Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2024; 12(21): 4590-4600
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4590
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4590
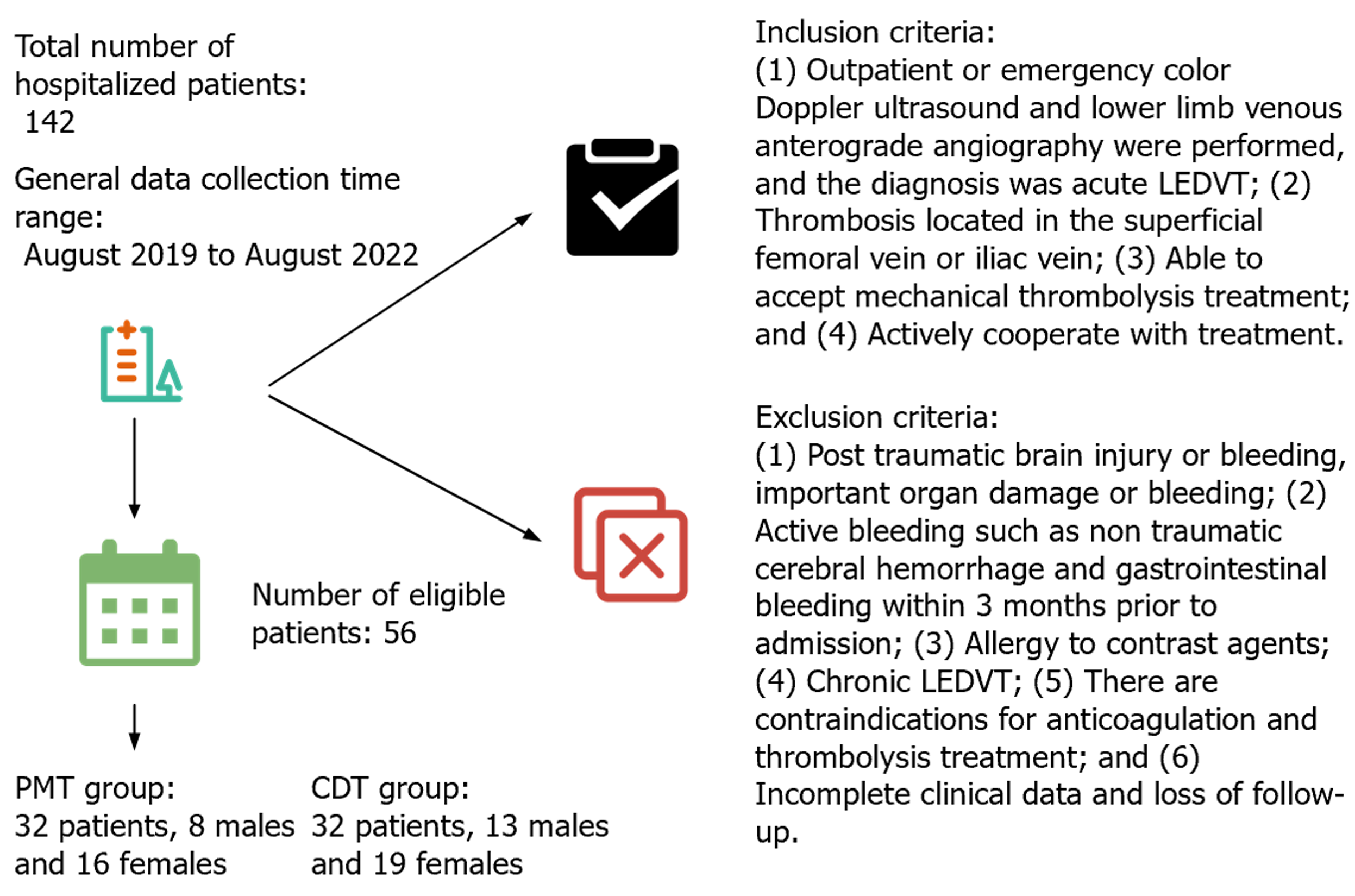
Figure 1 General information about the patient.
