Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2024; 12(20): 4272-4288
Published online Jul 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4272
Published online Jul 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4272
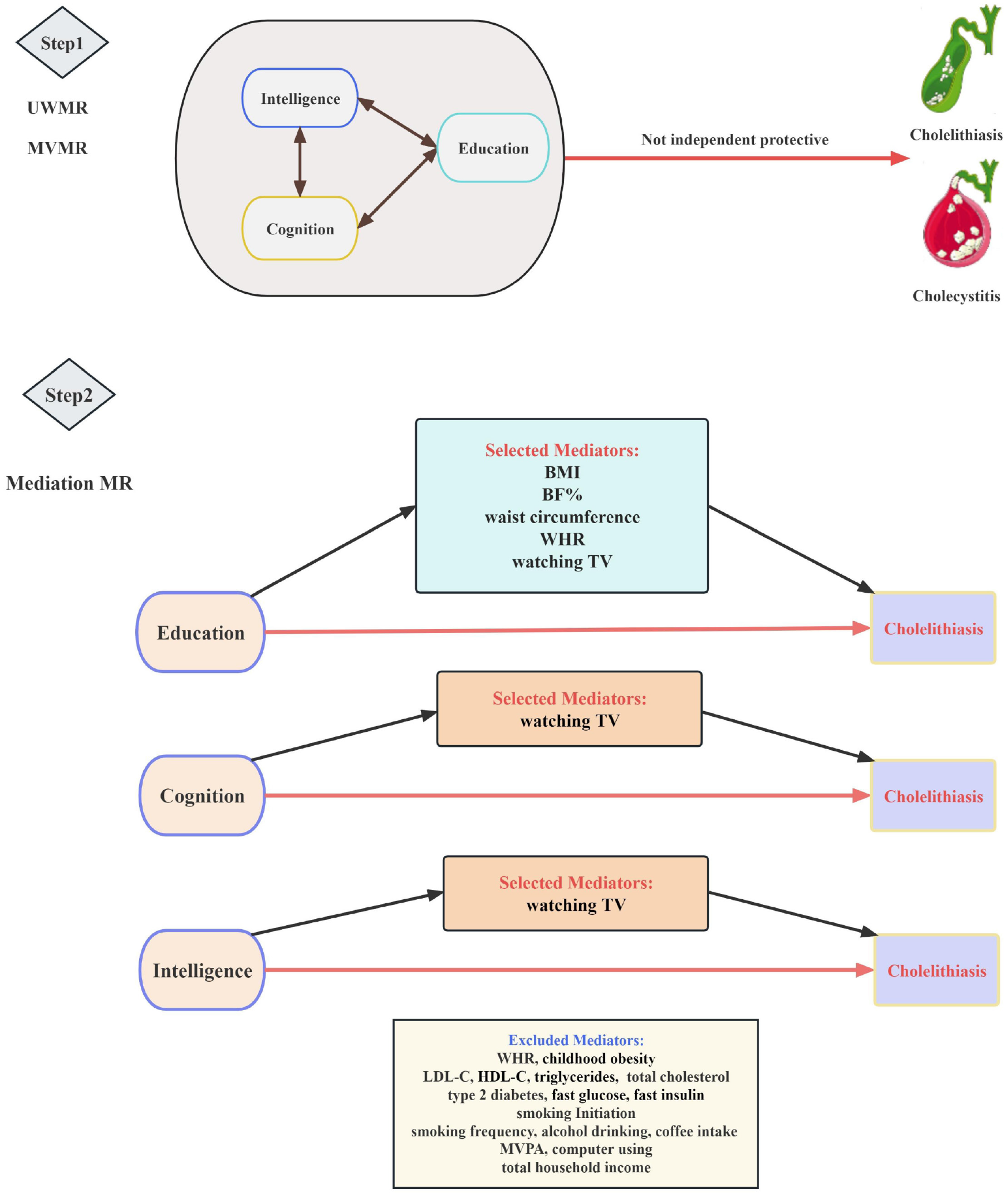
Figure 1 Overview of study design: Mediator selection process in two steps.
In step 1, we assessed the causal associations of education, cognition, and intelligence with cholelithiasis and cholecystitis using UVMR and MVMR to evaluate the overall and independent causal effects, respectively. In step 2, we first screened candidate mediators for the association between each exposure and cholelithiasis by critical criteria, and then estimated their mediating effects using two-step mediation Mendelian randomization. BF: Body fat; BMI: Body mass index; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TV: Television; UVMR: Univariable Mendelian randomization; WHR: Waist-to-hip ratio; MVMR: Multivariable Mendelian randomization; MVPA: Moderate to vigorous physical activity.
