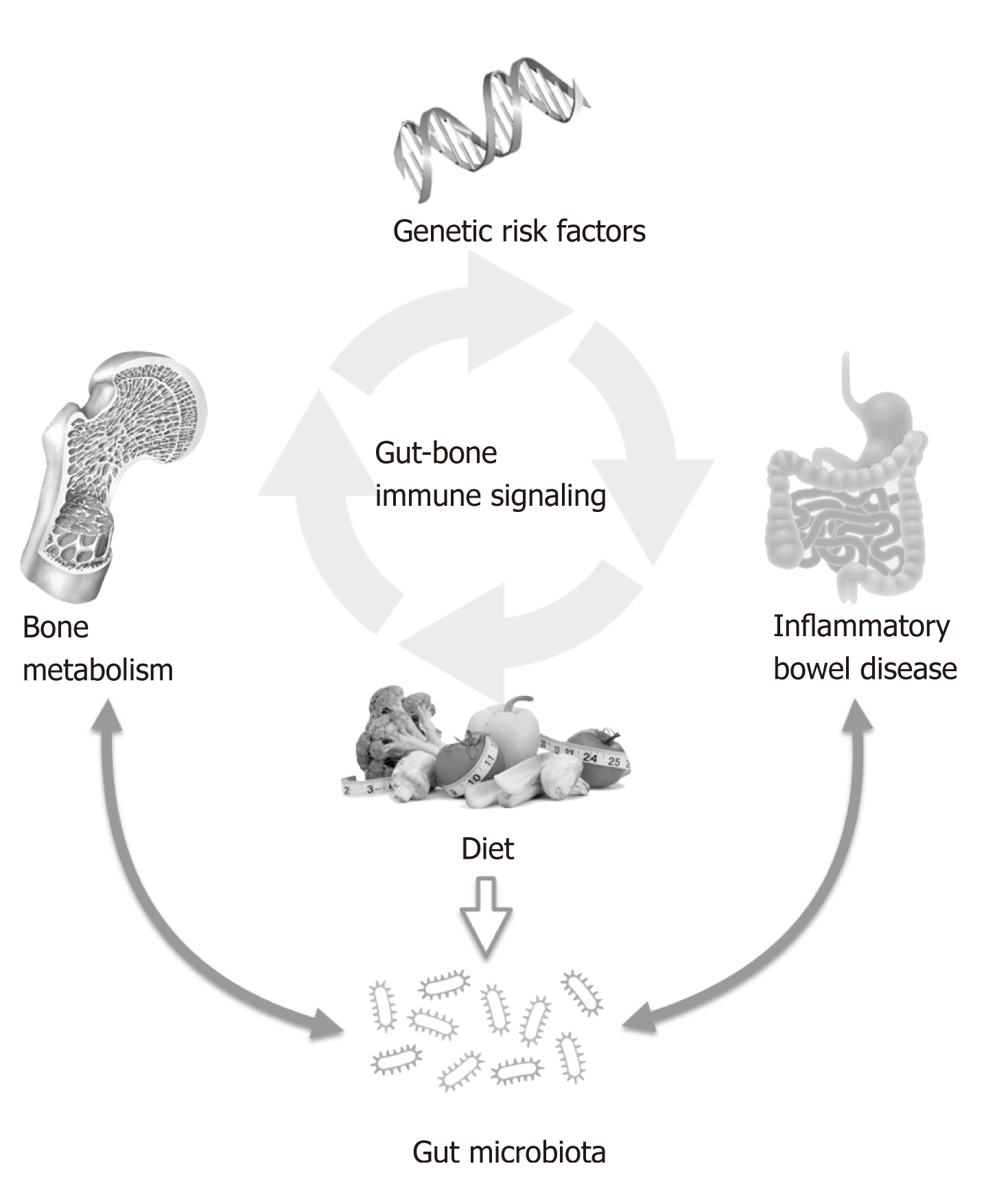
Figure 2 Gut-bone immune signaling: interplay between different factors which may affect bone metabolism in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases.
