Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2024; 12(25): 5681-5696
Published online Sep 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i25.5681
Published online Sep 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i25.5681
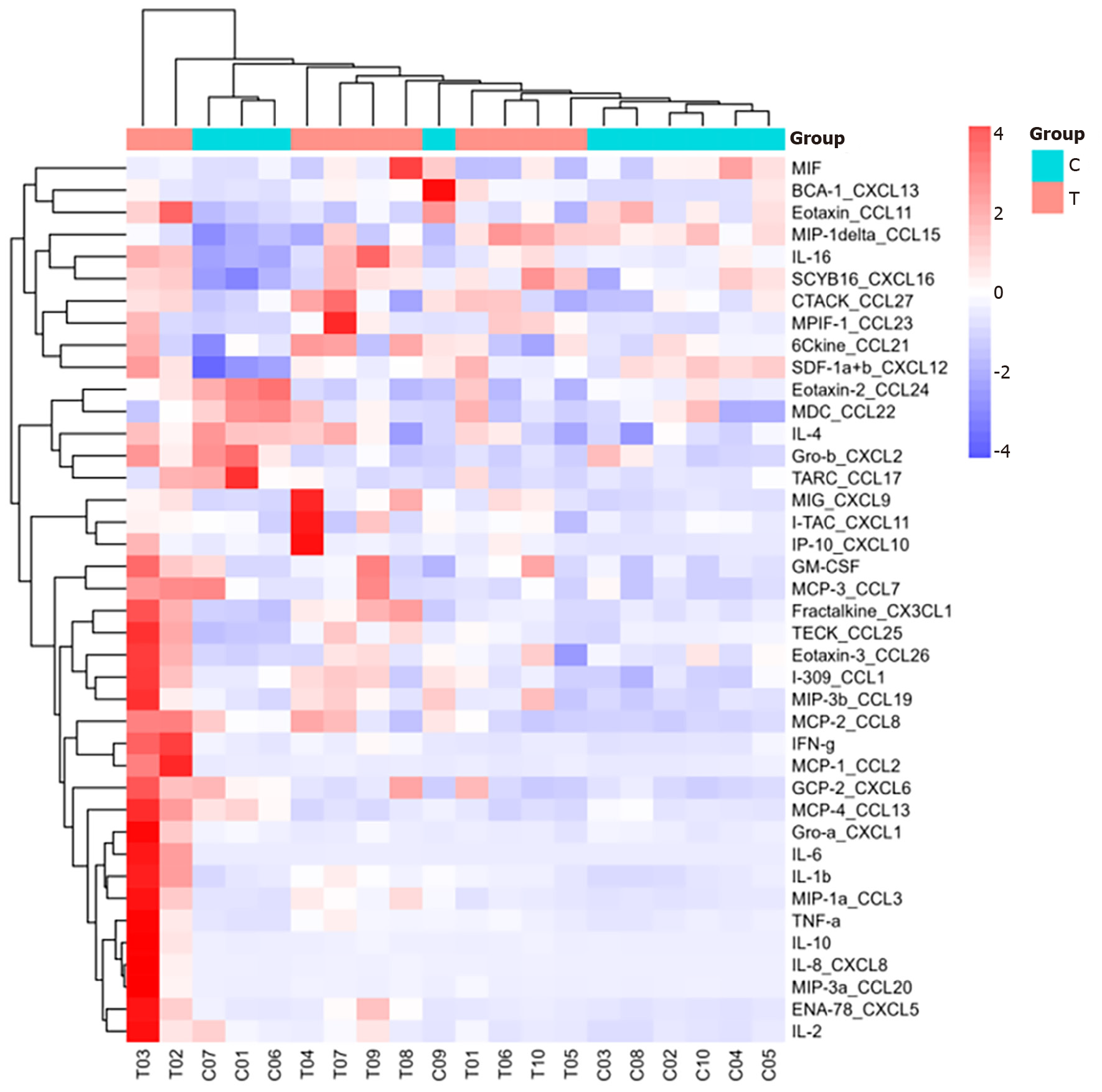
Figure 1 Clustering heatmap of all 40 cytokines.
In the cluster diagram, each row represents a cytokine, and each column represents a sample. Red indicates high expression of cytokines in the sample, whereas blue indicates low expression. T: The sepsis group; C: The non-sepsis control group.
