Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2025; 13(17): 99924
Published online Jun 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i17.99924
Published online Jun 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i17.99924
Figure 1
Diabetes prevalence in Malaysia.
Figure 2
Risk factors for cardiovascular/kidney disease in type 2 diabetes.
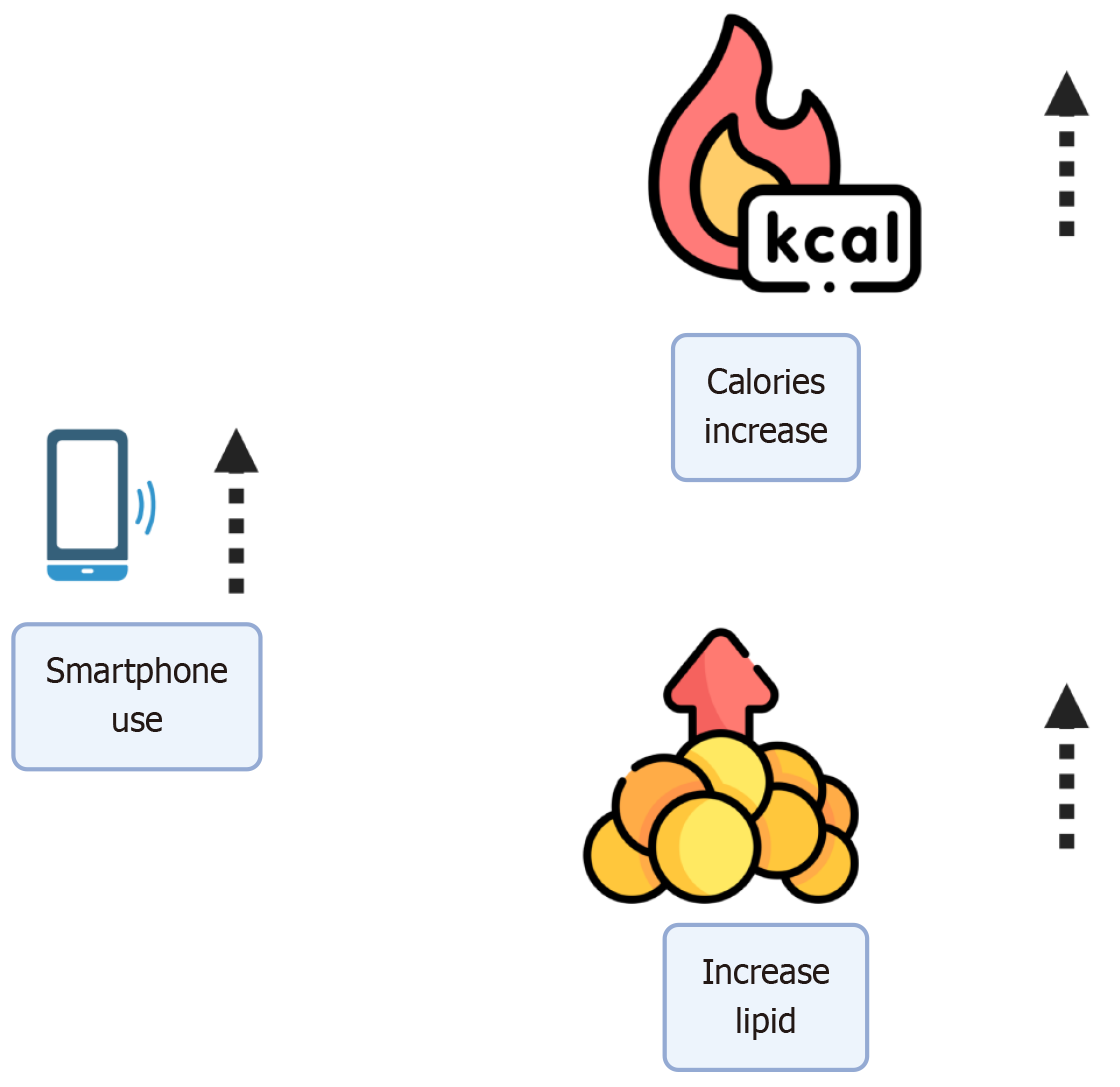
Figure 3
Relationship between smart phone use, calories and lipid profile.
Figure 4 Therapeutic effects of time-restricted eating in rodents made obese by high-fat diet feeding.