PMT: Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; CDT: Catheter-directed thrombolysis; LEDVT: Lower extremity deep venous thrombosi.
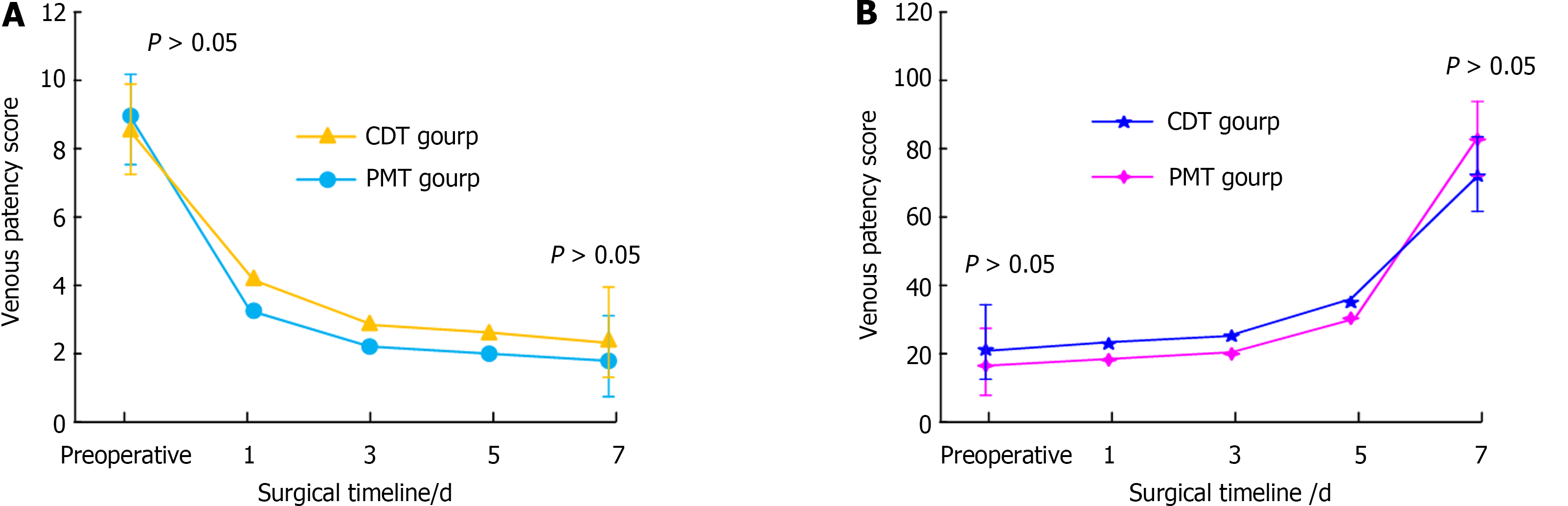
Figure 2 Comparative results of venous patency score and venous patency rate in two groups of patients.
A: Venous patency score for two groups of patients; B: Venous patency rates in two groups of patients. PMT: Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; CDT: Catheter-directed thrombolysis.