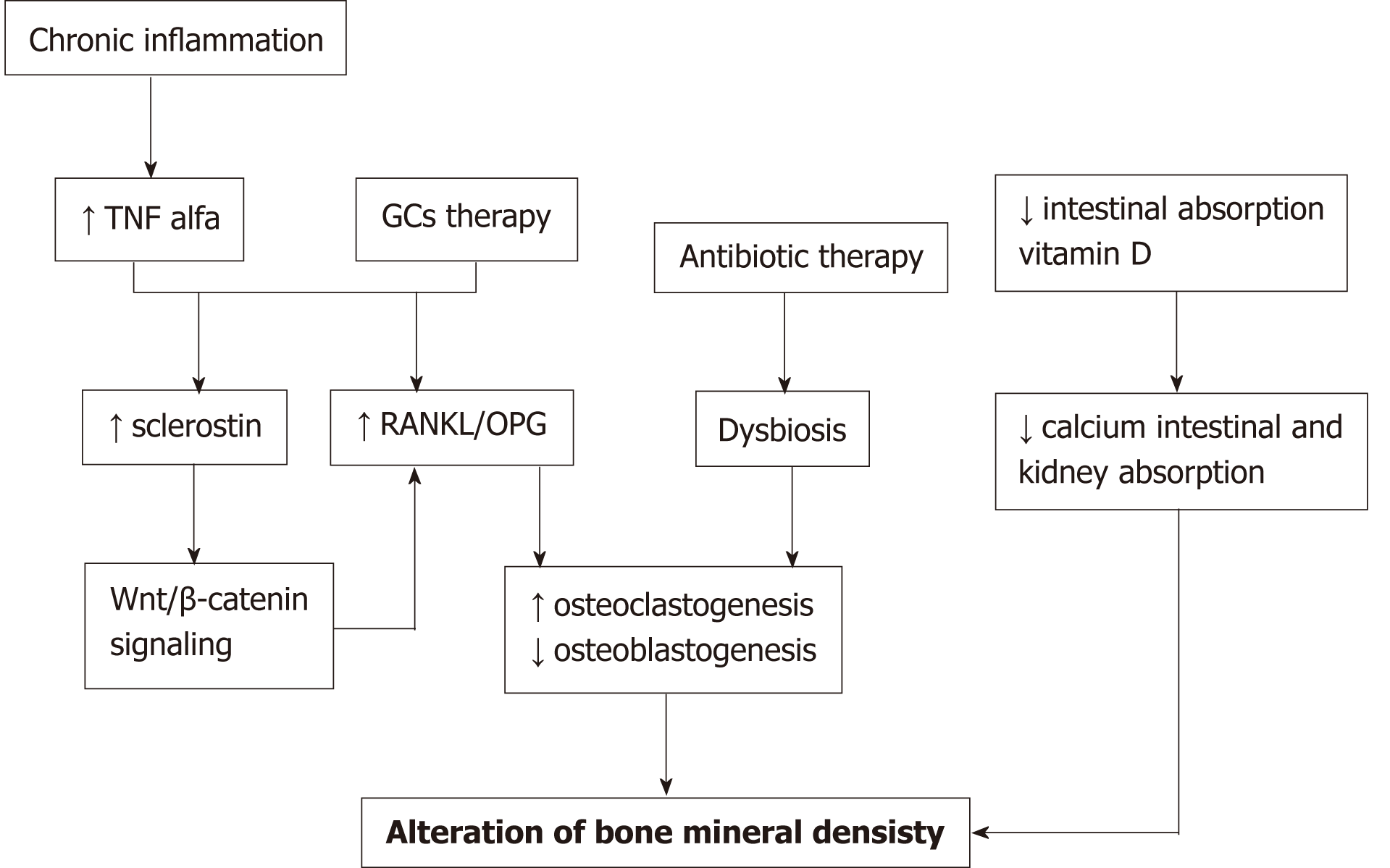
Figure 3 Diagramatic representation of the pathogenic mechanisms involved in alteration of bone mineral density in inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Citation: Sgambato D, Gimigliano F, De Musis C, Moretti A, Toro G, Ferrante E, Miranda A, De Mauro D, Romano L, Iolascon G, Romano M. Bone alterations in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(15): 1908-1925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i15/1908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i15.1908