Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2019; 7(14): 1865-1875
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1865
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1865
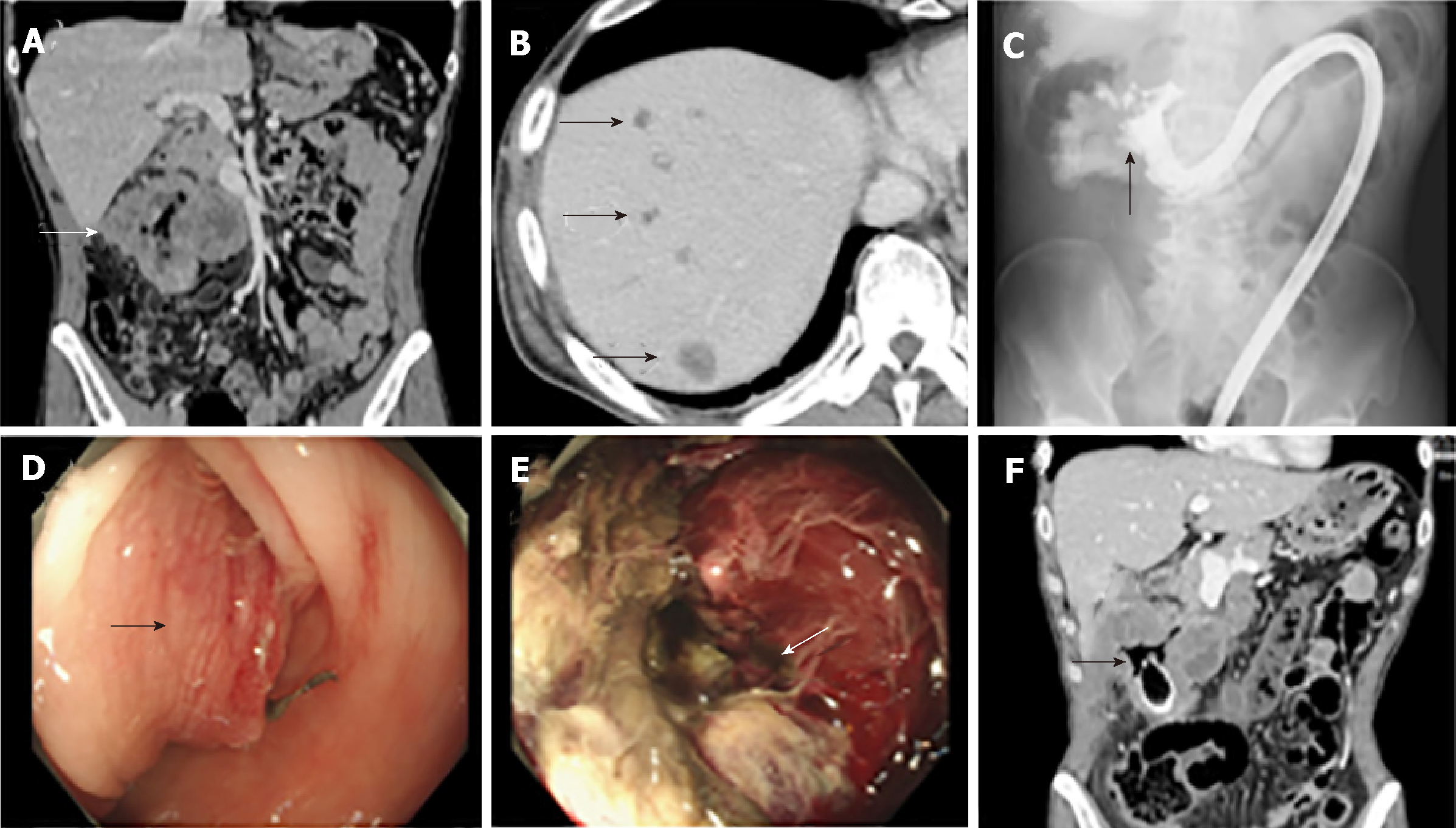
Figure 1 Imaging findings.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen shows an irregularly shaped and enhanced mass (10 cm) at the right colonic flexure. White arrow indicates the tumor; B: CT showed multiple low-density tumors in the liver with no enhancement effect. Black arrows indicate the tumors; C: Colonic enema with water-soluble contrast medium (Gatrografin®) shows an irregular shape in the lumen of colon. Black arrow indicates the stenotic and irregular lesion; D: Colonoscopy showed the mass in the right transverse colon with significant stenosis due to submucosal elevation of the tumor. Black arrow indicates the submucosal elevation; E: Colonoscopy showed the necrotic tissue in the lumen of the tumor. White arrow indicates the necrotic lesion; F: Perforation of the colon by stenting. Black arrow indicates the free-air and intratumoral air outside the stent.
