Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2018; 6(10): 308-321
Published online Sep 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.308
Published online Sep 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.308
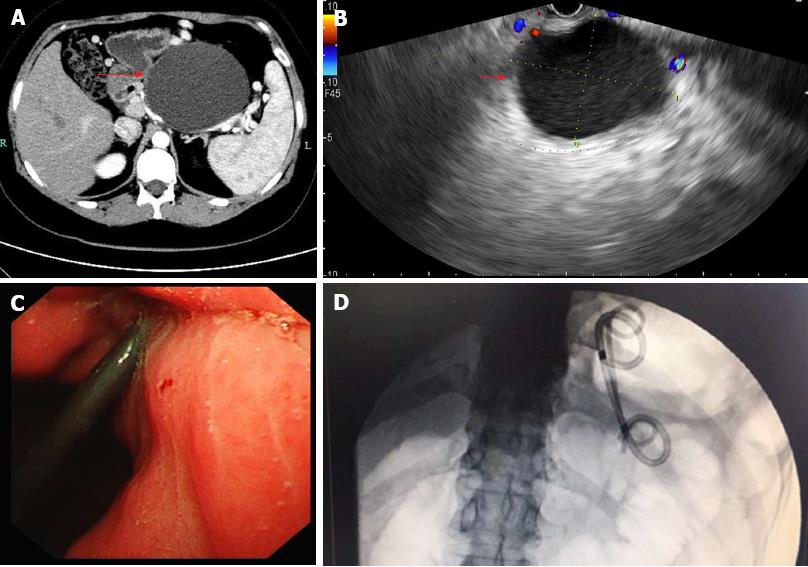
Figure 1 Imaging findings of pancreatic pseudocyst.
A: A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of the upper abdomen. A relatively homogenous cystic mass is identified in the region of the pancreatic tail (arrow). B: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) image showing a pancreatic pseudocyst (PPC) (arrow). C: Endoscopic image showing plastic stent deployment. D: Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) image revealing double pigtail plastic stent deployment.
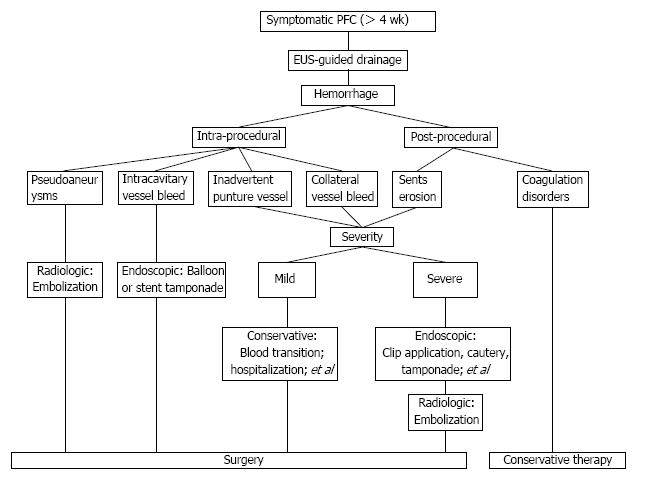
Figure 2 Imaging of a meaningful treatment algorithm.
An integrated and multidisciplinary treatment algorithm is proposed for the endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. PFC: Pancreatic fluid collections.
- Citation: Jiang TA, Xie LT. Algorithm for the multidisciplinary management of hemorrhage in EUS-guided drainage for pancreatic fluid collections. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(10): 308-321
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i10/308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.308