Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2024; 12(5): 880-890
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.880
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.880
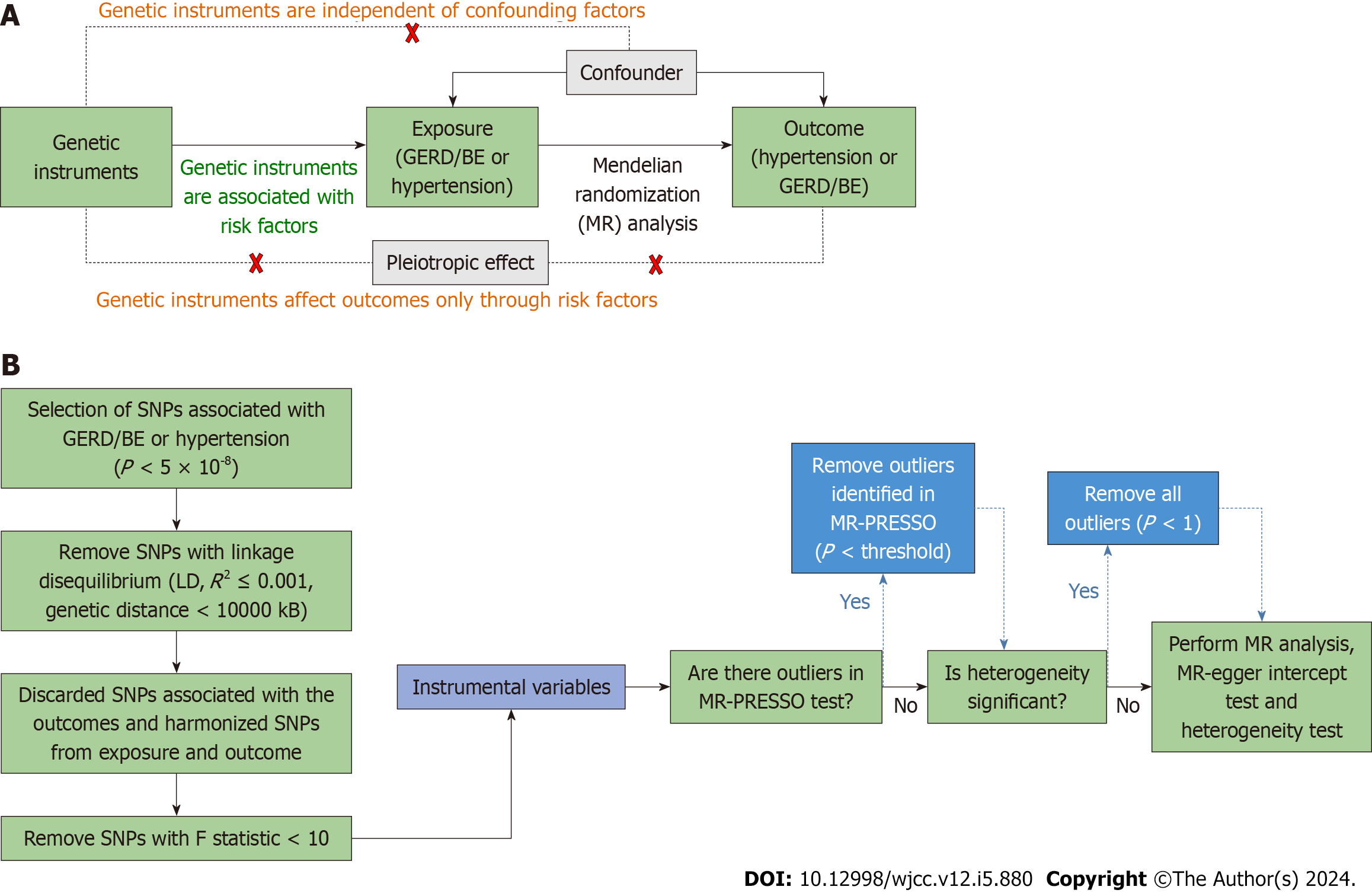
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the bidirectional Mendelian randomization study on the causal relationship between gastro
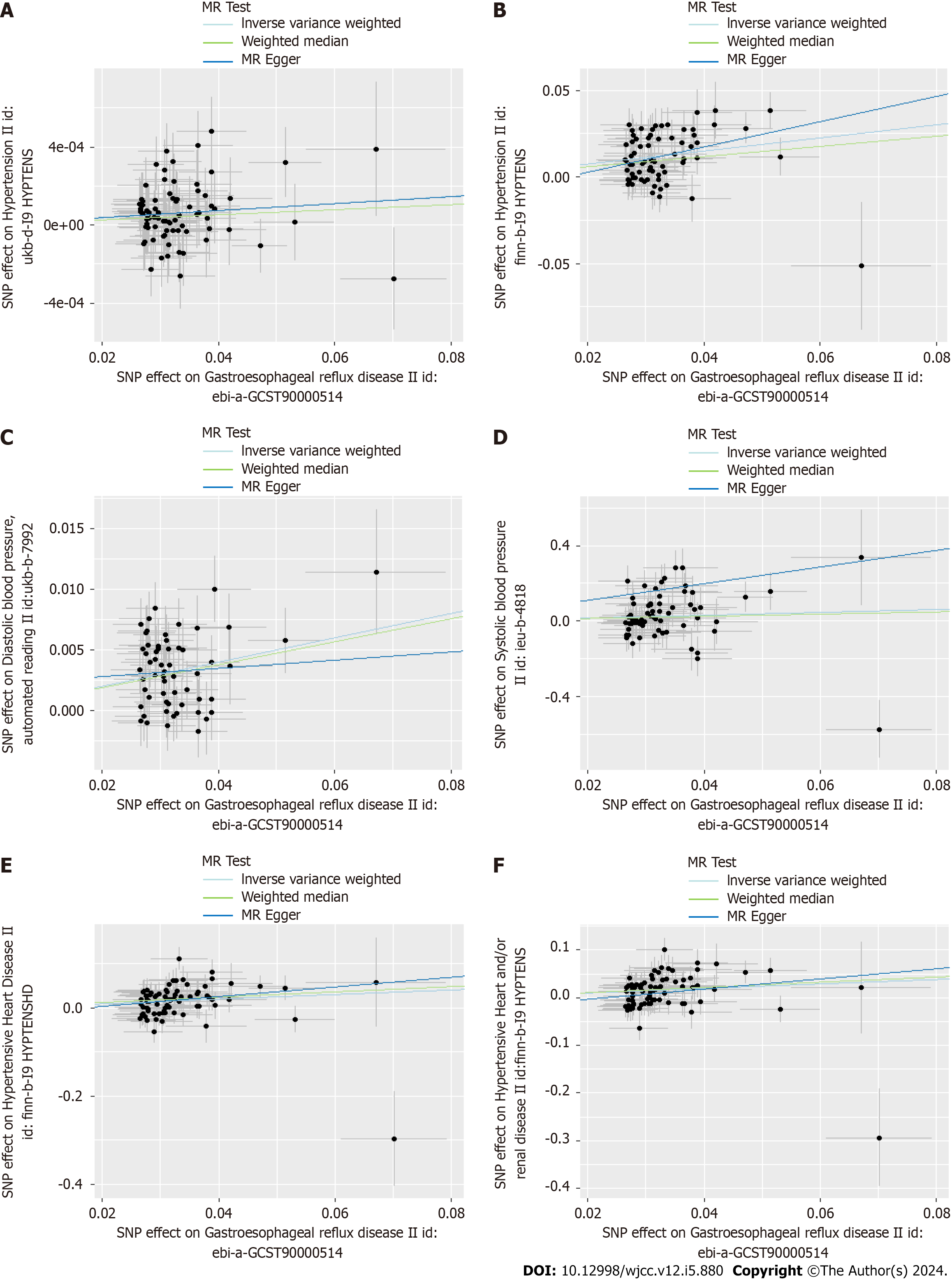
Figure 2 Scatter plots for the causal association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and hypertension.
A: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) on essential hypertension; B: Replication practice for GERD on essential hypertension; C: GERD on diastolic blood pressure; D: GERD on systolic blood pressure; E: GERD on hypertensive heart disease; F: GERD on hypertensive heart and/or renal disease. MR: Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphism.