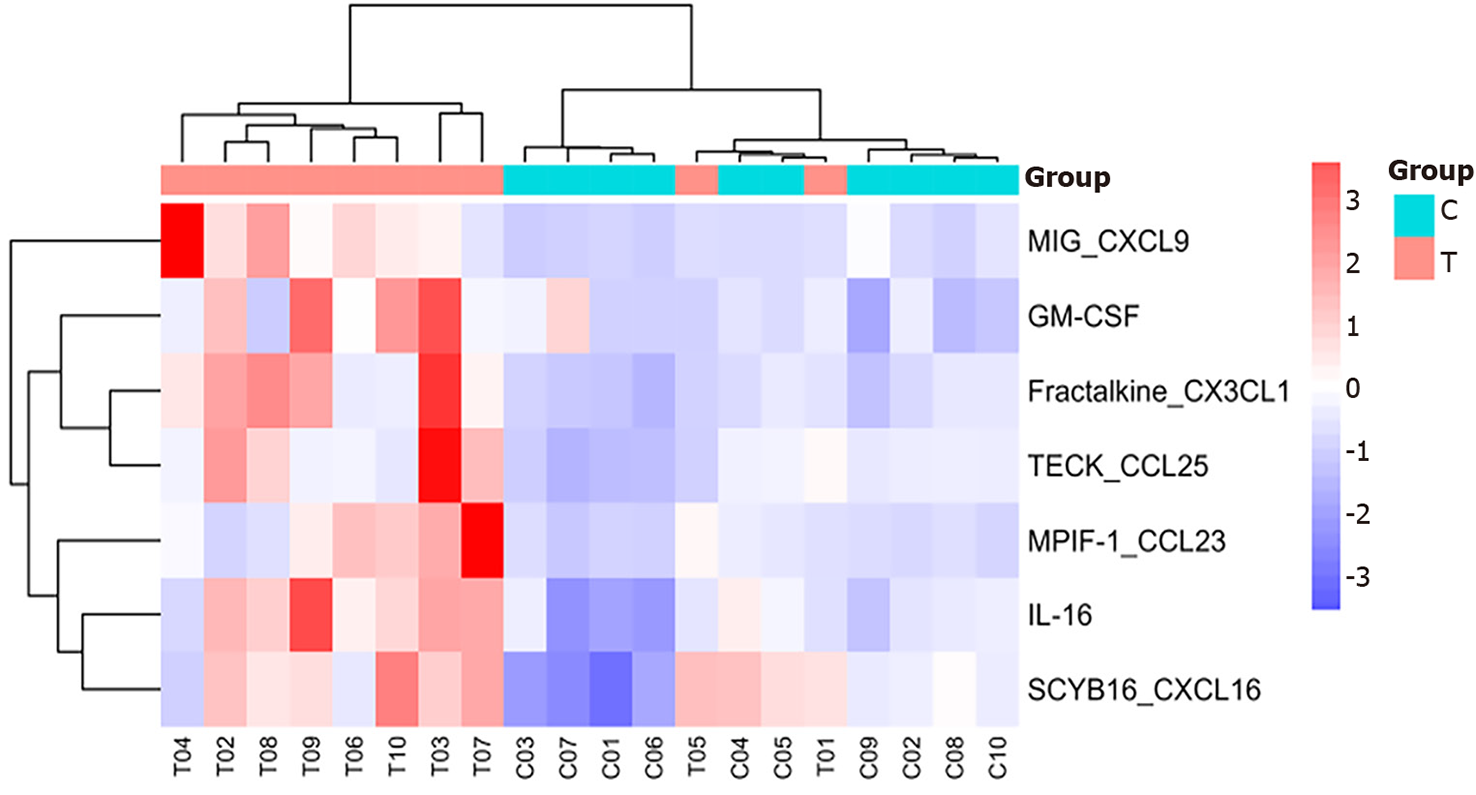
Figure 2 Heatmap analysis of CXCL9, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, CX3CL1, CCL25, CCL23, interleukin-16, CXCL16.
In the Heatmap analysis, each row represents a cytokine, and each column represents a sample. Red indicates high expression of cytokines in the sample, whereas blue indicates low expression. T: The sepsis group; C: The non-sepsis control group; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; Interleukin-16: IL-16.
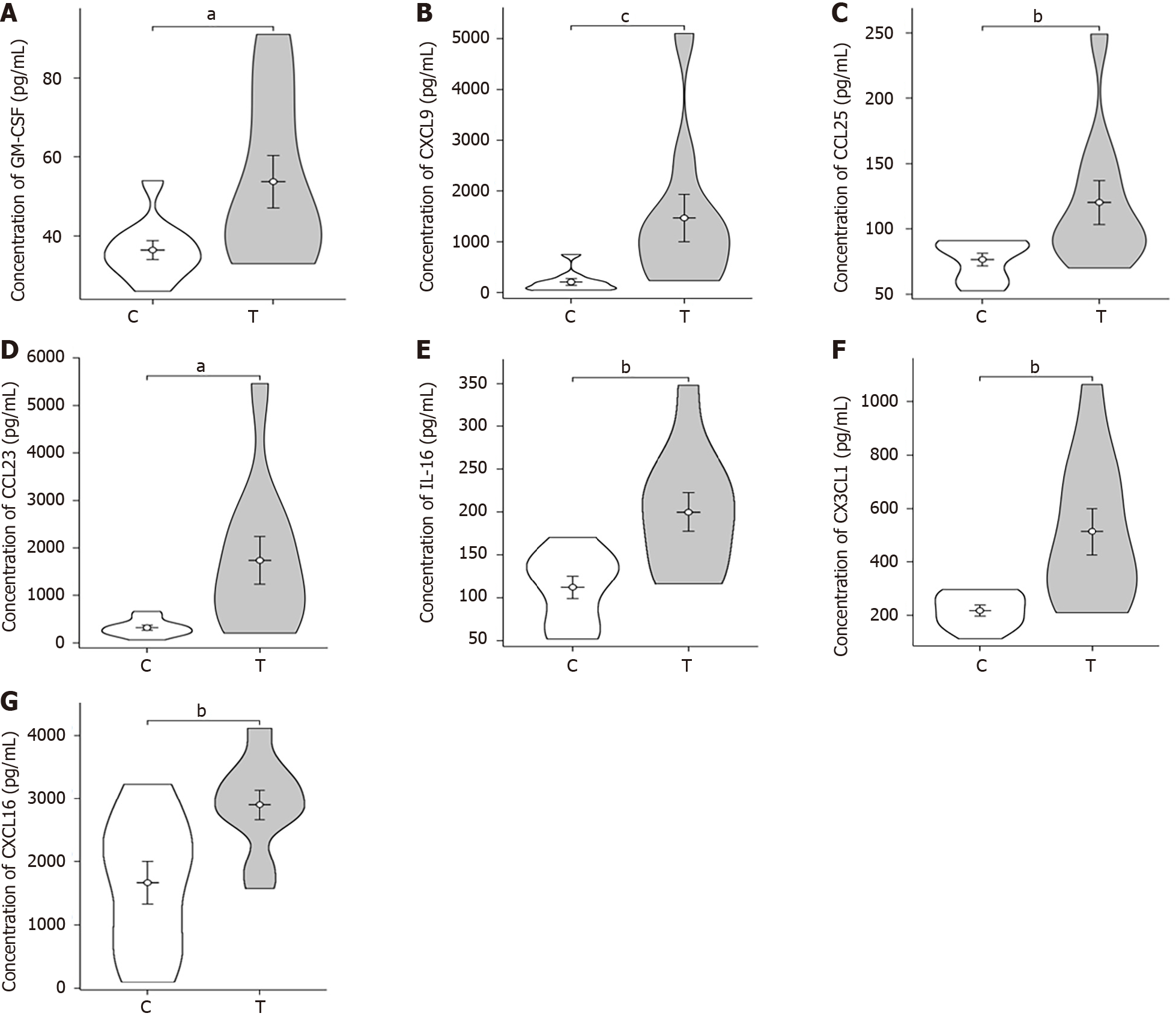
Figure 3 Violin plots of differential expression of plasma cytokine in patient both sepsis and non-sepsis groups.
