Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2024; 12(36): 6916-6925
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6916
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6916
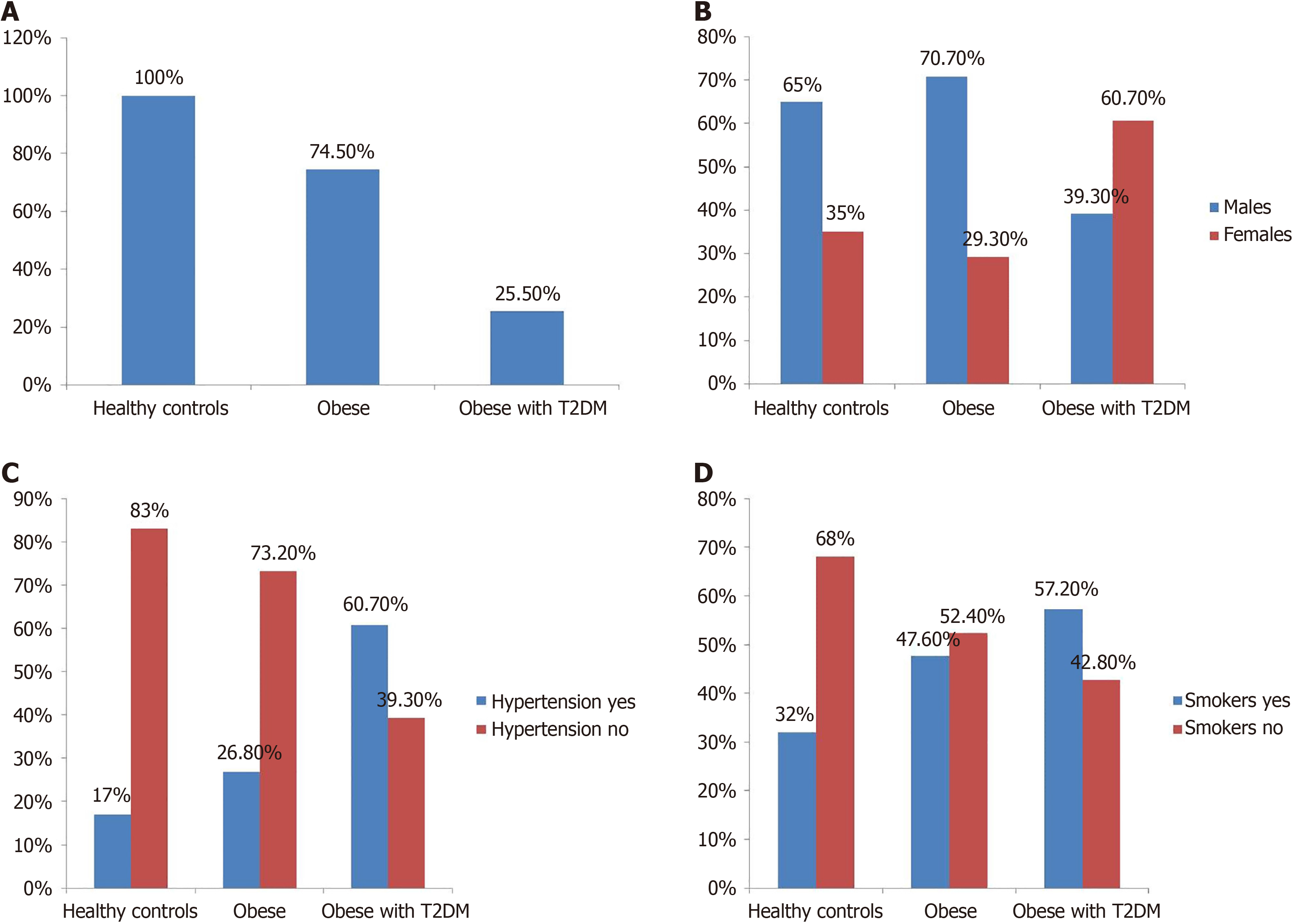
Figure 1 Demographic parameters of the participants.