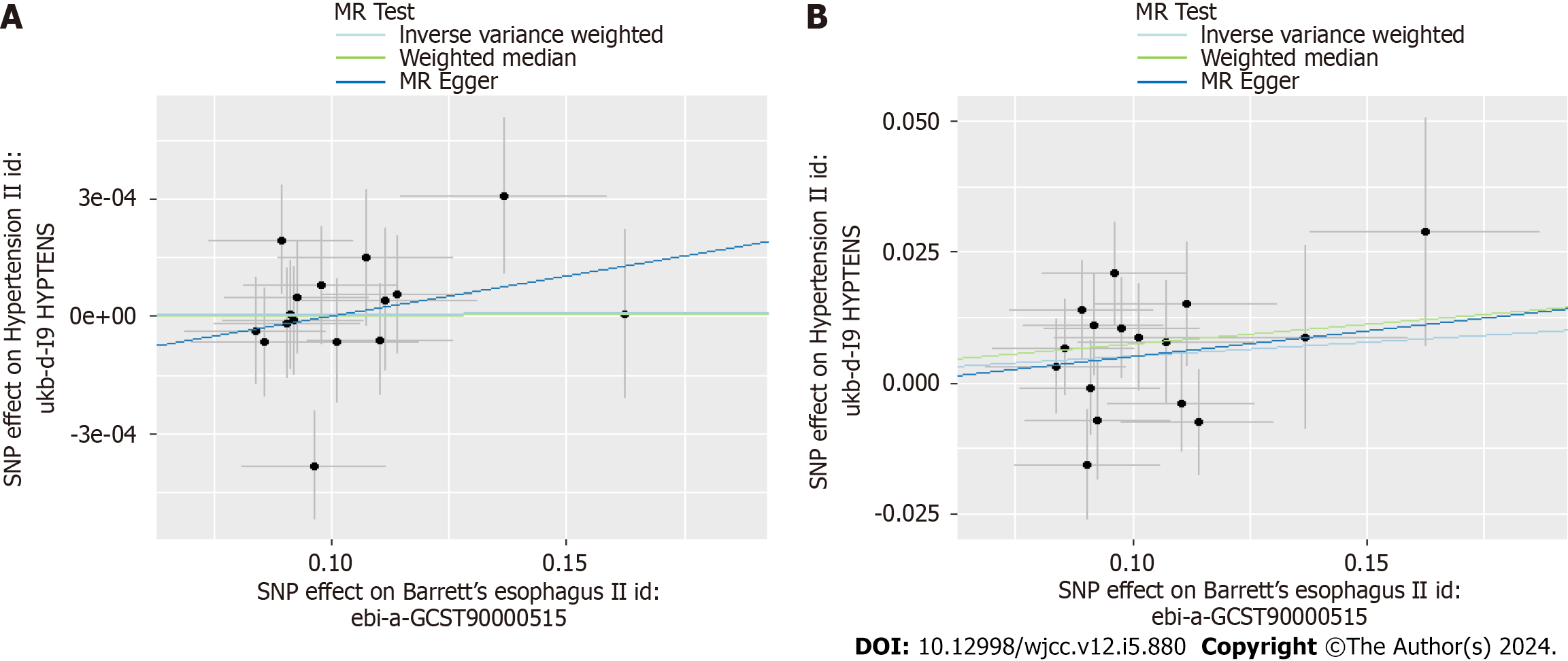
Figure 3 Scatter plots for the causal association between Barret's esophagus and hypertension.
A: Barret's esophagus (BE) on essential hypertension; B: Replication practice for BE on essential hypertension. MR: Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphism.
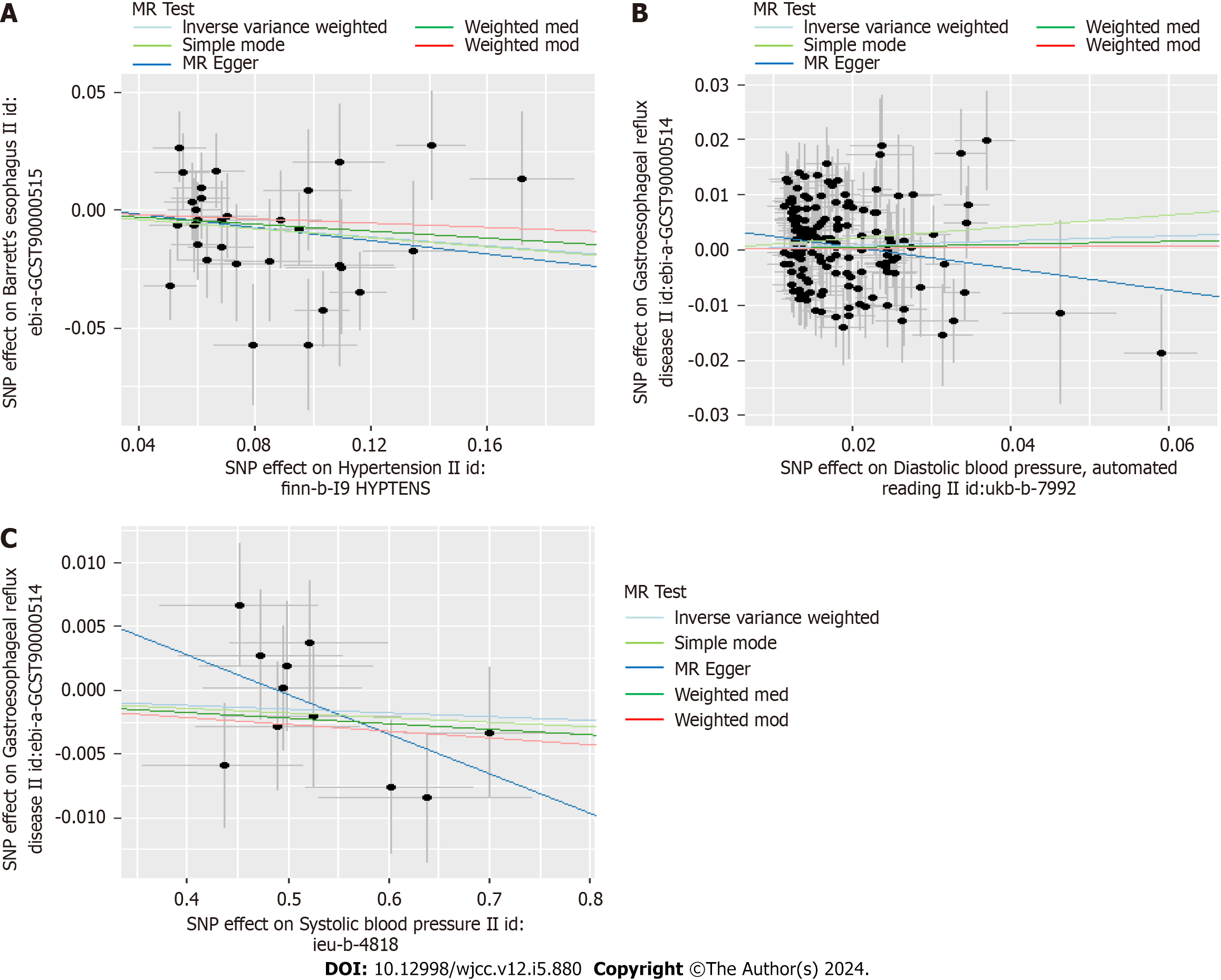