A: Differential expression of plasma colony-stimulating factor; B: Differential expression of plasma CXCL9; C: Differential expression of plasma CCL25; D: Differential expression of plasma CCL23; E: Differential expression of plasma interleukin-16; F: Differential expression of plasma CX3CL1; G: Differential expression of plasma CXCL16. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. T: The sepsis group; C: The non-sepsis control group; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; Interleukin-16: IL-16.
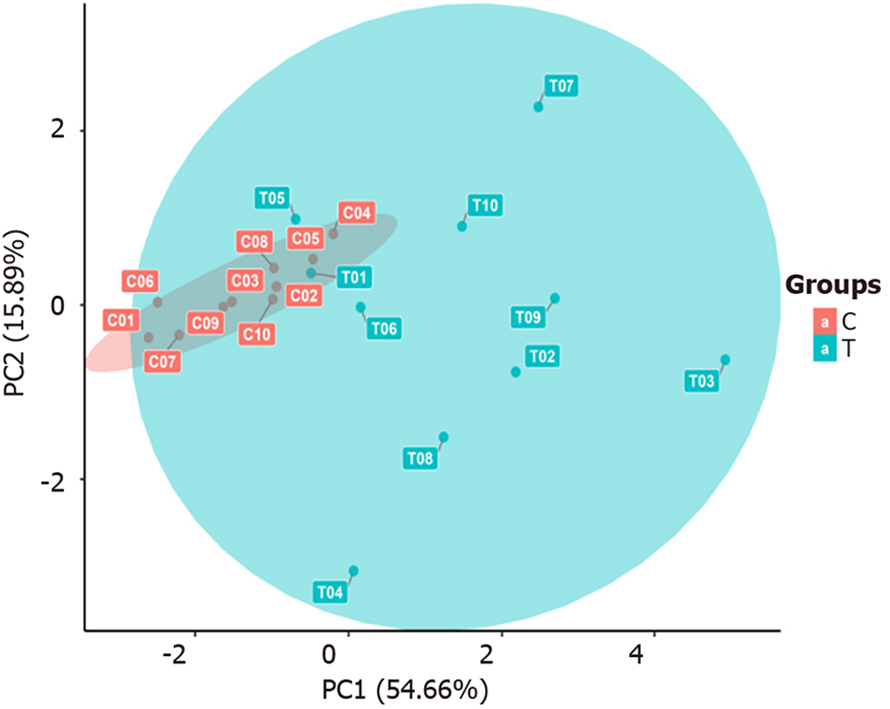
Figure 4 Plot of the principal component analysis results.
