Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2024; 12(11): 1885-1899
Published online Apr 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i11.1885
Published online Apr 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i11.1885
Figure 1 Incidental focal right breast fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
A: Focal mild to moderate uptake (arrow) is observed in the right chest on the maximum intensity projection image of a 32-year-old woman diagnosed with endometrial cancer; B: Axial image of fused positron emission tomography/computed tomography showing hypermetabolism (maximum standardized uptake value 3.3) in her right breast and the uptake was histopathologically confirmed as a ductal carcinoma in situ.
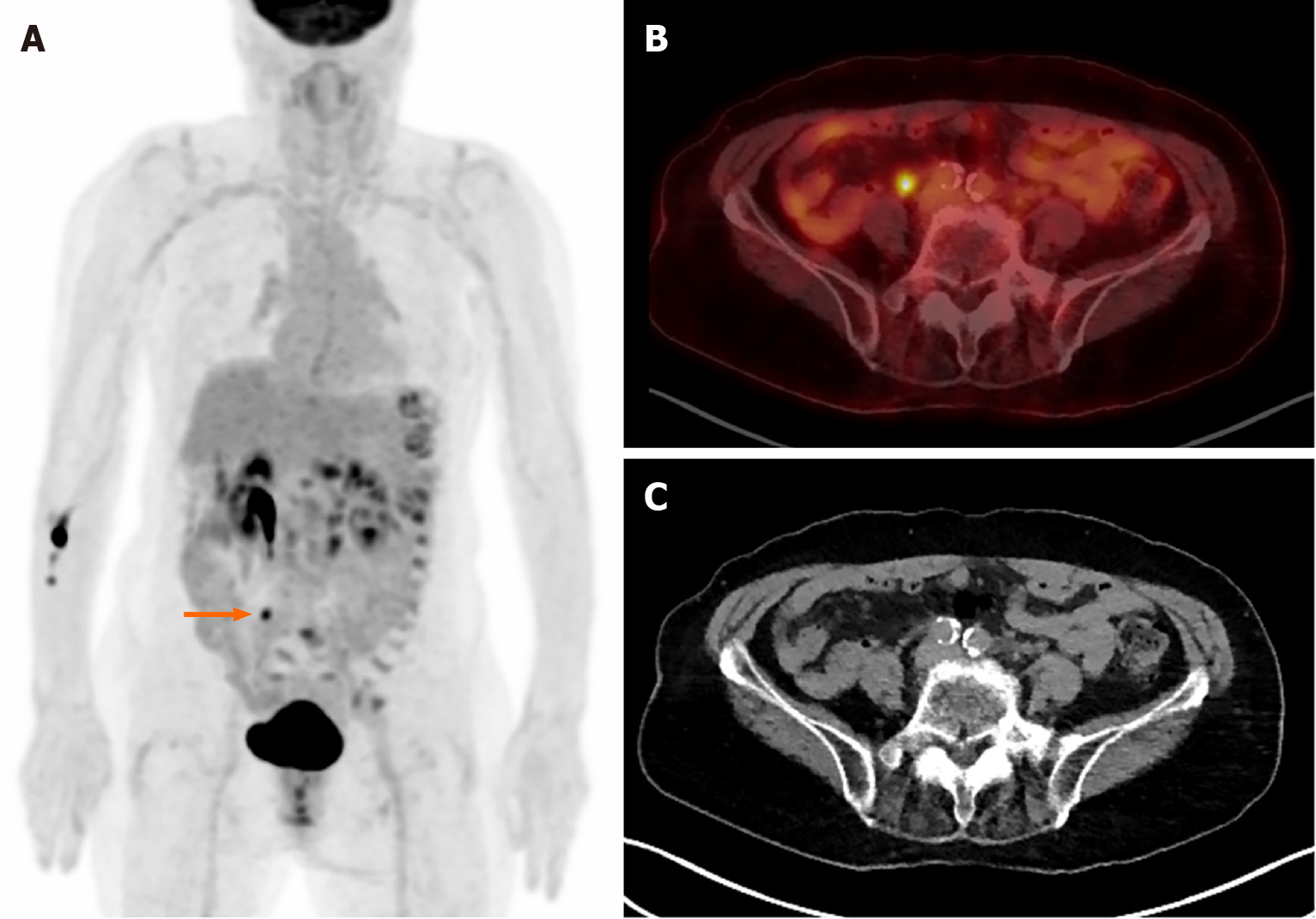
Figure 2 Multiple foci of physiological fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
Images of a 79-year-old woman diagnosed with pancreatic body cancer. A: Focal uptake is observed in the right lower abdomen (arrow); B: Suspicious uptake as a lesion; C: No lesion but right ureter. Multiple hypermetabolic areas are observed along the descending and sigmoid colon in image A. Colonoscopy found nothing abnormal, and the uptake is probably due to normal physiological uptake.