Figure 4 Scatter plots for the causal association between hypertension and Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
A: Duplicate essential hypertension on Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); B: Diastolic blood pressure and GERD; C: Systolic blood pressure and GERD. MR: Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphism.
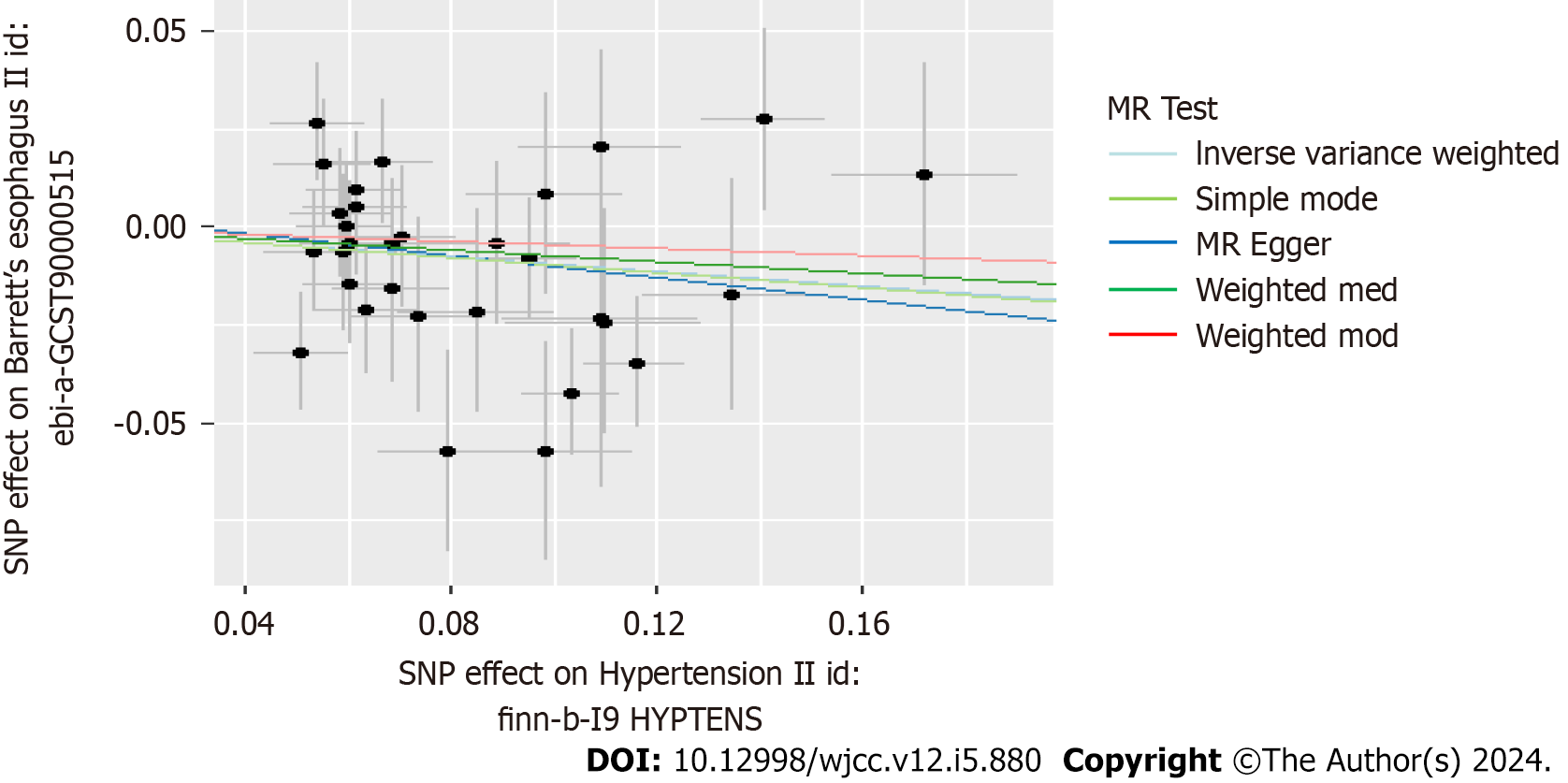