The horizontal axis represents the first principal component, and the vertical axis represents the second principal component. T: The sepsis group; C: The non-sepsis control group.
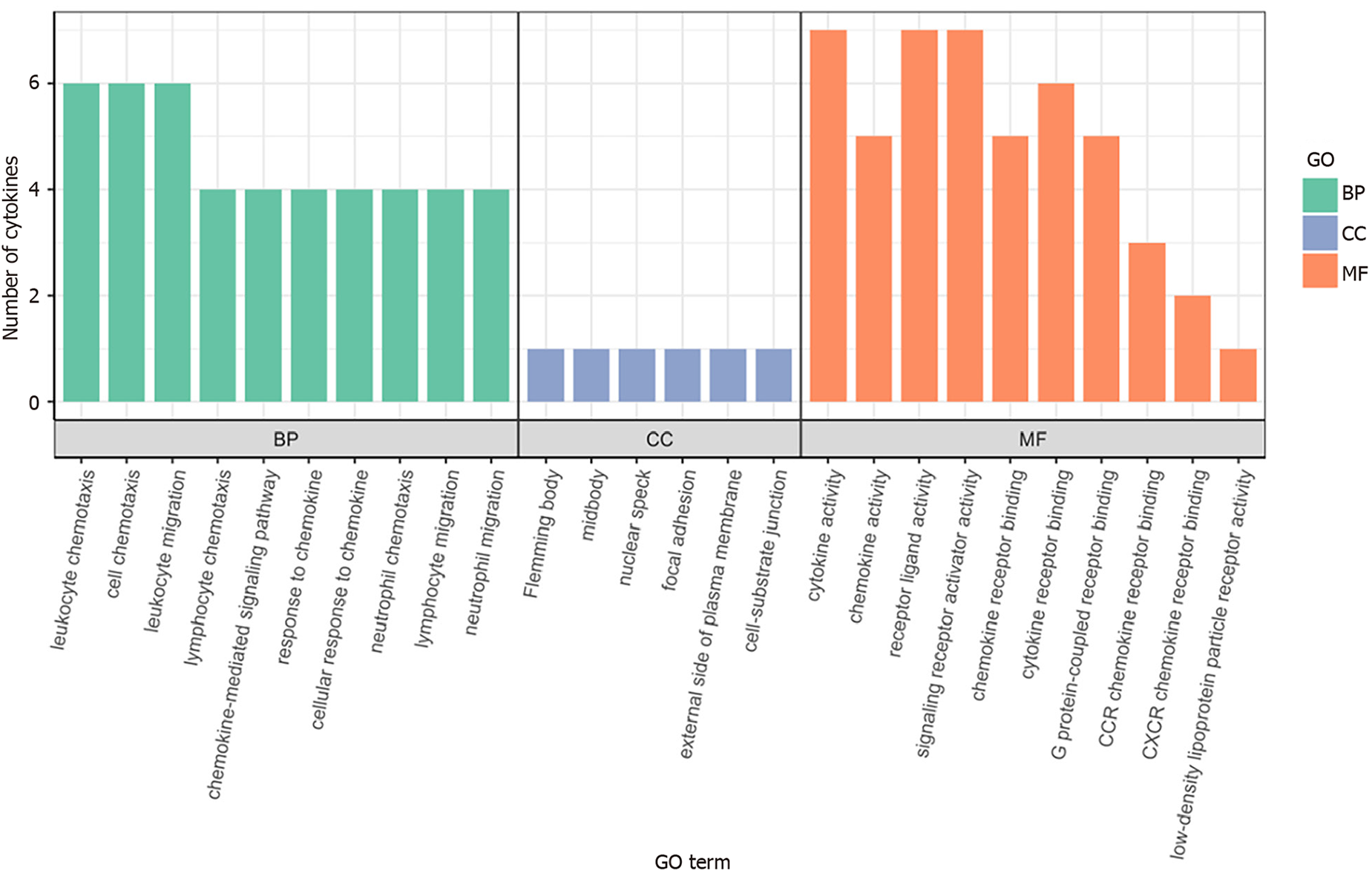
Figure 5 Histogram of Gene Ontology functional enrichment analysis results.
BP: Biological process; CC: Cell composition; MF: Molecular function; GO: Gene Ontology.