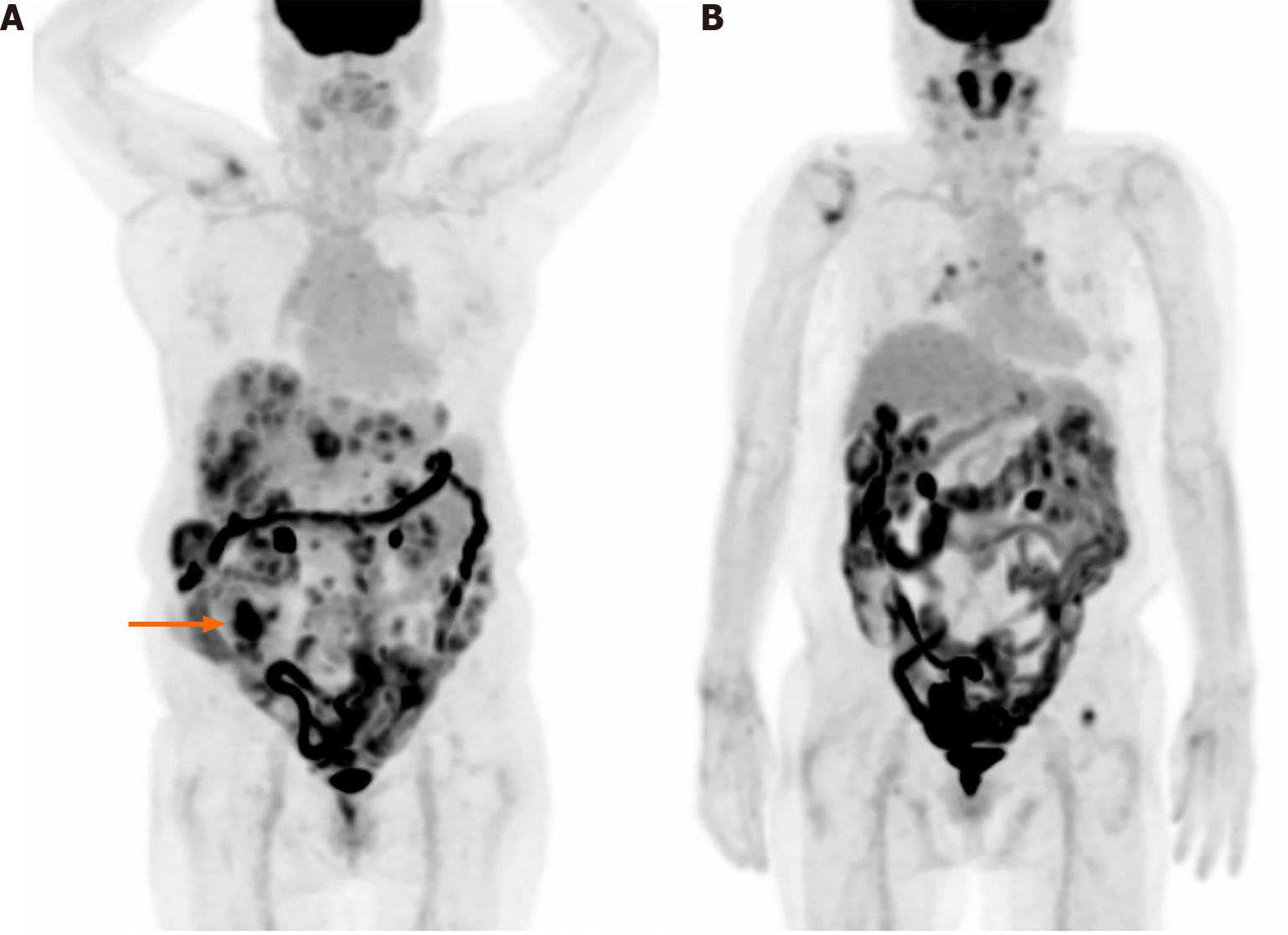
Figure 3 Diffuse intestinal fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
A: 76-year-old woman diagnosed with cecal cancer and multiple metastases/seeding nodules. Primary cecal cancer is observed in the right lower abdomen (arrow) and diffuse intestinal uptake is also shown. The diffuse uptake may be physiological; however, pathological lesions may be obscured by the intense intestinal uptake; B: 79-year-old woman diagnosed with mantle cell lymphoma, and also had a history of colon cancer about three decades ago. Mixed focal and diffuse intestinal uptake is challenging.
