Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2019; 7(10): 1206-1212
Published online May 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i10.1206
Published online May 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i10.1206
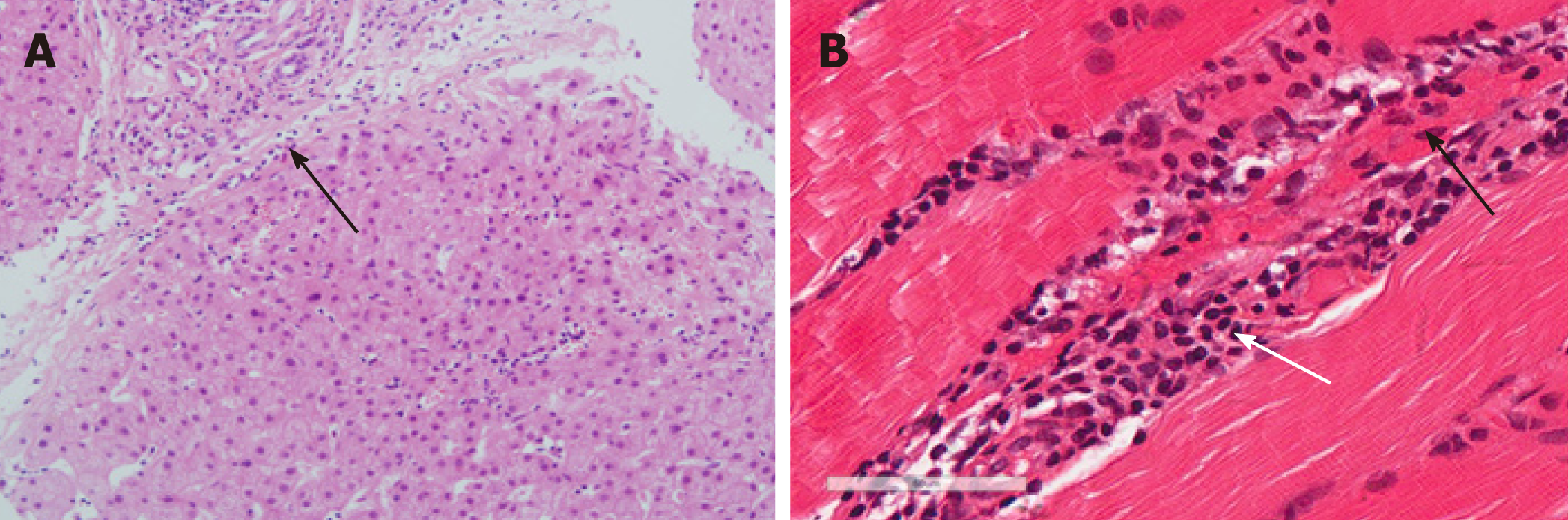
Figure 1 Histopathologic manifestations.
A: A hematoxylin-eosin stained liver biopsy (200× magnification) showed nodular cirrhosis with extensive lymphocytes and few plasmocytes infiltrating fibrous septa (black arrow); B: A hematoxylin-eosin stained muscle biopsy (400× magnification) showed nuclear migration in local sarcolemma (black arrow) and infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells (white arrow).
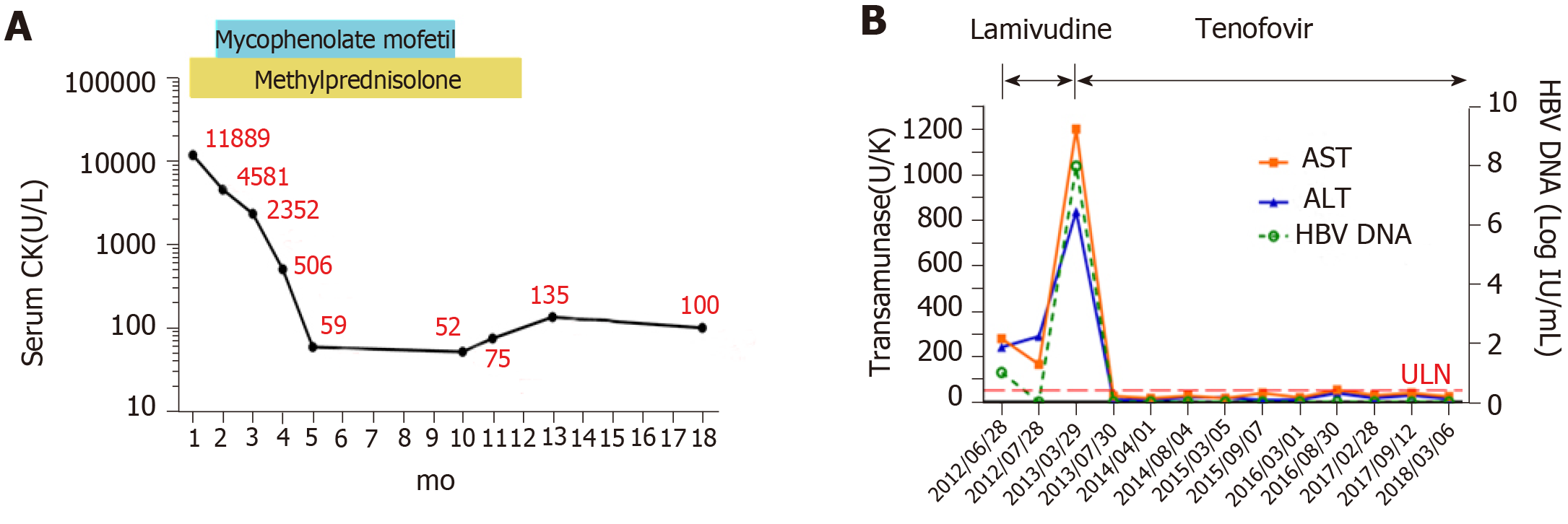
Figure 2 Laboratory examination results during patient follow-up.
A: Serum creatine kinase levels during the 18-mo follow-up. After the patient’s symptoms improved and he underwent biochemical remission, the methylprednisolone treatment was tapered at a rate of 10% per week until the dose reached 4 mg per day. The patient was on the 4 mg per day dose until one year. The mycophenolate mofetil dose remained at 750 mg twice a day for nine months; B: Changes in transaminase (Alanine transaminase; aspartate transminase) and hepatis B virus desoxyribonucleic acid levels during antiviral therapy. ULN: Upper limit of normal for transaminases; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate Transminase; CK: Creatine kinase; HBV DNA: Hepatis B virus desoxyribonucleic acid.
- Citation: Zhang J, Wen XY, Gao RP. Hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis complicated with dermatomyositis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(10): 1206-1212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i10/1206.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i10.1206