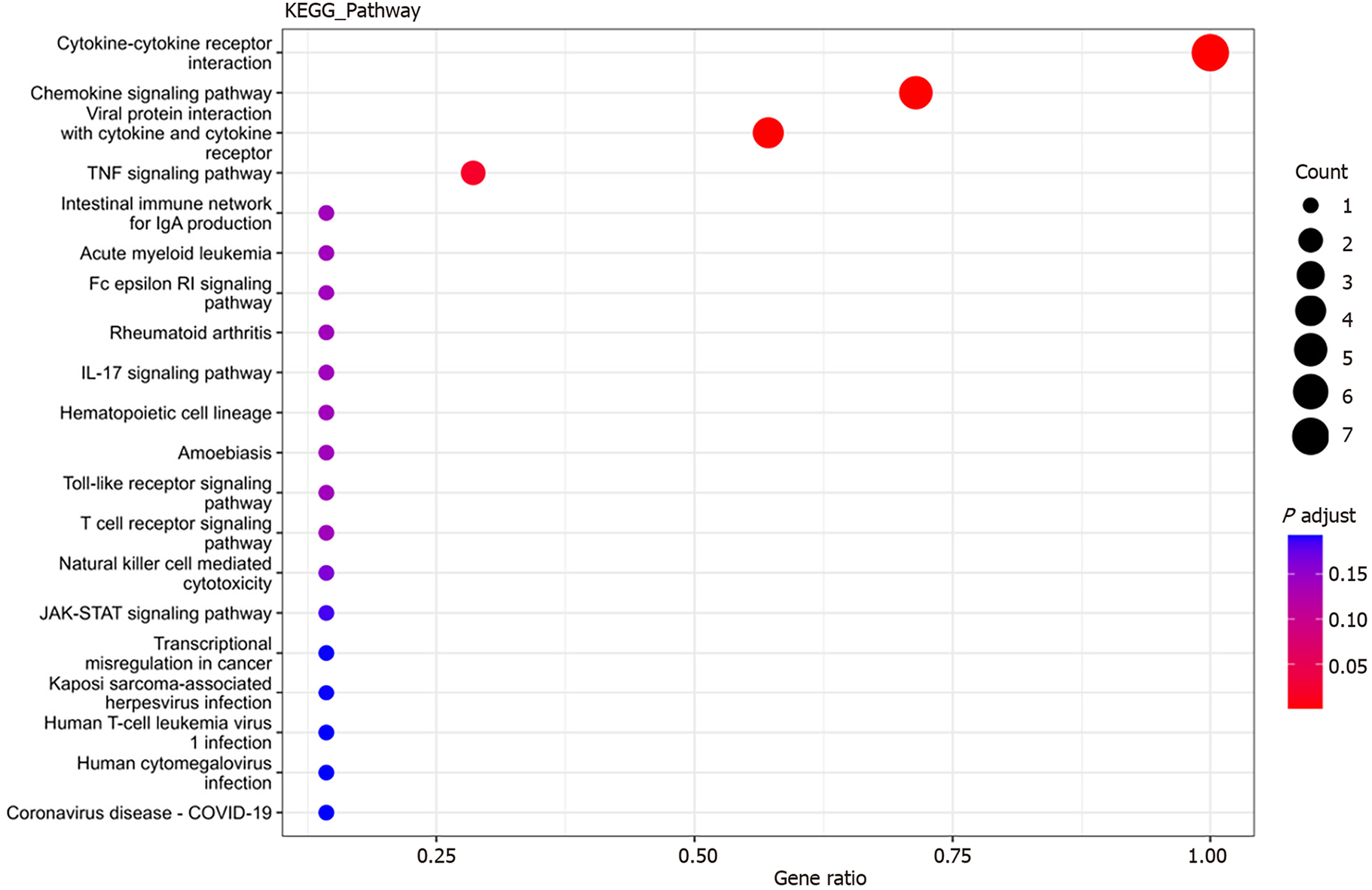
Figure 6 Bubble plot of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways associated with differentially expressed cytokines.
The x-axis represents the ratio of differential genes in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways to the total number of differentially expressed genes (GeneRatio). A higher ratio indicates a greater degree of protein enrichment. The y-axis represents the