Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2018; 6(14): 767-775
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.767
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.767
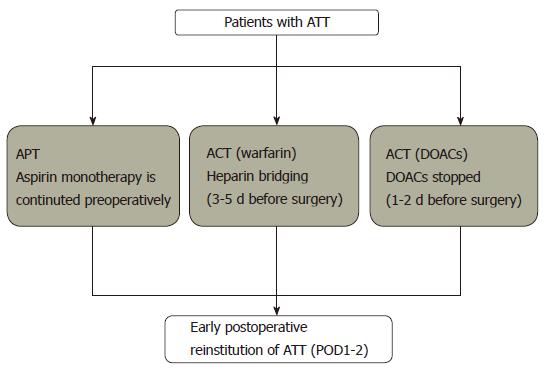
Figure 1 Recommended perioperative management protocol for patients undergoing antithrombotic therapy in the case of elective laparoscopic digestive surgery.
The management generally consists of three ways according to the types of antithrombotic therapy (ATT); antiplatelet therapy (APT), warfarin, and Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs). In patients with thromboembolic risks, aspirin monotherapy is continued in patients with APT, and/or warfarin was substituted by heparin bridging 3-5 d before surgery. In the case of DOACs, ATT is stopped 1-2 d before surgery (with some modification needed if decreased renal function exists); if the thromboembolic risk is very high, heparin bridging might be considered. Postoperatively, every antithrombotic agent is reinstituted as soon as possible (POD1-2). ATT: Antithrombotic therapy; APT: Antiplatelet therapy; TE: Thromboembolism; ACT: Anticoagulation therapy; DOAC: Direct-acting oral anticoagulant.
- Citation: Fujikawa T, Ando K. Safety of laparoscopic surgery in digestive diseases with special reference to antithrombotic therapy: A systematic review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(14): 767-775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i14/767.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.767