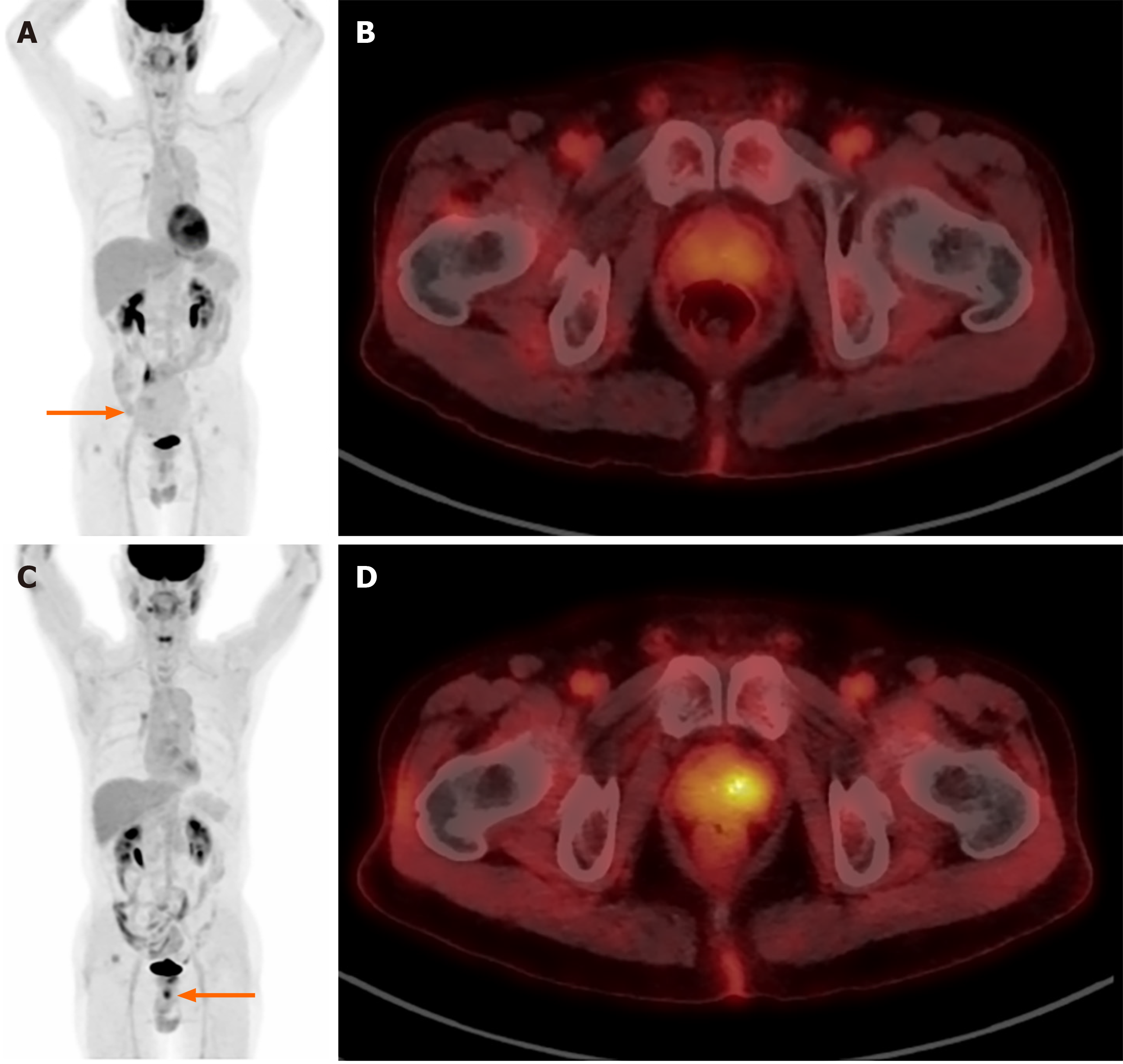
Figure 4 Incidental prostate fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
A 74-year-old man diagnosed with small bowel gastrointestinal stromal tumor. A: On the initial image, known small bowel gastrointestinal stromal tumor with low uptake is observed (arrow); B: Also, nearly symmetrical low prostate uptake is shown; C: An incidental focal uptake is observed beneath urinary bladder (arrow) on the five-year follow-up image; D: The uptake is at the left side of prostate (maximum standardized uptake value 5.6) and it was proved histopathologically as an adenocarcinoma of prostate.
- Citation: Lee H, Hwang KH. Unexpected focal fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in main organs; pass through or pass by? World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(11): 1885-1899
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i11/1885.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i11.1885