corresponding KEGG pathway names, with bubble size indicating the number of genes annotated to the KEGG pathway. Larger bubbles represent a greater number of enriched proteins. The color gradient from blue to red indicates decreasing P values, signifying greater significance. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
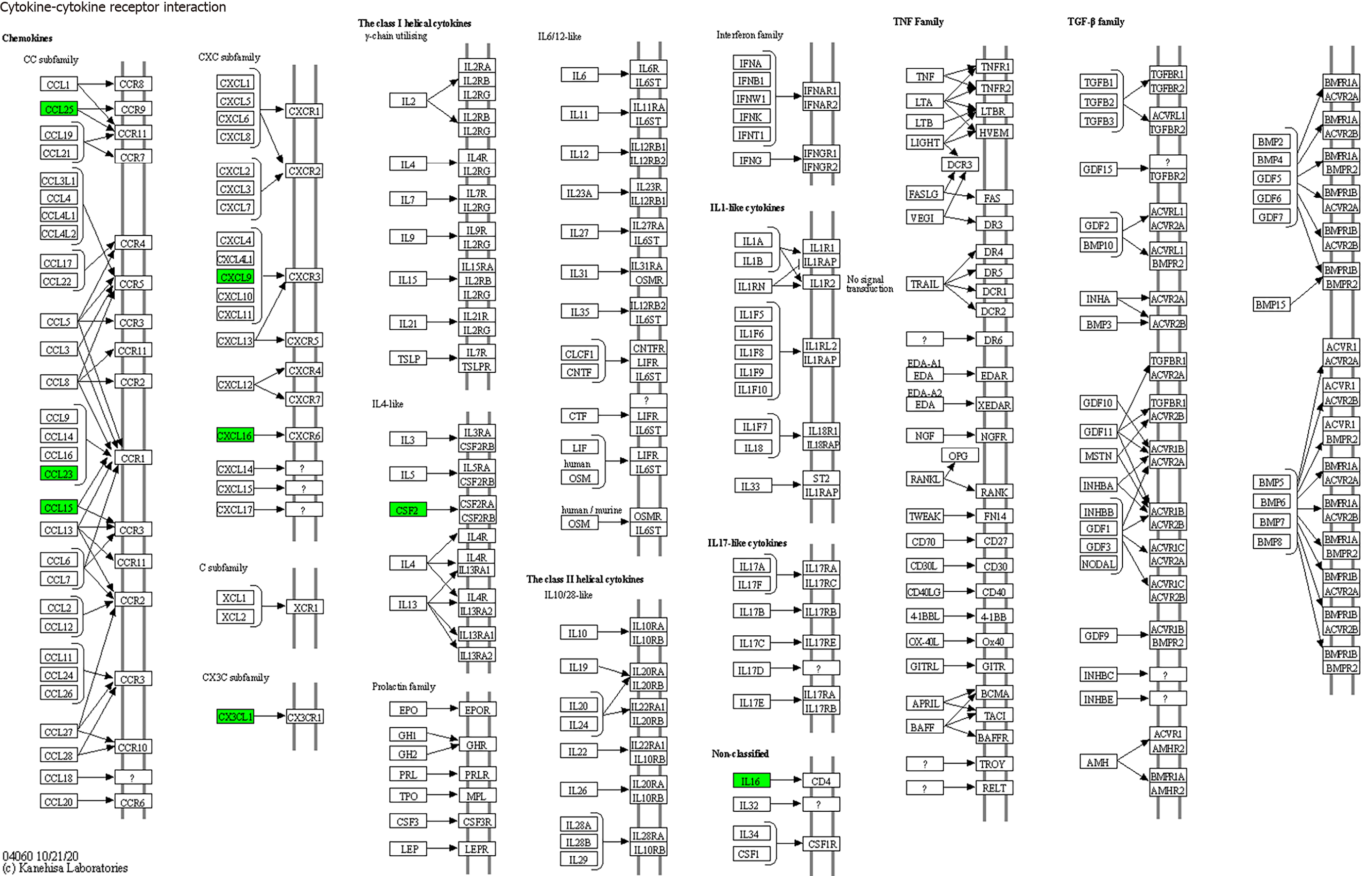
Figure 7 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions (mainly involving