A: Healthy controls, obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus participants; B: Male and female participants in the healthy controls, obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus; C: Hypertensive and non-hypertensive participants in the healthy controls, obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus; D: Smoking and nonsmoking participants in the healthy controls, obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
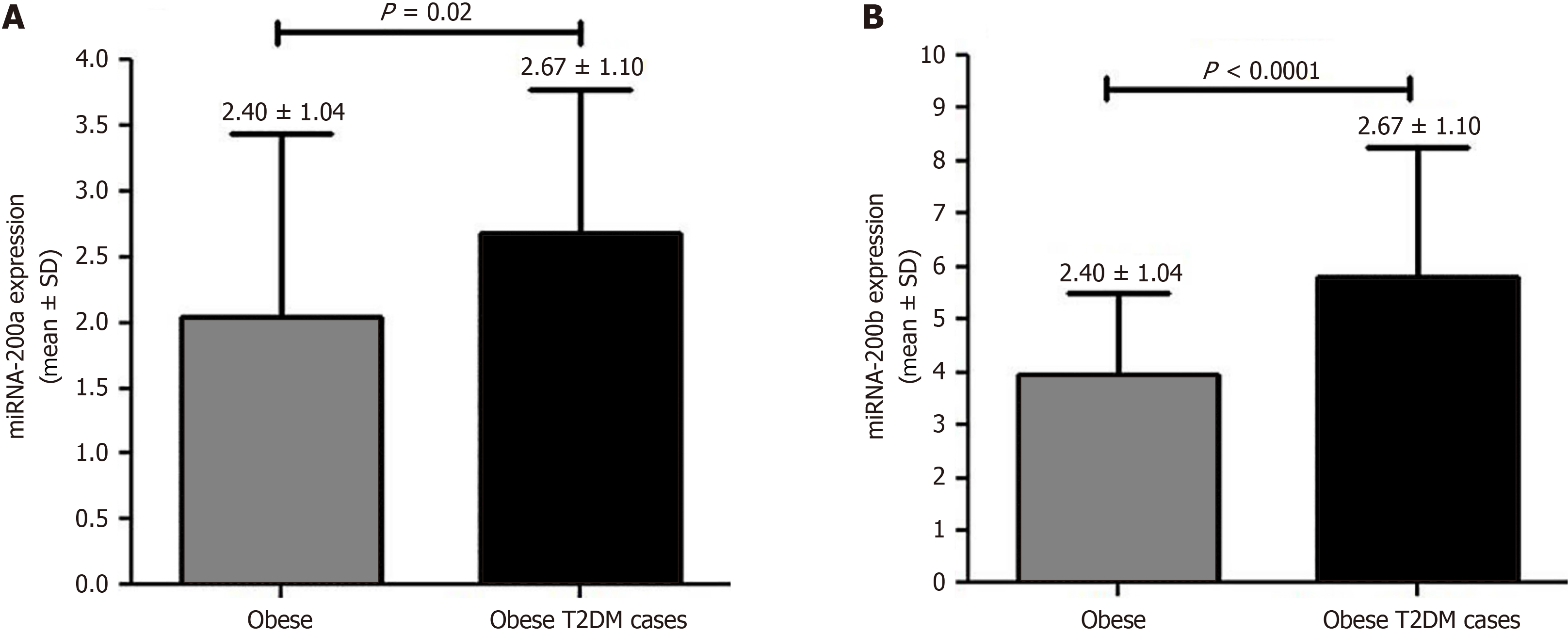
Figure 2 MiRNA-200a and miRNA-200b expression.
A: Obese; B: Obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus. T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
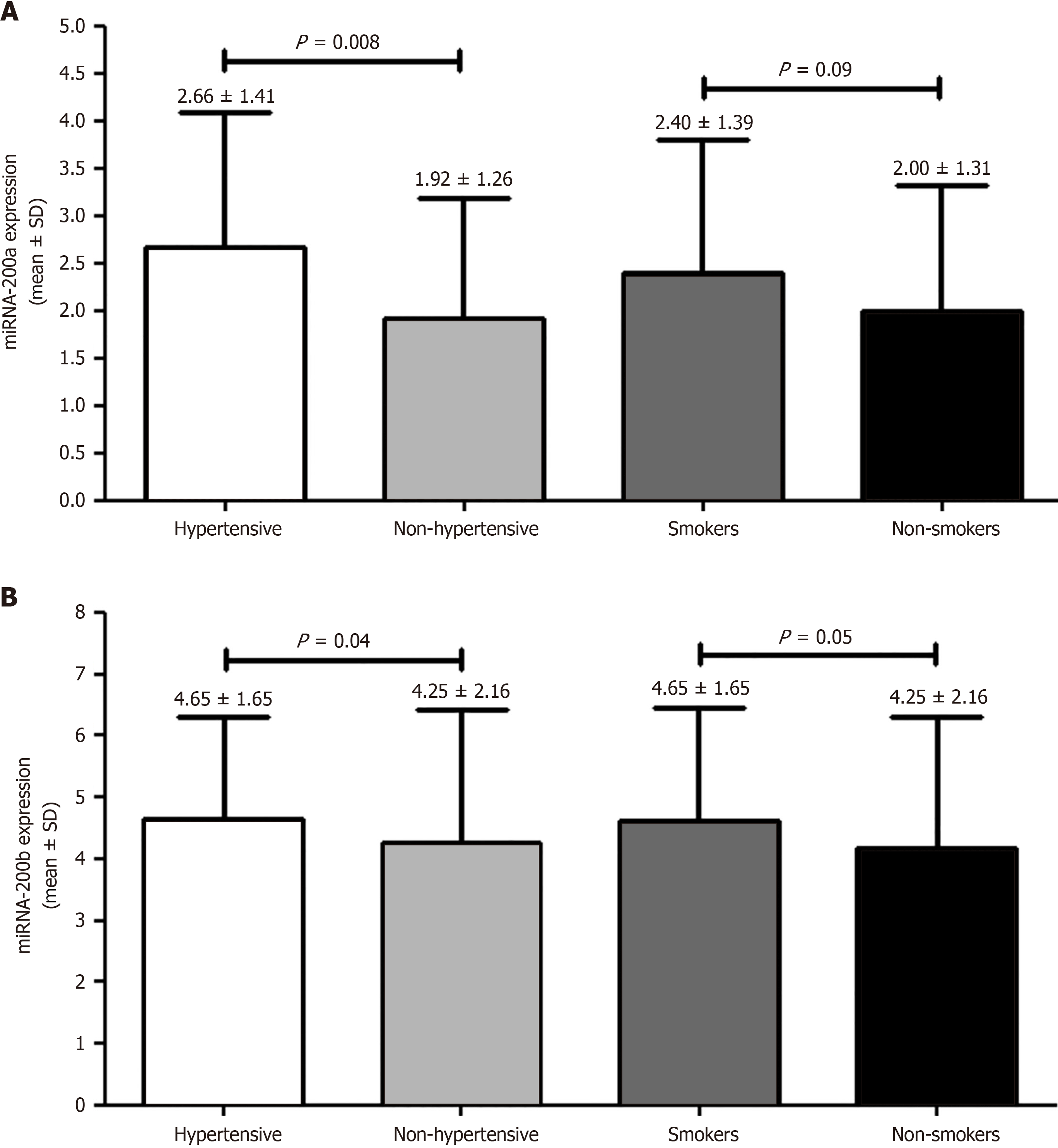
Figure 3 Comparison of miRNA-200a and miRNA-200b expression with regard to hypertension and smoking in obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus participants.