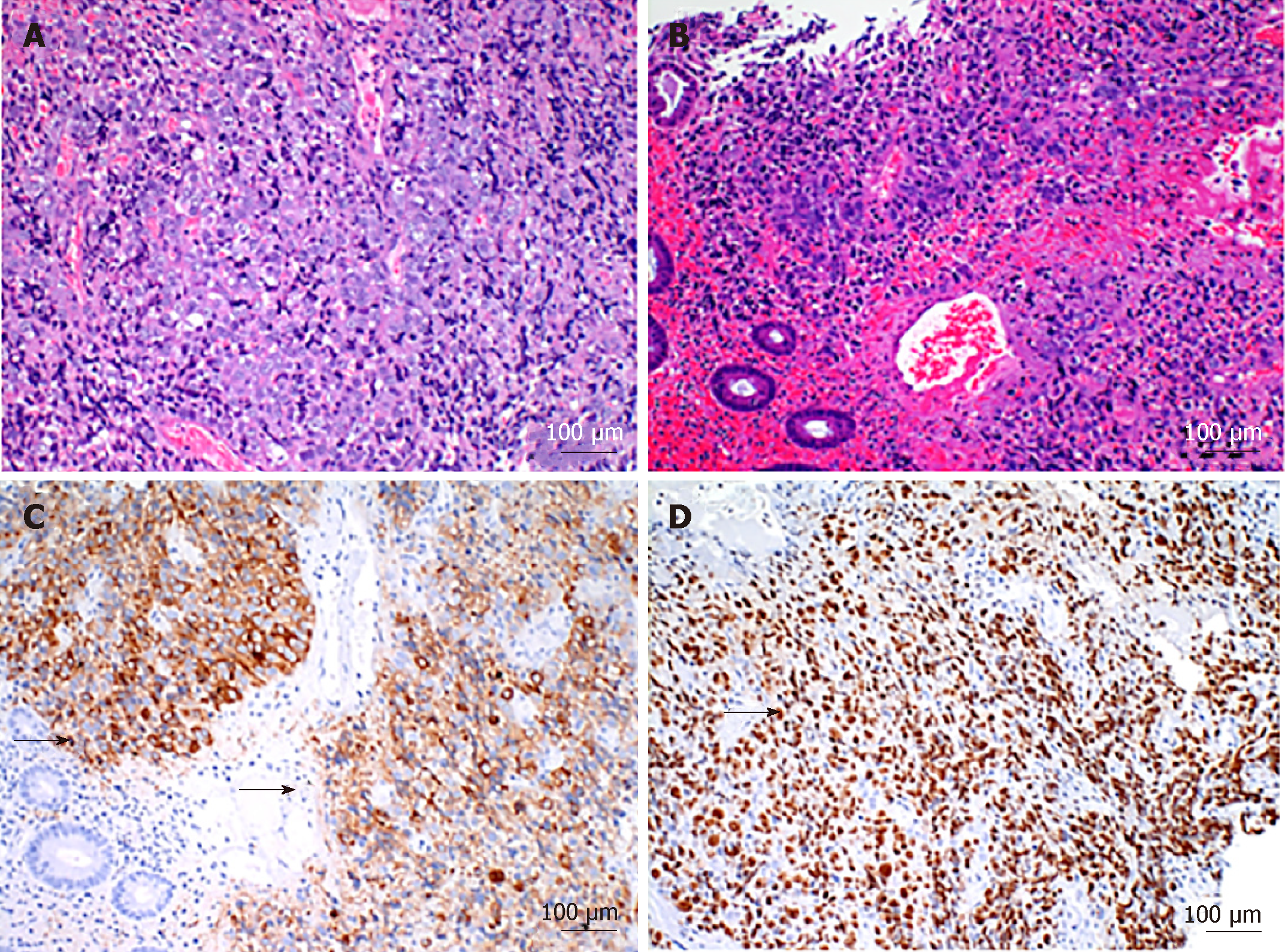
Figure 2 Histological findings of the tumor.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that the tumor cells were poorly differentiated; B: Complicated with the intratumoral bleeding; C: Tumor cells underwent immunohistochemical staining for Synaptophysin. Black arrows indicate the positively stained cells; D: A high proliferative fraction of immunohistochemical staining for Ki67 staining. Black arrows indicate the positively stained cells.
- Citation: Yoshida T, Kamimura K, Hosaka K, Doumori K, Oka H, Sato A, Fukuhara Y, Watanabe S, Sato T, Yoshikawa A, Tomidokoro T, Terai S. Colorectal neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(14): 1865-1875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i14/1865.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1865