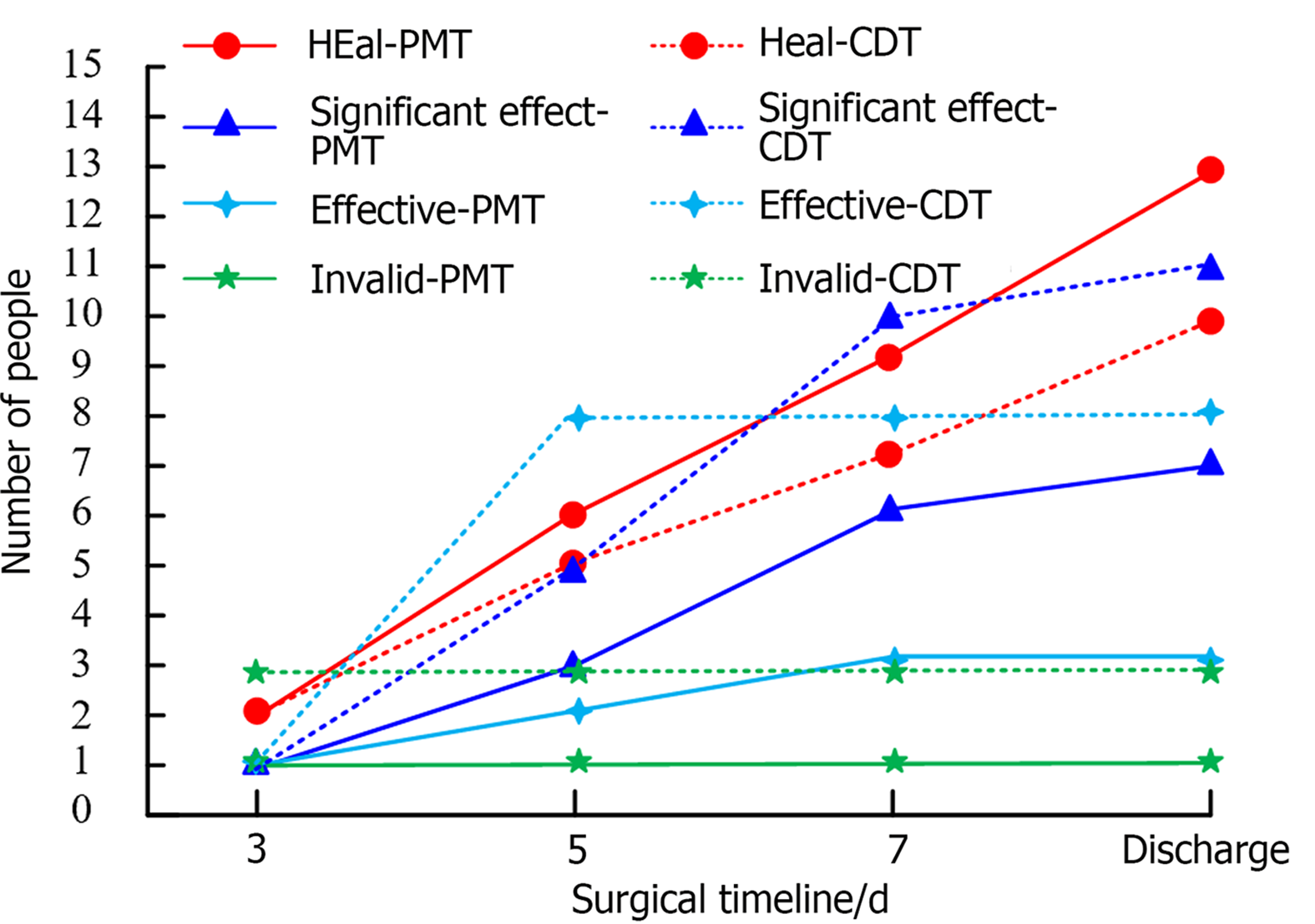
Figure 3 Clinical evaluation of treatment comparison between the two patient groups.
PMT: Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; CDT: Catheter-directed thrombolysis.