Citation: Petersen MC, Gallop MR, Flores Ramos S, Zarrinpar A, Broussard JL, Chondronikola M, Chaix A, Klein S. Complex physiology and clinical implications of time-restricted eating. Physiol Rev 2022; 102: 1991-2034. Copyright © the American Physiological Society. Published by American Physiological Society.
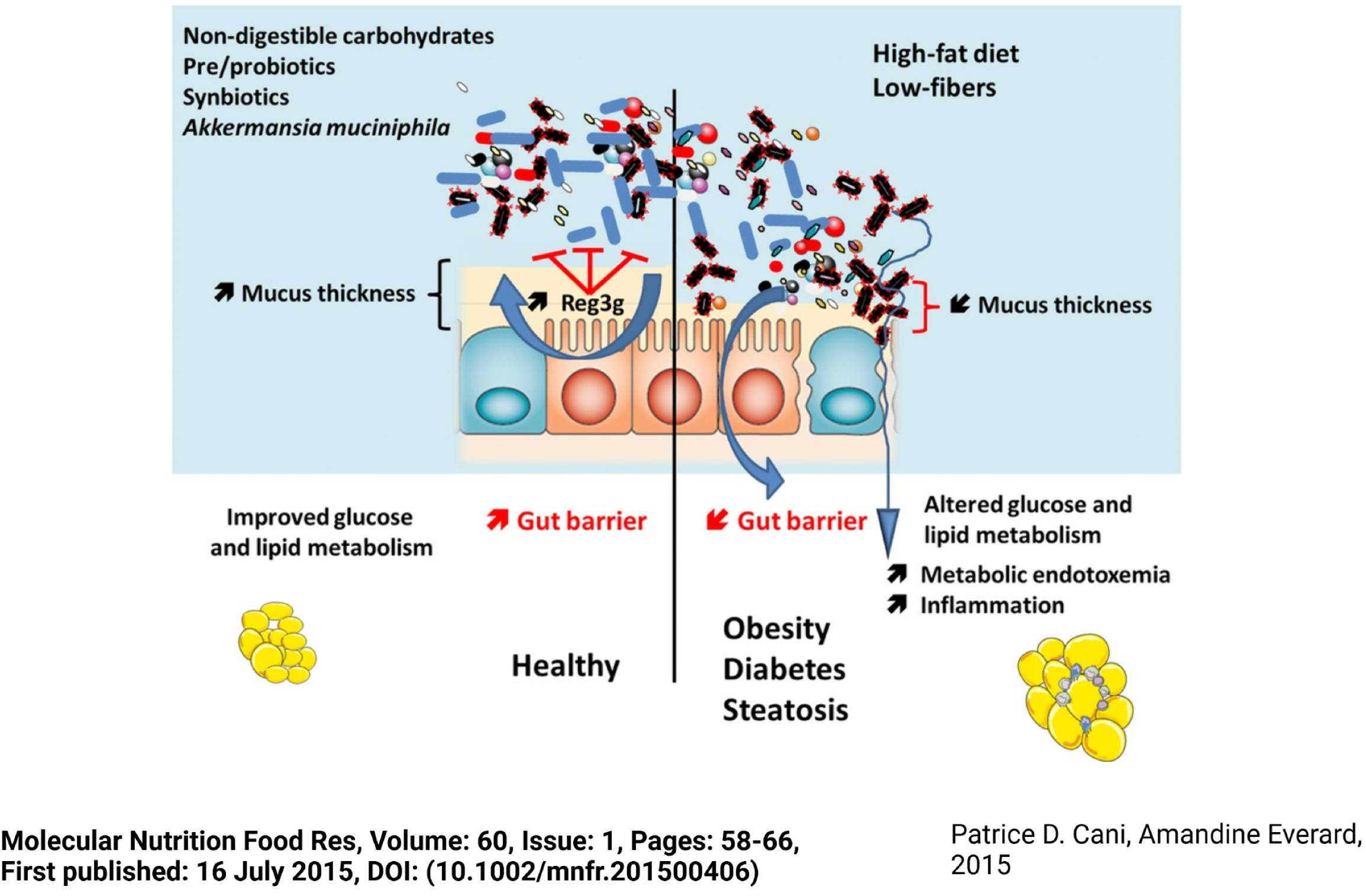
Figure 5 Crosstalk between host and microbes: Impact on metabolism.
