Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2025; 13(11): 99748
Published online Apr 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i11.99748
Published online Apr 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i11.99748
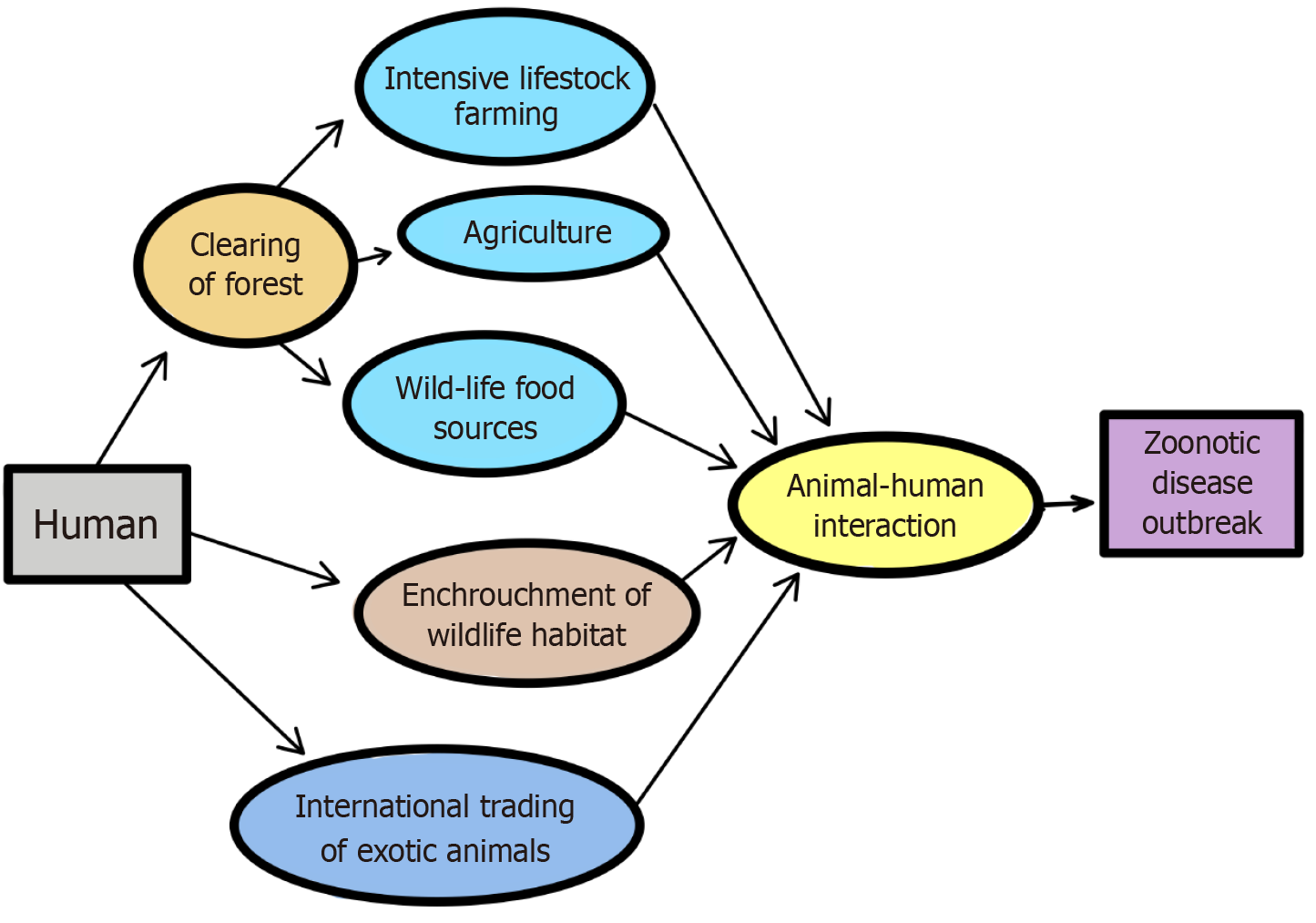
Figure 1 Anthropogenic factors promoting zoonotic spillover.
The menace of zoonotic spillover is result of consortium of factors which determine the interplay of ecological dynamics of infection in reservoir hosts, its’ transmission, and exposure among susceptible host. The geographical distribution of reservoir hosts, its propensity for human interaction, human behavior towards the reservoir and viral load carried by it are factors determining the possible site of attack. Host immunity and health status in conjunction with the viral load and virulence of the pathogen decide the probability and severity of infection.
