Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2024; 12(17): 3243-3252
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3243
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3243
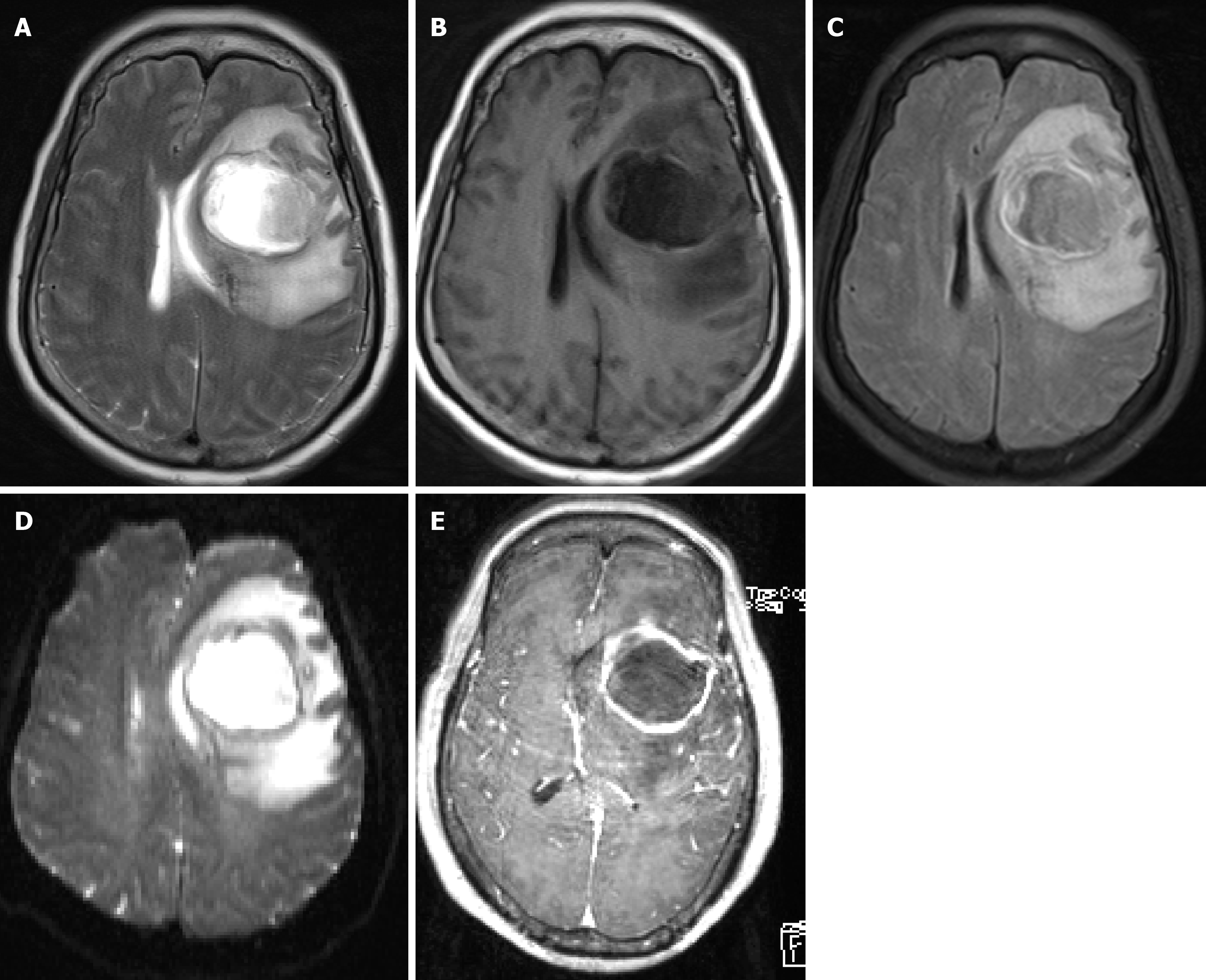
Figure 1 The preoperative magnetic resonance imaging scan from April 16 2019.
A space-occupying lesion in the left frontal lobe with extensive surrounding edema, showing marked ring enhancement on the enhanced scan. The left lateral ventricle is compressed, and the midline is shifted to the right. A brain abscess with ring enhancement is the primary diagnosis. A: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2; B: MRI T1; C: MRI T2 suppressed water imaging; D: MRI diffusion-weighted imaging scans; E: MRI enhanced scans.