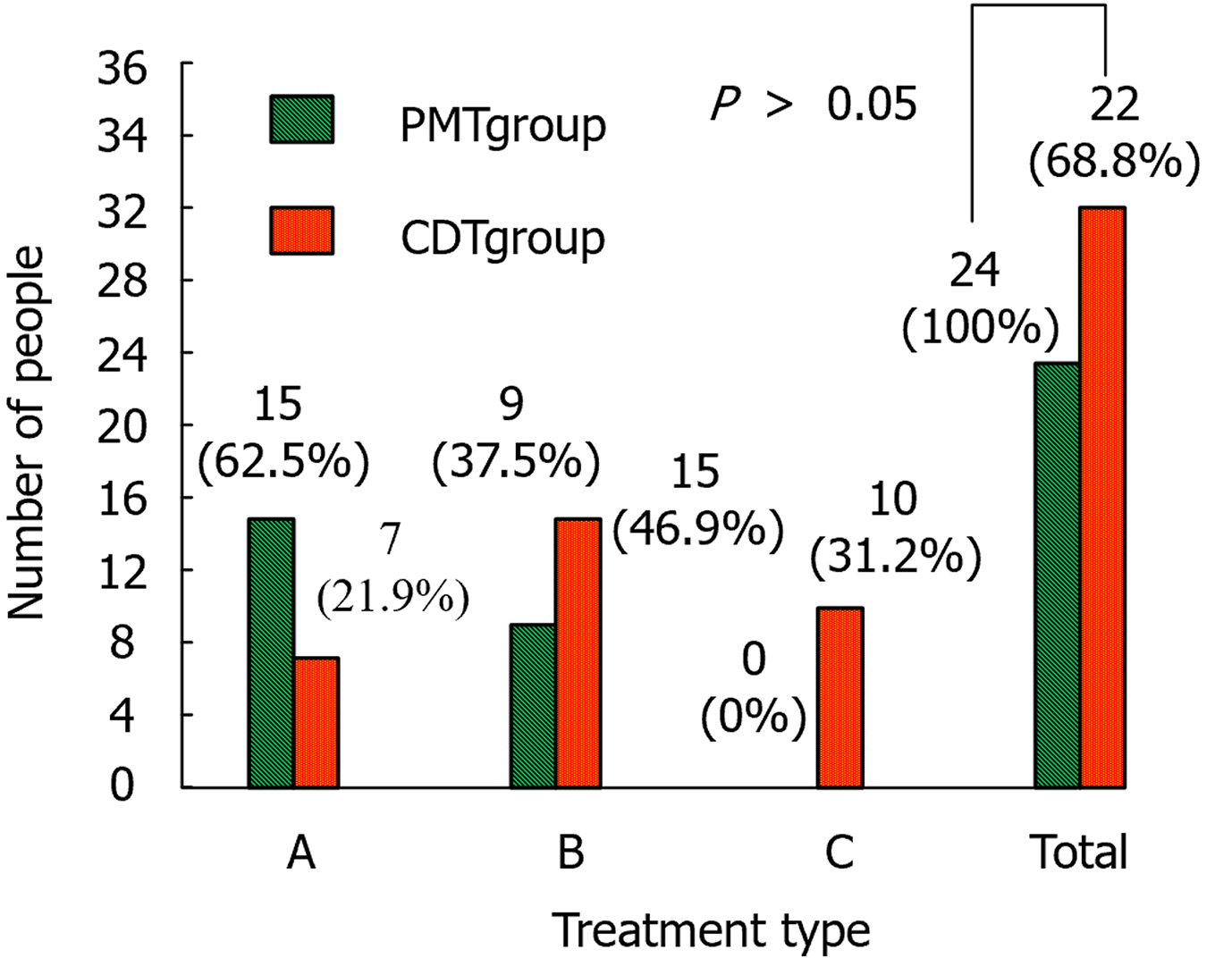
Figure 4 Tolerance of patients in both groups.
PMT: Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; CDT: Catheter-directed thrombolysis.