interleukin-16, colony-stimulating factor, CX3CL1, CXCL9, CXCL16, CCL25, and CCL23).
GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-16: Interleukin-16.
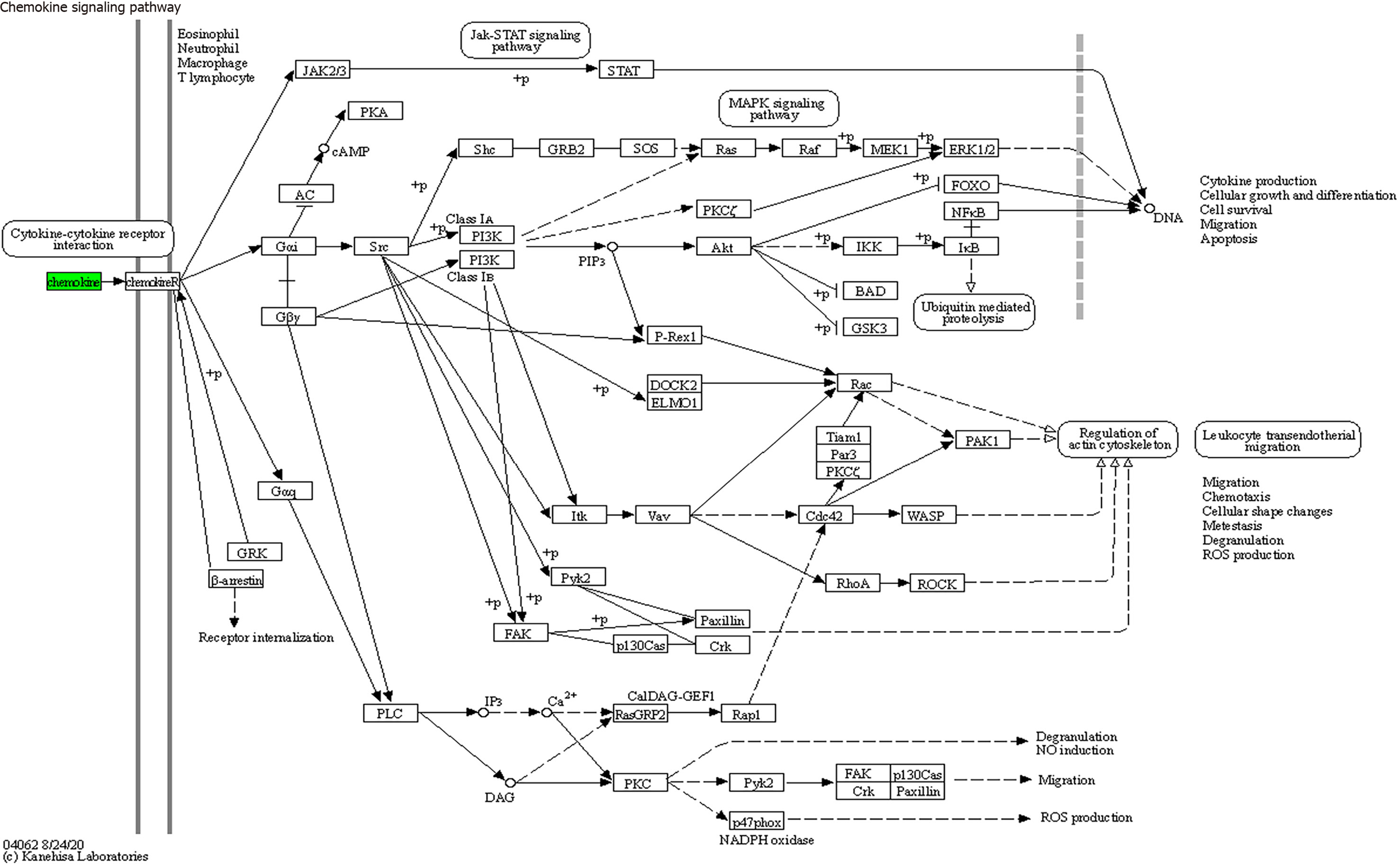
Figure 8 Chemokine signaling pathways (mainly involving CX3CL1, CXCL9, CXCL16, CCL25, and CCL23).
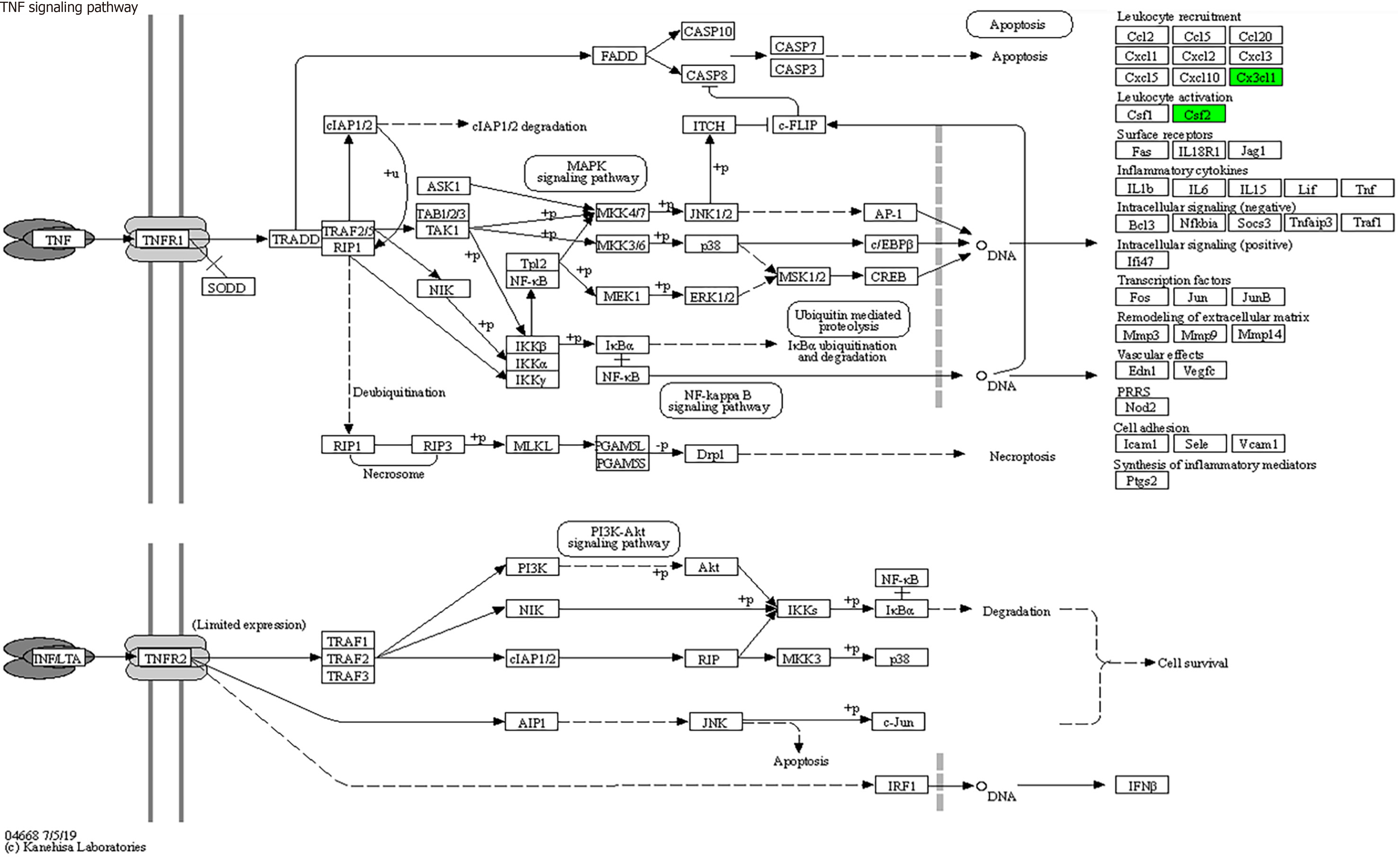
Figure 9 Tumor necrosis factor signaling pathways (mainly involving colony-stimulating factor and CX3CL1).