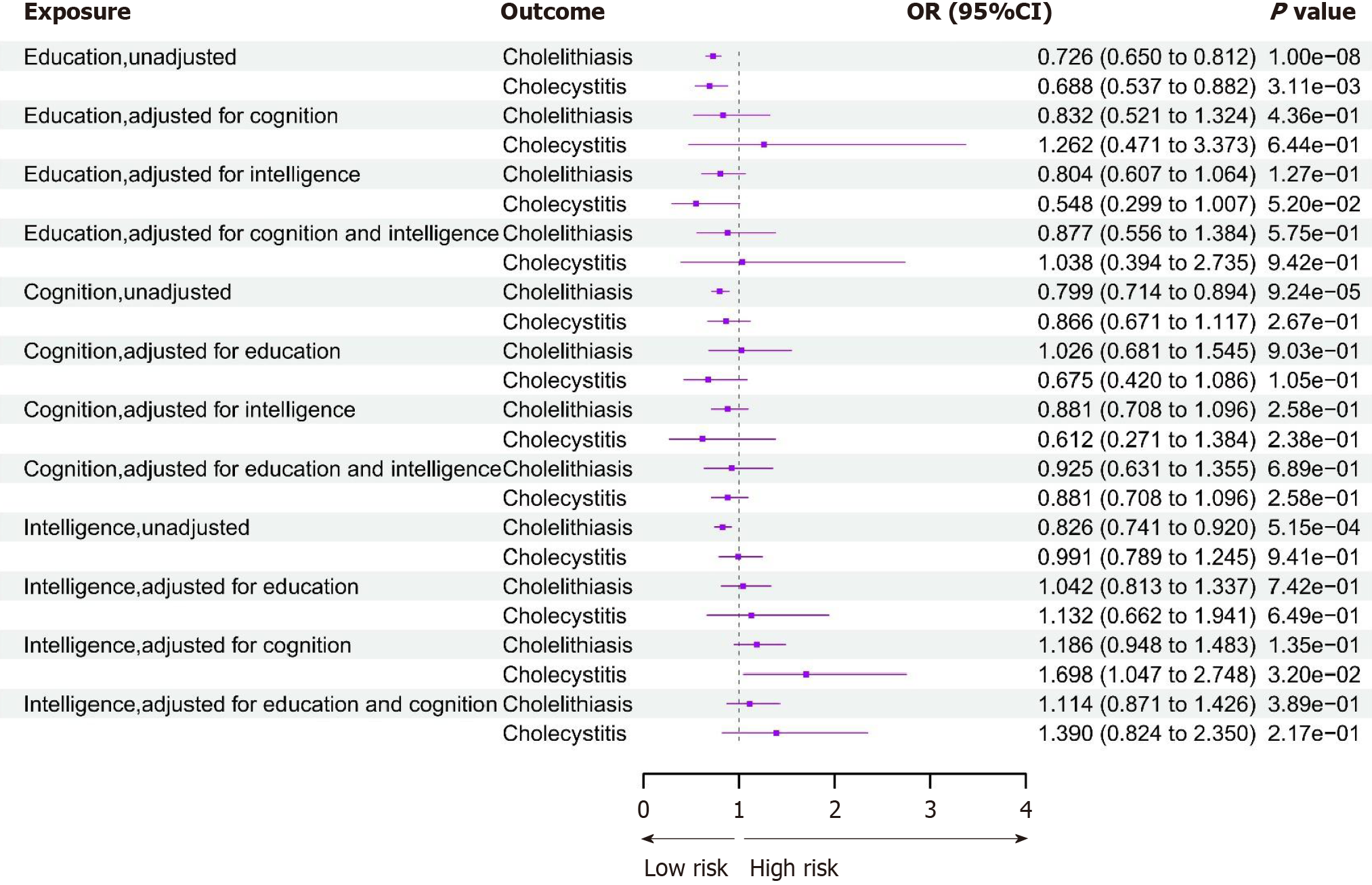
Figure 2 UVMR and MVMR estimates of causal associations of education, intelligence, and cognition with cholelithiasis and chole
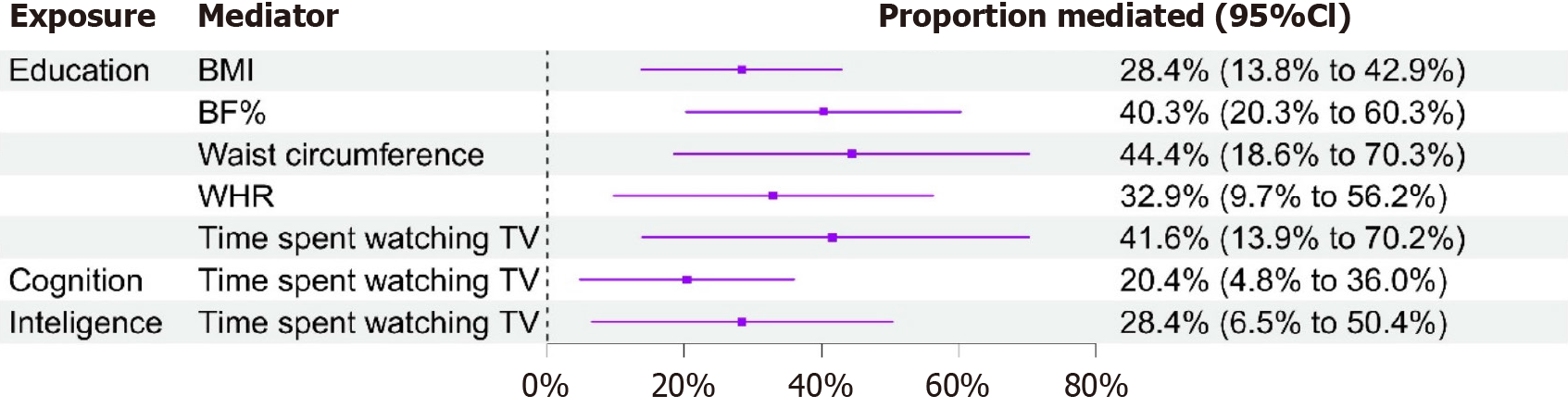
Figure 3 Mendelian randomization estimates of proportions mediated by mediators in causal associations between education, cognition, or intelligence and cholelithiasis.
TV: Television; BF: Body fat; BMI: Body mass index; WHR: Waist-to-hip ratio.
- Citation: Li CL, Liu YK, Lan YY, Wang ZS. Association of education with cholelithiasis and mediating effects of cardiometabolic factors: A Mendelian randomization study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(20): 4272-4288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i20/4272.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4272