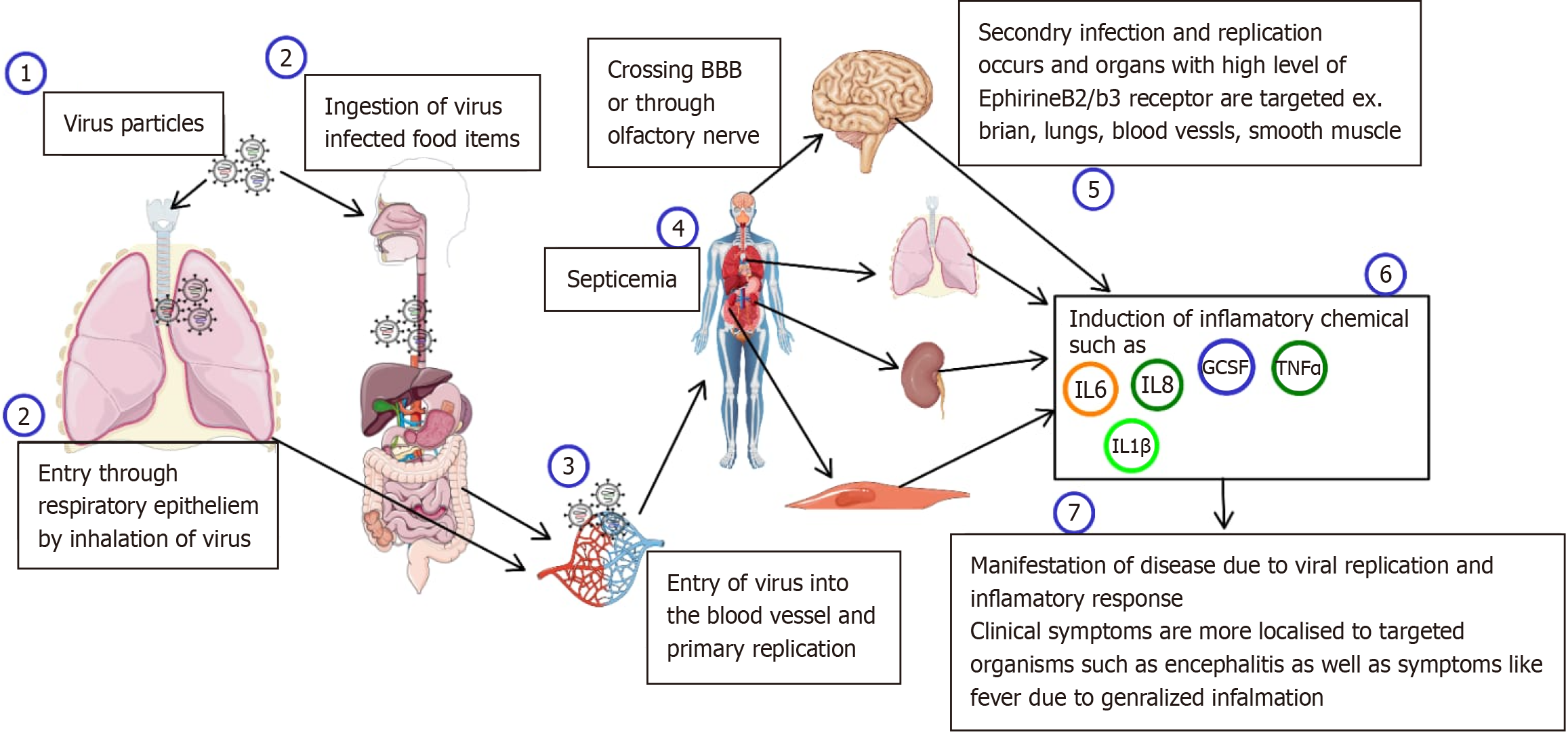
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of Nipah virus.
The Nipah virus (1) may enter the human body through oral or nasal route (2). From these sites it reaches the blood stream (3) and gets carried away to brain either by crossing the blood brain barrier or through the olfactory nerve. While in the blood stream it may cause generalized septicemia (4). So the secondary infections (5) can occour in organs with epinephrin b2/b3 receptors i.e. brain, blood vessels and smooth muscles. Inflammatory cytokine come into play like IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α. BBB: Blood brain barrier; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; G-CSF: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
- Citation: Tyagi S, Upadhyay S, Bharara T, Sahai S. Nipah virus: Preventing the next outbreak. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(11): 99748
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i11/99748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i11.99748