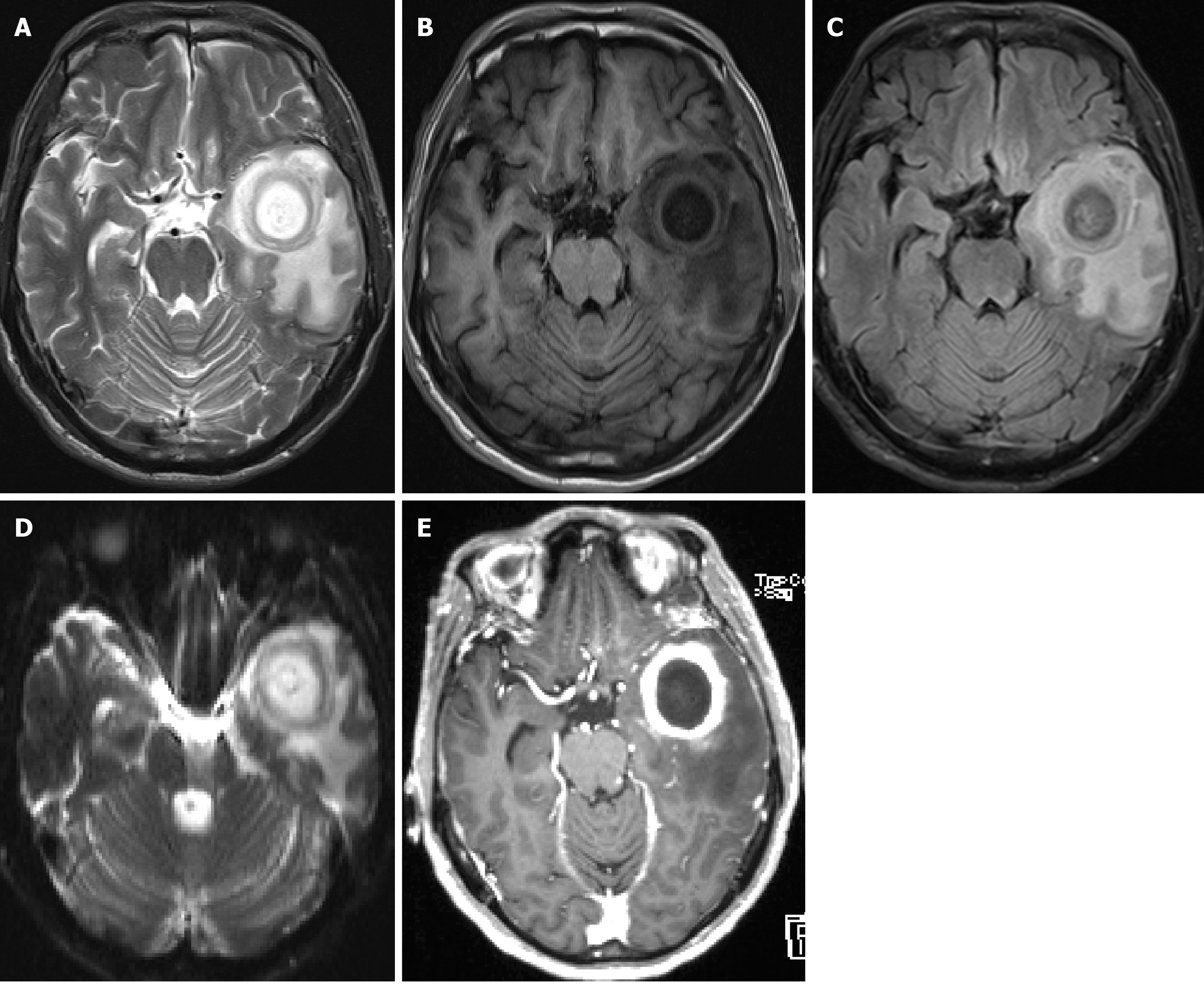
Figure 2 The preoperative magnetic resonance imaging scans from March 30 2017.
An oval-shaped mass in the left temporal lobe with visible patchy edema surrounding it. The contrast-enhanced scan shows prominent ring enhancement, with fluffy and small patchy enhancements around the ring. The left lateral ventricle and midline structures are slightly compressed and shifted. A brain abscess in the left temporal lobe is highly probable, however, tumor-like lesions cannot be completely ruled out due to the presence of fluffy enhancements. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) shows that the edema around brain abscess lesions can vary from mild to severe, showing high or relatively high signals, while the edema around necrotic brain tumors is generally severe and shows high signals. Finally, the contrast-enhanced scan shows that the wall of a brain abscess is regular and relatively uniform, while the wall of a necrotic brain tumor is uneven in thickness, with mural nodules, showing a flower ring-like or annular enhancement. A: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2; B: MRI T1; C: MRI T2 water suppression imaging; D: MRI DWI scans; E: MRI contrast-enhanced scans.