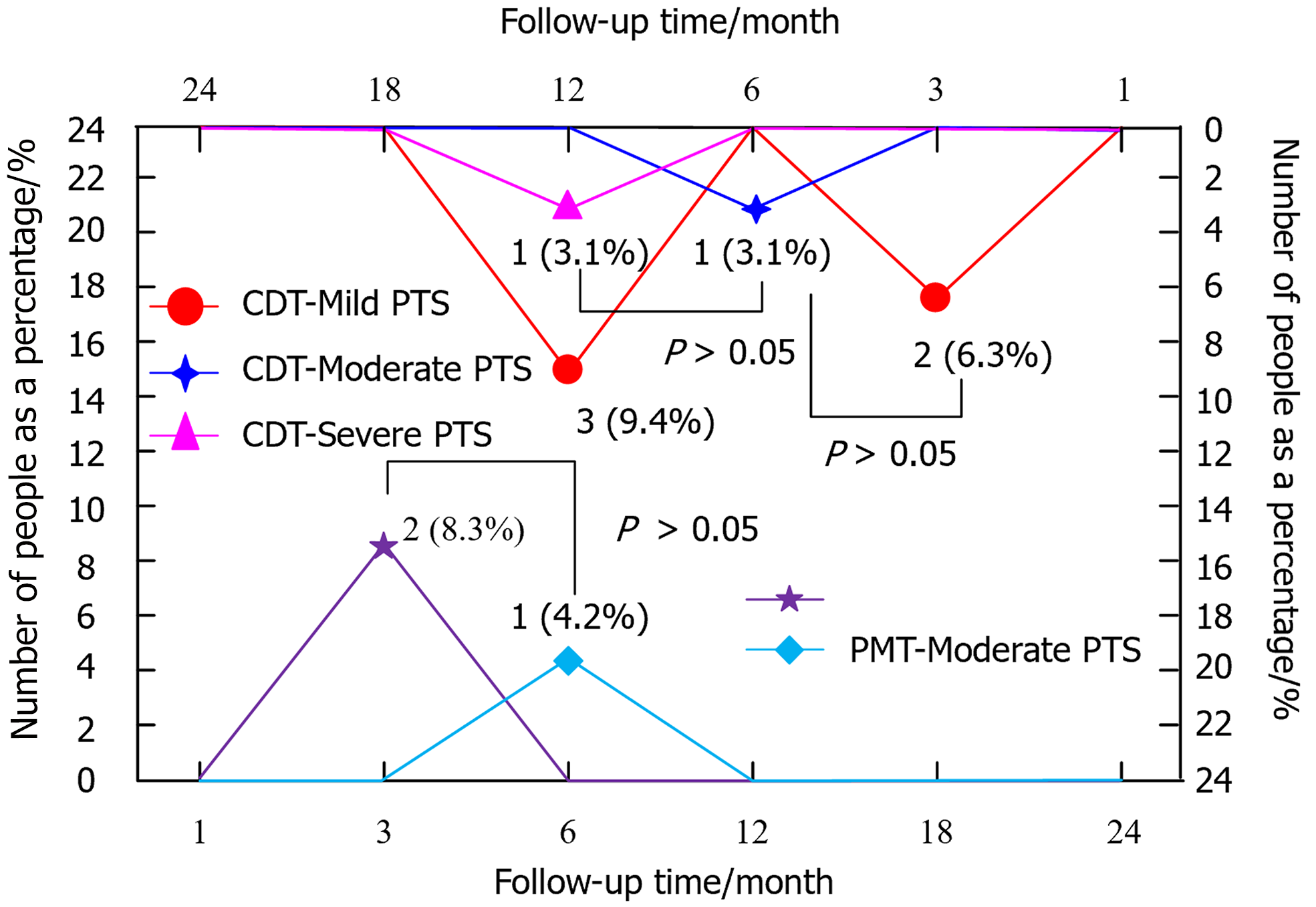
Figure 5 Follow-up results of the two groups of patients.
PMT: Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; CDT: Catheter-directed thrombolysis.
- Citation: Xue JQ, Yin P, He JP, Wei H, Geng CJ, Luo YX. Efficacy of percutaneous mechanical thrombus removal in acute lower extremity deep venous thrombosis. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(21): 4590-4600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i21/4590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4590