Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2024; 12(14): 2370-2381
Published online May 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i14.2370
Published online May 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i14.2370
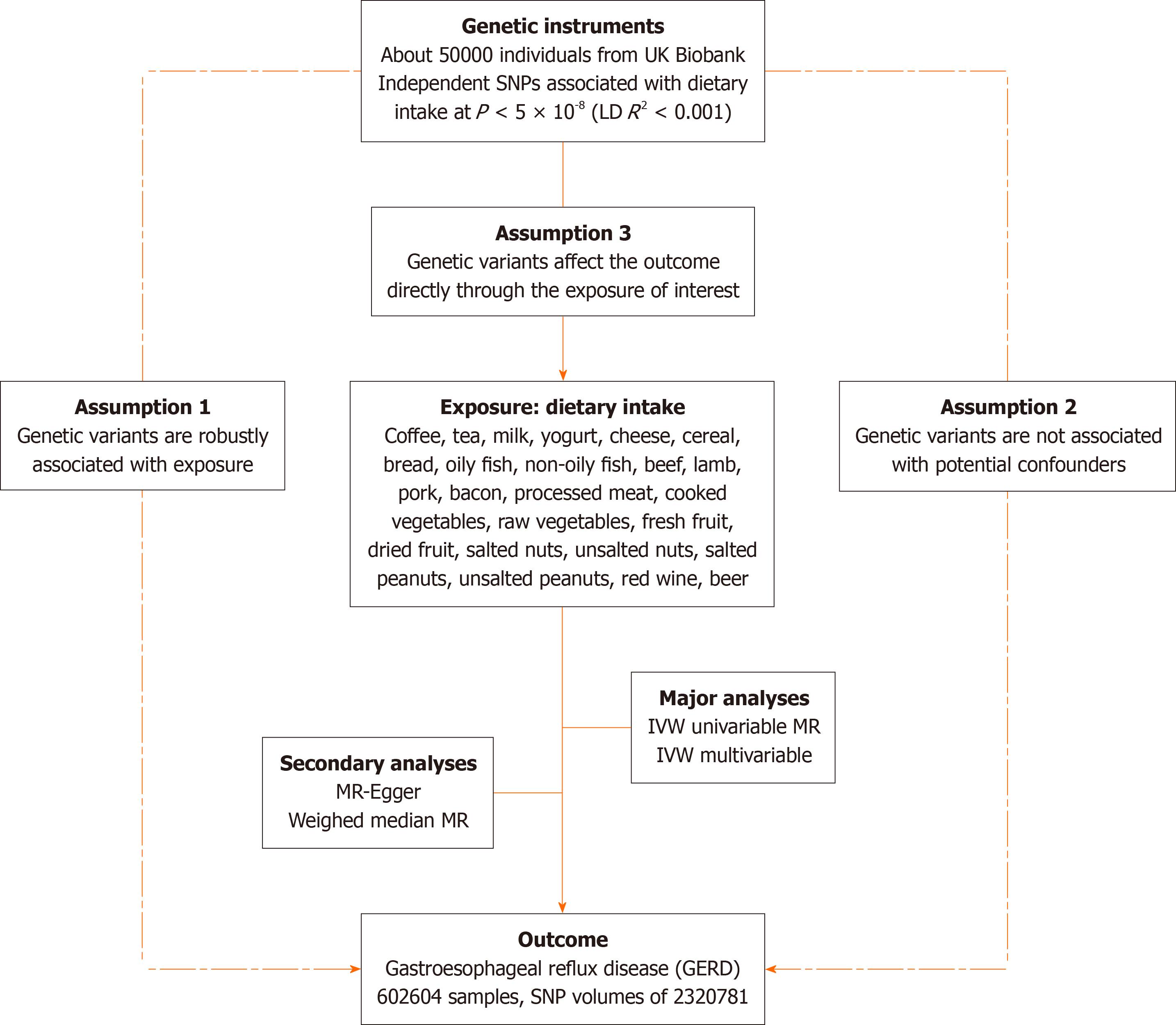
Figure 1 Overview of mendelian randomization rationale, design, and procedures.
UVMR: Univariate mendelian randomization; MVMR: Multivariate Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; IVW: Inverse variance weighted; LD: Linkage disequilibrium; UK: United Kingdom.