The intestinal barrier is composed of different factors such as epithelial cells, a mucus layer, and antimicrobial peptides produced by host cells. The inner mucus layer and the antimicrobial peptides help segregate microbes from the epithelium. Moreover, specific microbes such as Akkermansia muciniphila improve gut barrier function and mucus layer thickness. During high-fat diet feeding and low fibers intake, the gut microbiota composition is different, inflammatory components translocate into the blood via the altered gut barrier function. Citation: Cani PD, Everard A. Talking microbes: When gut bacteria interact with diet and host organs. Mol Nutr Food Res 2016; 60: 58-66. Copyright © Authors 2015. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
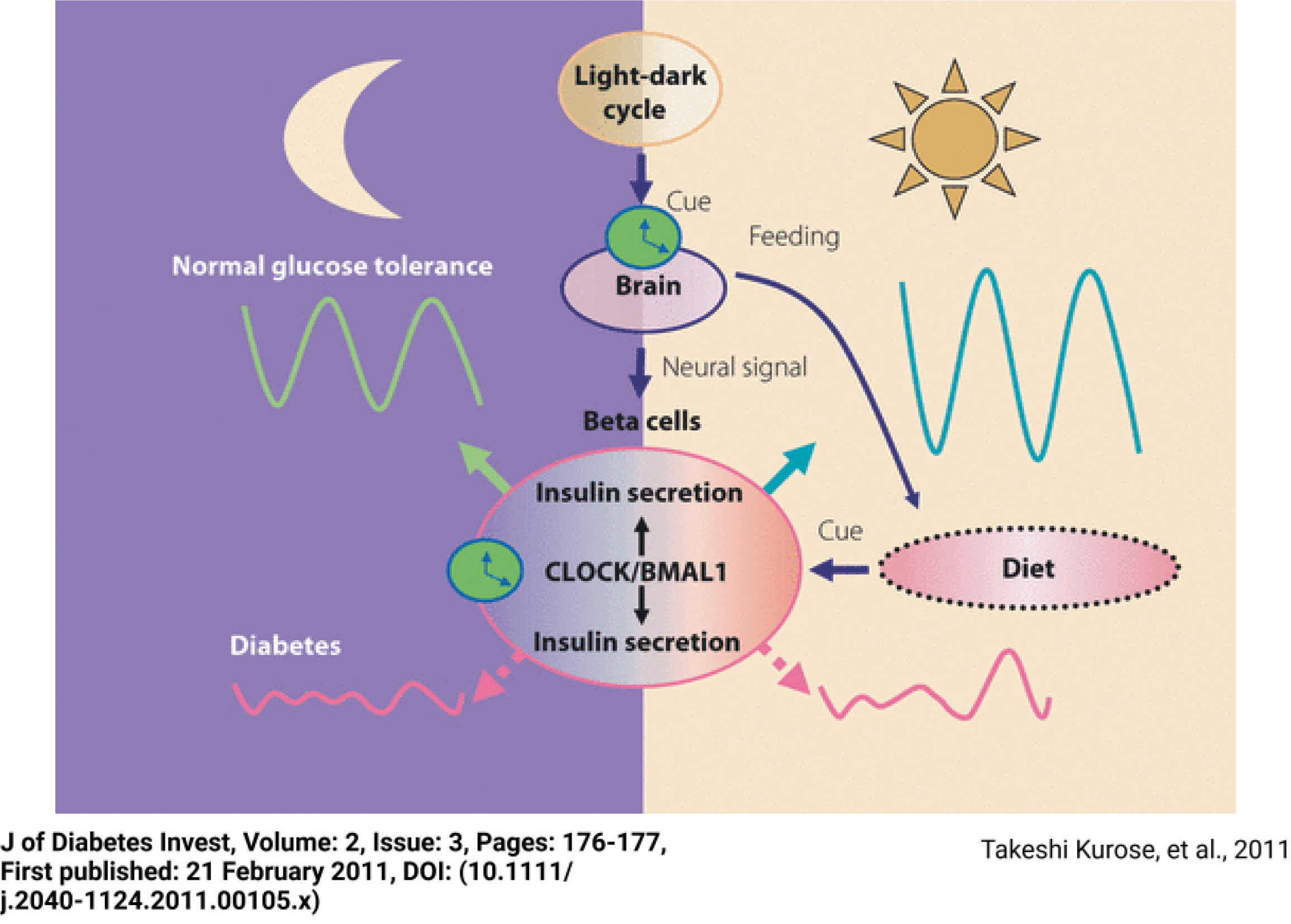
Figure 6 Pancreatic clock machinery and glucose metabolism.