A: MiRNA-200a; B: MiRNA-200b.
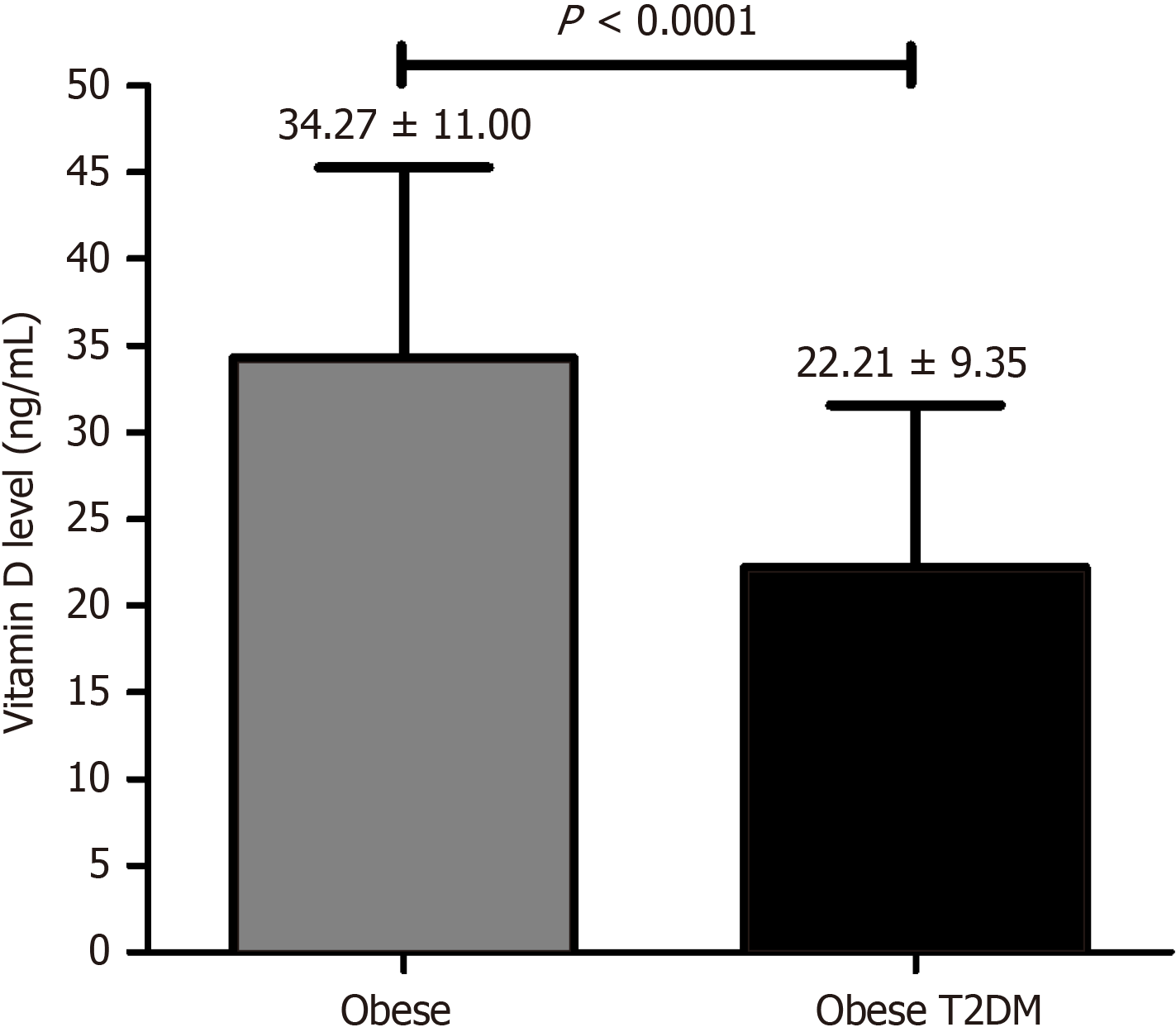
Figure 4 Level of vitamin D in obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus participants.
T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
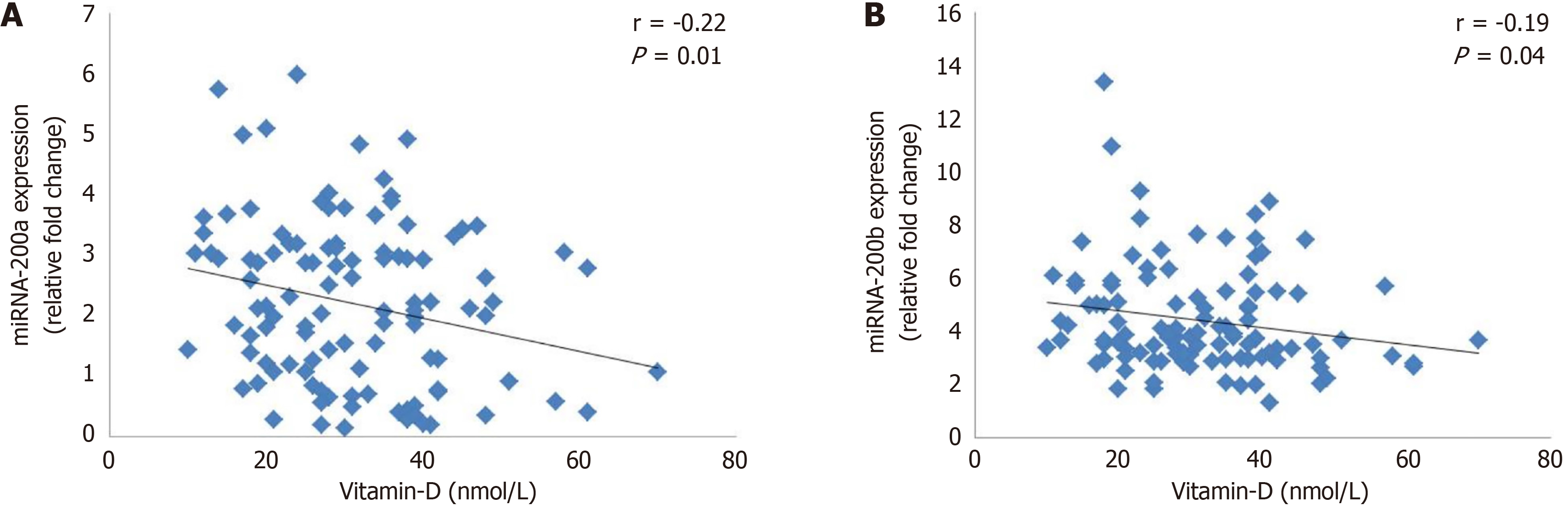
Figure 5 Correlation of vitamin D with miRNA-200a and miRNA-200b in obese and obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus participants.