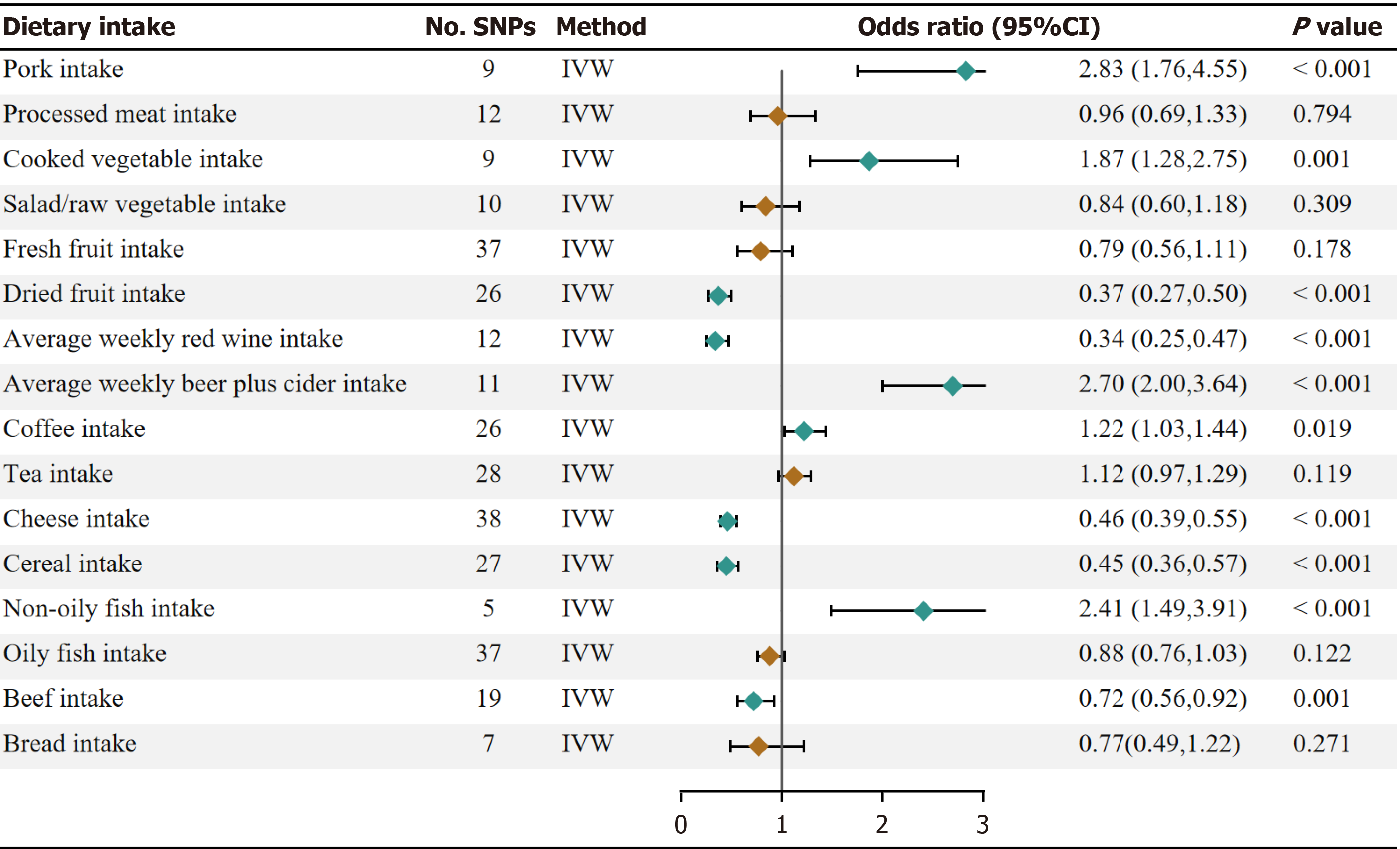
Figure 2 Univariate mendelian randomization analysis for genetically causal associations of dietary intakes with gastroesophageal reflux disease risk.
SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; IVW: Inverse variance weighted.
