Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2014; 2(12): 873-882
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.873
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.873
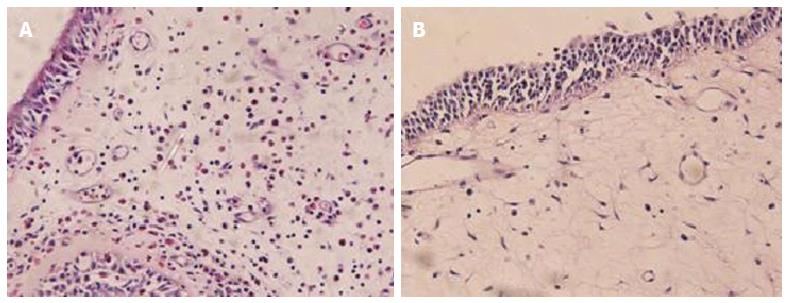
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining for nasal polyp tissues.
Predominant eosinophil infiltration is showed in the subtype of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (A), but other forms of inflammatory cell infiltration in the subtype of non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (B) (× 400).
Figure 2 Nasal endoscopic findings.
Polyps in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (A) and in non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (B).
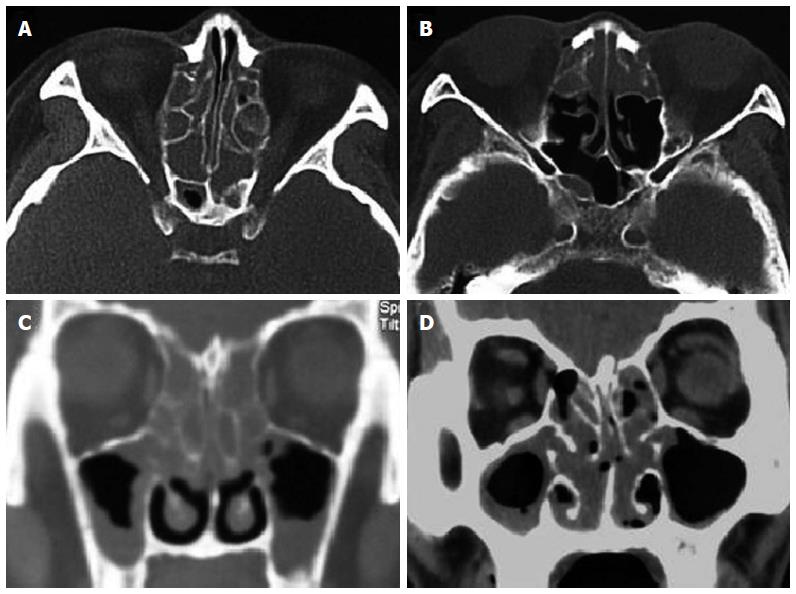
Figure 3 Computed tomography findings.
Axial and frontal sections in the subtypes of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (ECRSwNP) (A and C) and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (NECRSwNP) (B and D). Predominant diseases in bilateral anterior and posterior ethmoid sinuses are showed in ECRSwNP, while predominant diseases in anterior ethmoid sinuses in NECRSwNP.
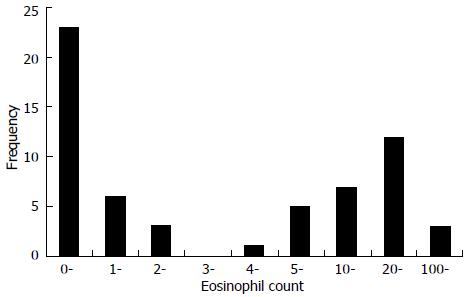
Figure 4 Frequency distribution and range of tissue eosinophil count per high power field for 60 patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.
- Citation: Wang ET, Zheng Y, Liu PF, Guo LJ. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in East Asians. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(12): 873-882
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i12/873.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.873