A: MiRNA-200a; B: MiRNA-200b.
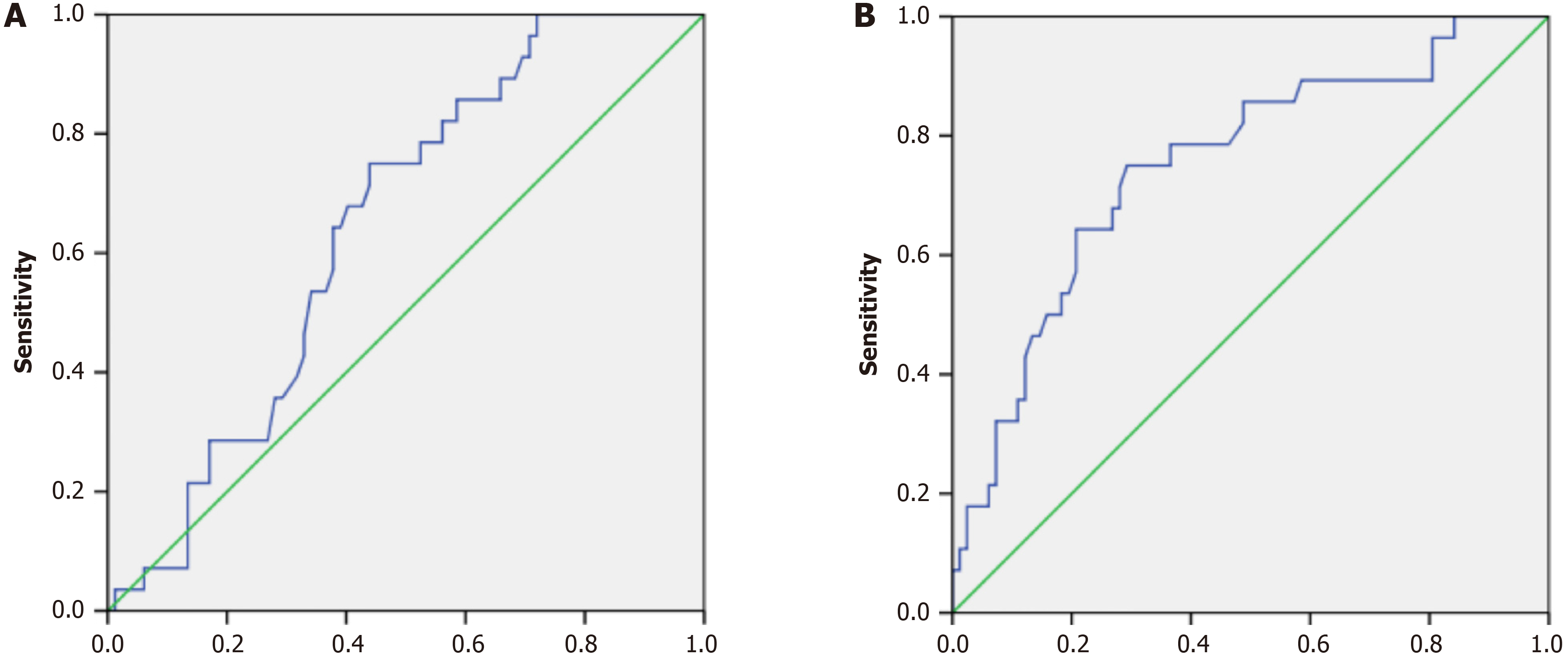
Figure 6 Prognostic importance of miRNA-200a and miRNA-200b in obese vs obese with type 2 diabetes mellitus participants.
A: MiRNA-200a; B: MiRNA-200b.
- Citation: Alshahrani AF, Ashfaq F, Alsayegh AA, Bajahzer M, Khan MI, Beg MMA. MiRNA-200a and miRNA-200b expression, and vitamin-D level: Prognostic significance in obese non-diabetic and obese type 2 diabetes mellitus individuals. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(36): 6916-6925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i36/6916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6916