Figure 5 Scatter plots for the causal association between hypertension and Barret's esophagus: Duplicate essential hypertension on Barret's esophagus.
MR: Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphism.
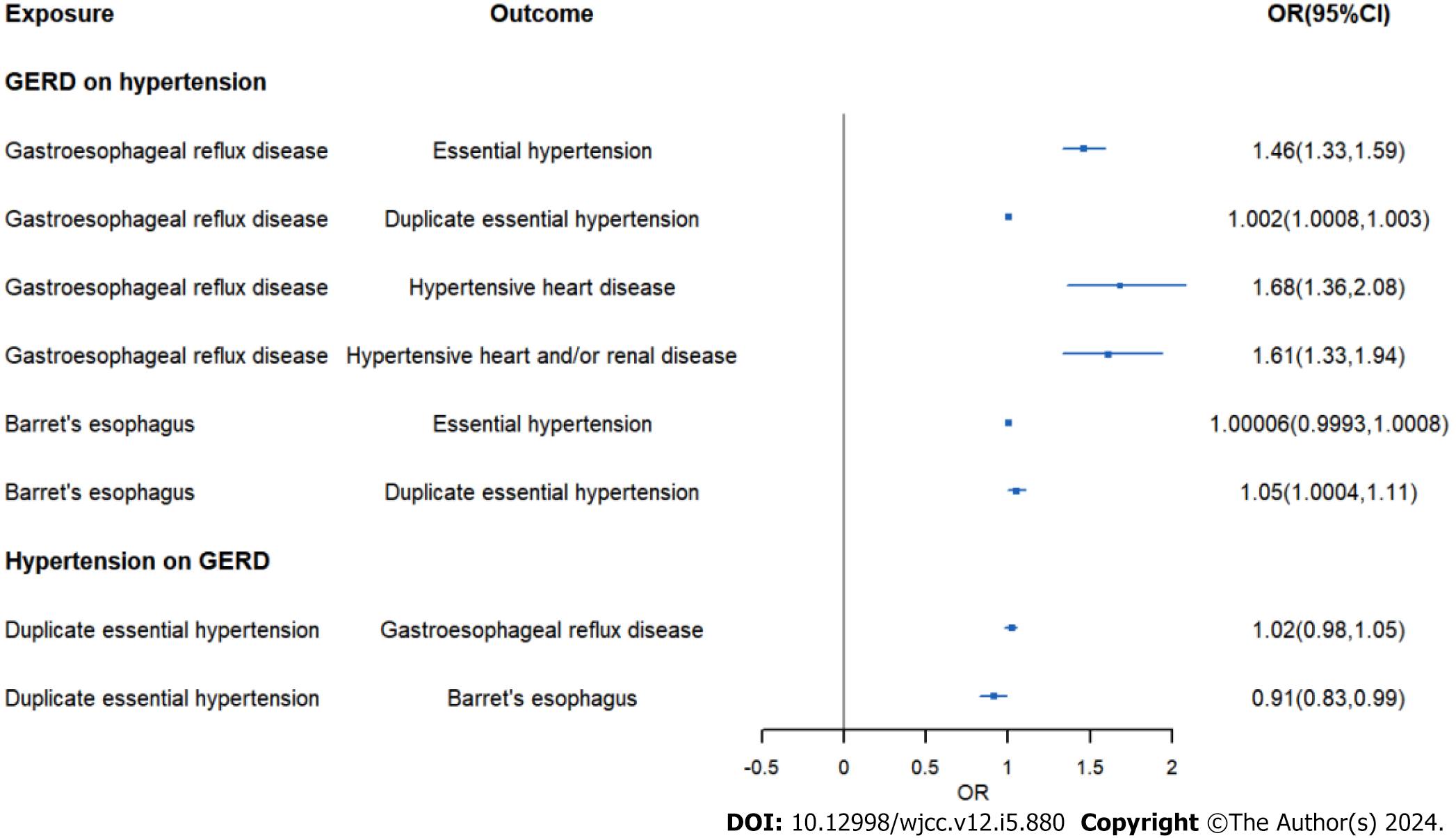
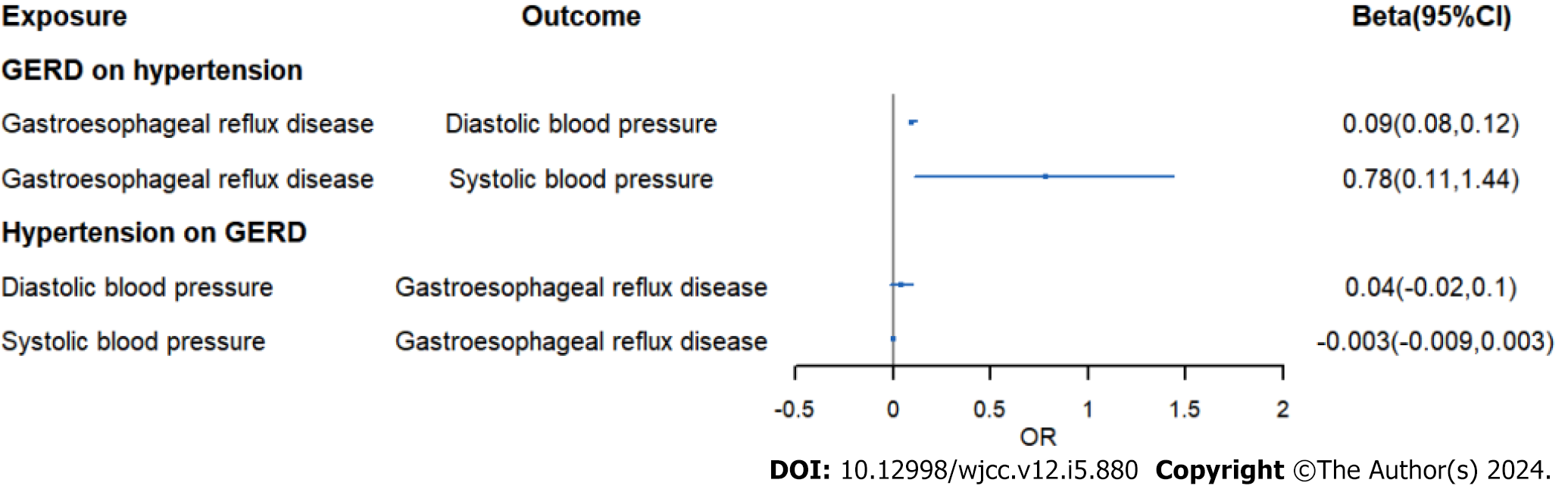
Figure 6 Forest plot for the causal association between hypertension and Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Figure 7 Forest plot for the causal association between hypertension and Barret's esophagus.
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Citation: Wei N, Liu MH, Song YH. Causal associations between gastroesophageal reflux disease and essential hypertension: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(5): 880-890
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i5/880.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.880