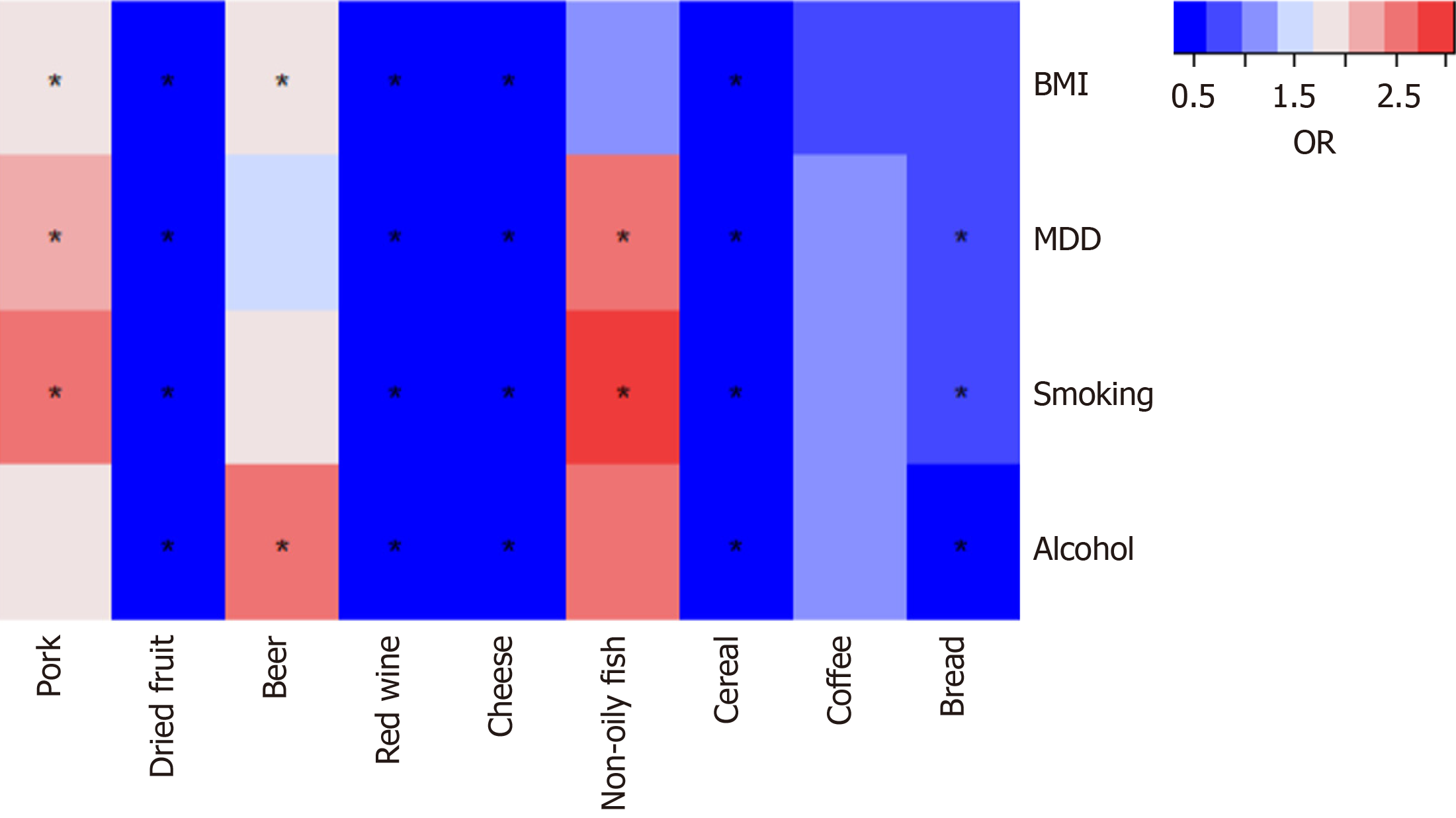
Figure 3 Associations between nine dietary intakes and gastroesophageal reflux disease after adjusting for each of the four risk factors.
Asterisk represents a significant correlation. OR: Odds ratio; BMI: Body mass index; MDD: Major depressive disorder.
- Citation: Liu YX, Yang WT, Li Y. Different effects of 24 dietary intakes on gastroesophageal reflux disease: A mendelian randomization. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(14): 2370-2381
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i14/2370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i14.2370