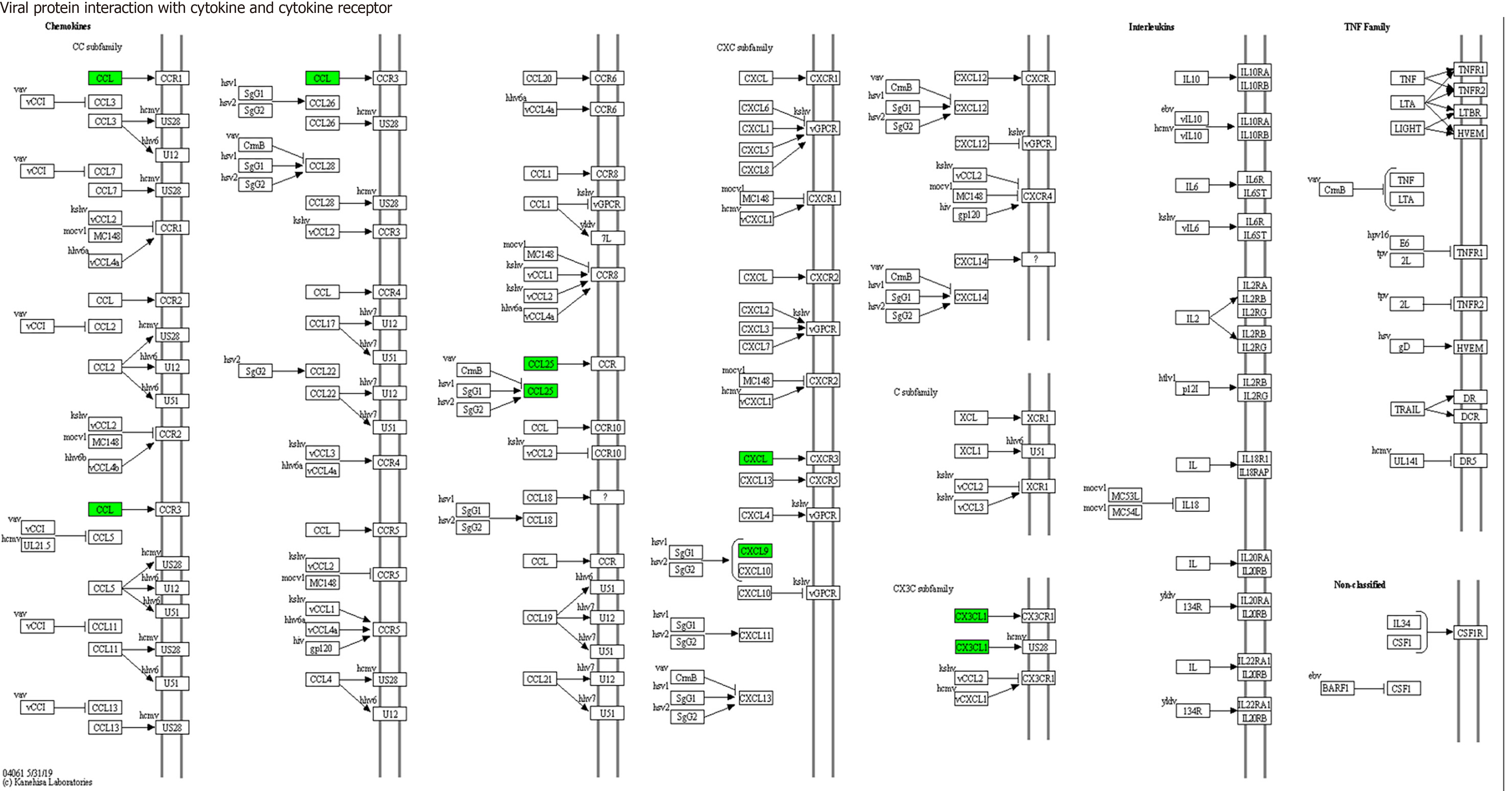
Figure 10 Viral proteins interact with cytokines and cytokine receptors (mainly involving CX3CL1, CXCL9 and CCL25).
- Citation: Liu HX, Wang YY, Yang XF. Differential expression of plasma cytokines in sepsis patients and their clinical implications. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(25): 5681-5696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i25/5681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i25.5681