Citation: Kurose T, Yabe D, Inagaki N. Circadian rhythms and diabetes. J Diabetes Investig 2011; 2: 176-177. Copyright © Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd 2011. Published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
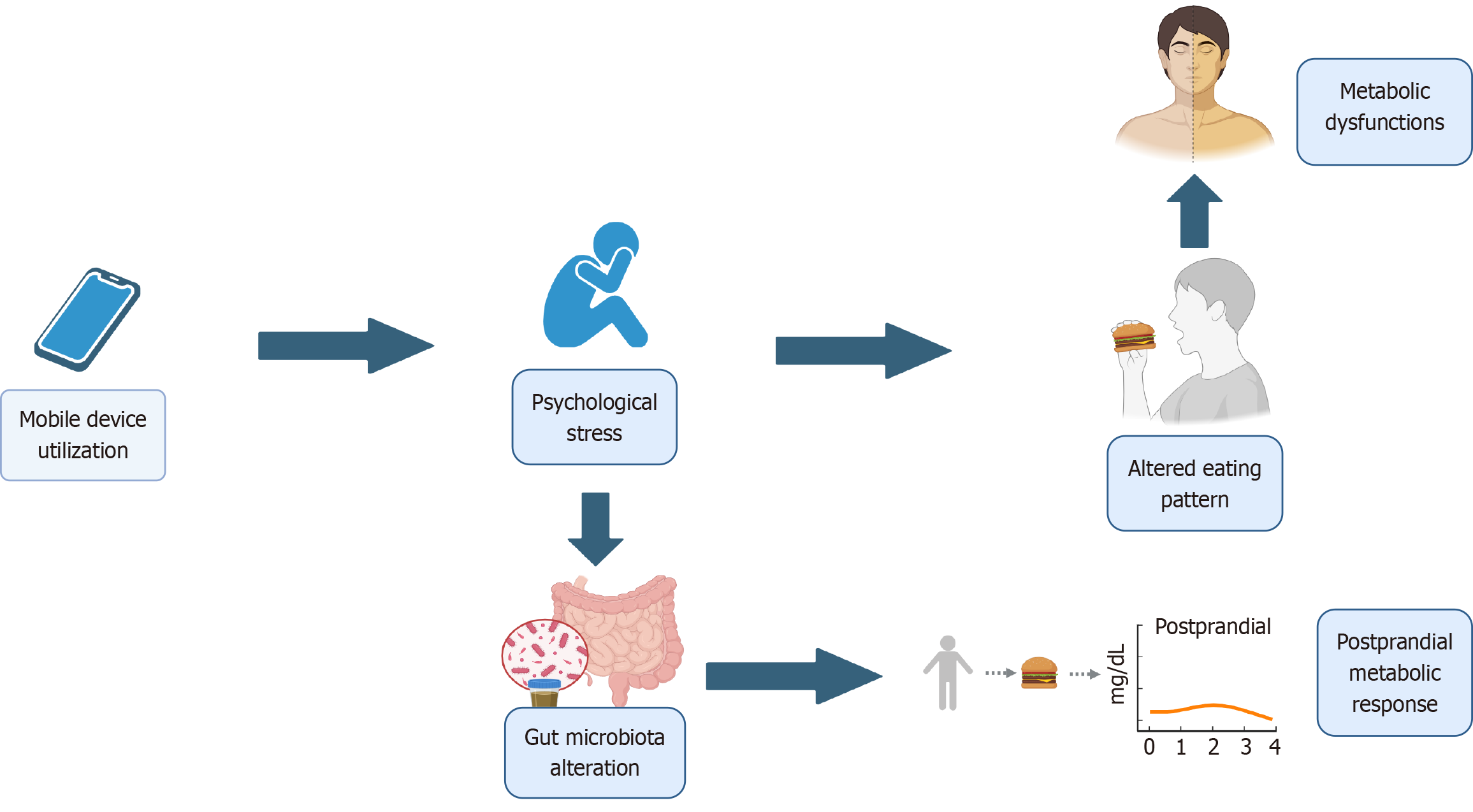
Figure 7
The complex relationship between mobile device utilization, mealtime distractions, and metabolic health.
- Citation: Aslam MS. Exploring the impact of mobile device use on mealtime distractions and its consequences for metabolic health: A narrative minireview. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(17): 99924
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i17/99924.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i17.99924