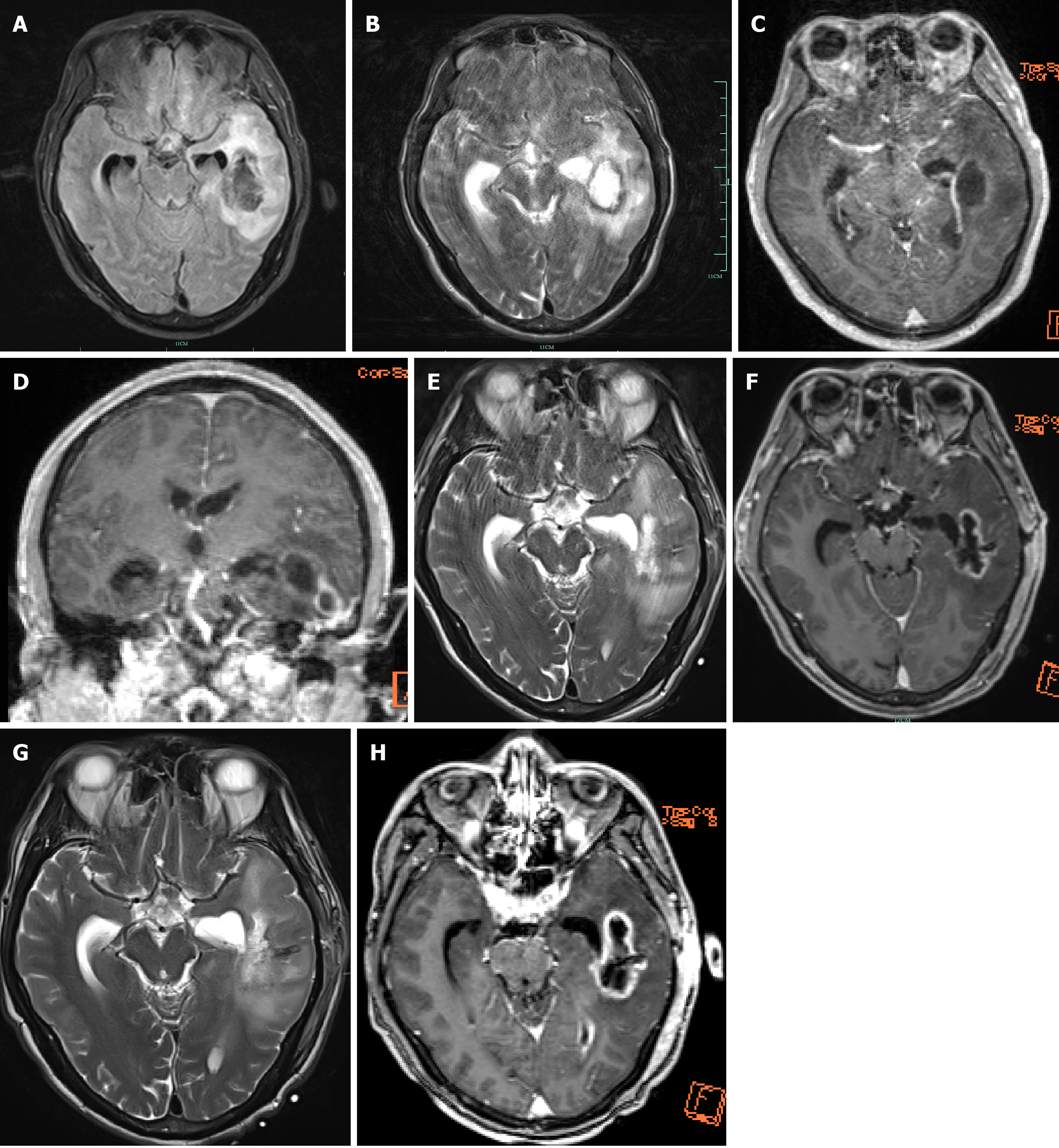
Figure 3 The lesion in the left temporal lobe with marked surrounding edema.
After enhancement, the lesion shows ring-like enhancement, the left lateral ventricle is compressed and narrowed, the midline structures are slightly shifted to the right, and purulent meningitis has ruptured into the ventricular system. Re-examination 6 days post-surgery, shows that compared to the previous image from September 06 2021, the left temporal lobe abscess has decreased in size, and purulent meningitis has ruptured into the ventricular system. Twenty days post-surgery, re-examination shows that the abscess cavity has significantly reduced in size, the surrounding edema has reduced, and the purulent meningitis has ameliorated compared to the initial status. The characteristic ring enhancement of a brain abscess is a primary feature, and the differ from brain tumors in that brain tumors rarely show this characteristic ring enhancement. Additionally, the internal enhancement of brain tumors is often unevenly distributed with signals, and surrounding tumor blood vessels are visible. T2 imaging reveals that they often appear as curve-shaped or pinpoint-shaped low-signal shadows due to the flow void effect. A-D: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2 suppressed water imaging, MRI T2 scans, both, MRI enhanced scans (C and D), respectively, from September 6 2021; E and F: MRI T2 scans, MRI enhanced scans, respectively, from September 12 2021; H and G: MRI T2 scans, MRI enhanced scans, respectively, from September 16 2021.
- Citation: Tan SD, Li MH. Brain abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus group: Three case reports. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(17): 3243-3252
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i17/3243.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3243