Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2023; 11(30): 7403-7412
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7403
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7403
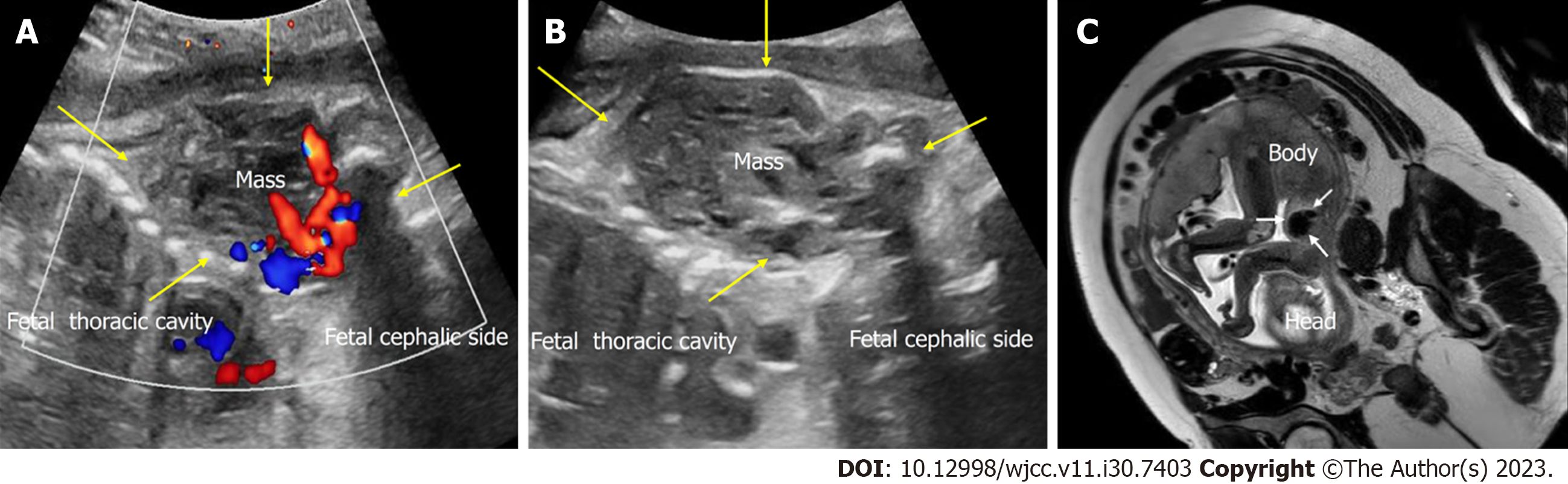
Figure 1 Prenatal imaging of congenital infantile fibrosarcoma in Case 1.
A: Color Doppler flow imaging of the axillary mass in the fetus at 34+5 wk of gestation, showing abundant blood flow within the mass. Yellow arrow, the mass; B: Two-dimensional ultrasound showing the longitudinal section of the fetus at 34+5 wk of gestation, revealing a heterogeneous mass in the left axilla. Yellow arrow, the mass; C: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 28+6 wk of gestation documenting a solid mass in the left axilla. White arrow, the fetal mass on MRI.
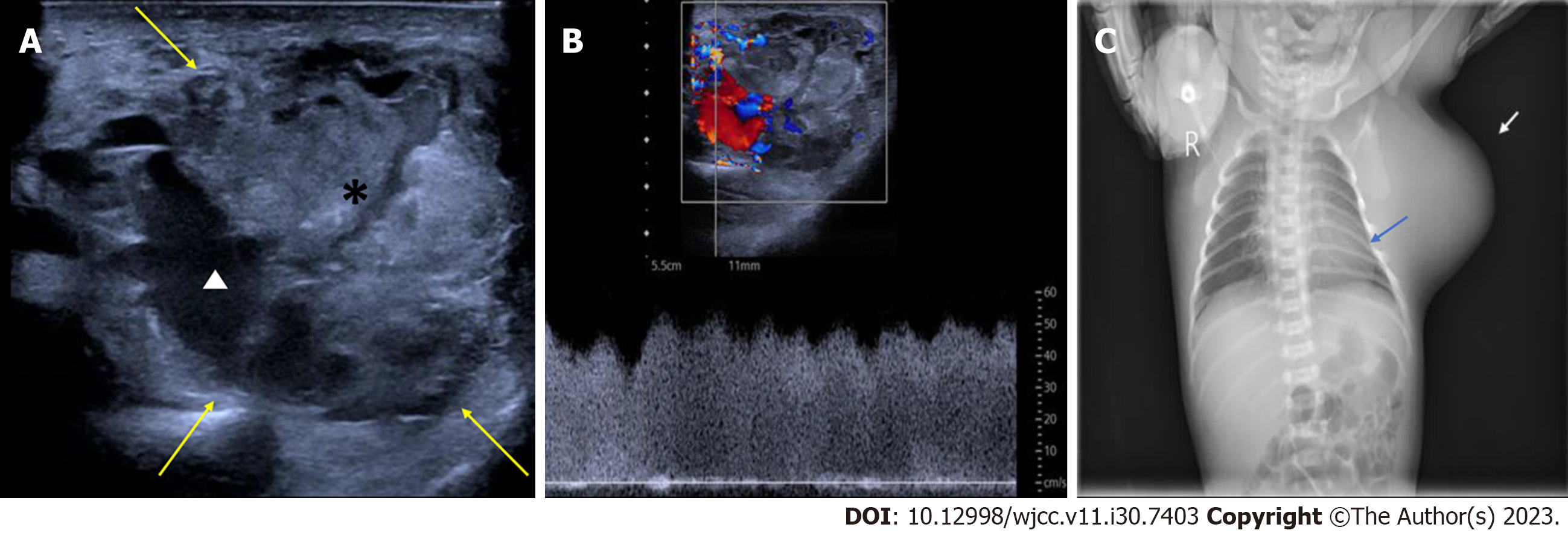
Figure 2 Postnatal imaging of the congenital infantile fibrosarcoma in Case 1.
A: One-day postnatal two-dimensional ultrasound using a linear array transducer with a frequency of 5-12 MHz, revealing a well-defined mass in the left axilla consisting mainly of isoechoic parenchymal components (*) with a few anechoic areas (white triangle) within the mass. Yellow arrow, the boundary of the mass; B: One-day postnatal pulse Doppler ultrasound revealing a rich blood flow and low resistance blood flow spectrum in the mass; C: Postnatal X-ray of the newborn showed a soft tissue density shadow protruding from the left axilla and lateral chest wall, resulting in compression of the adjacent ribs (blue arrow). White arrow, the mass on X-ray.
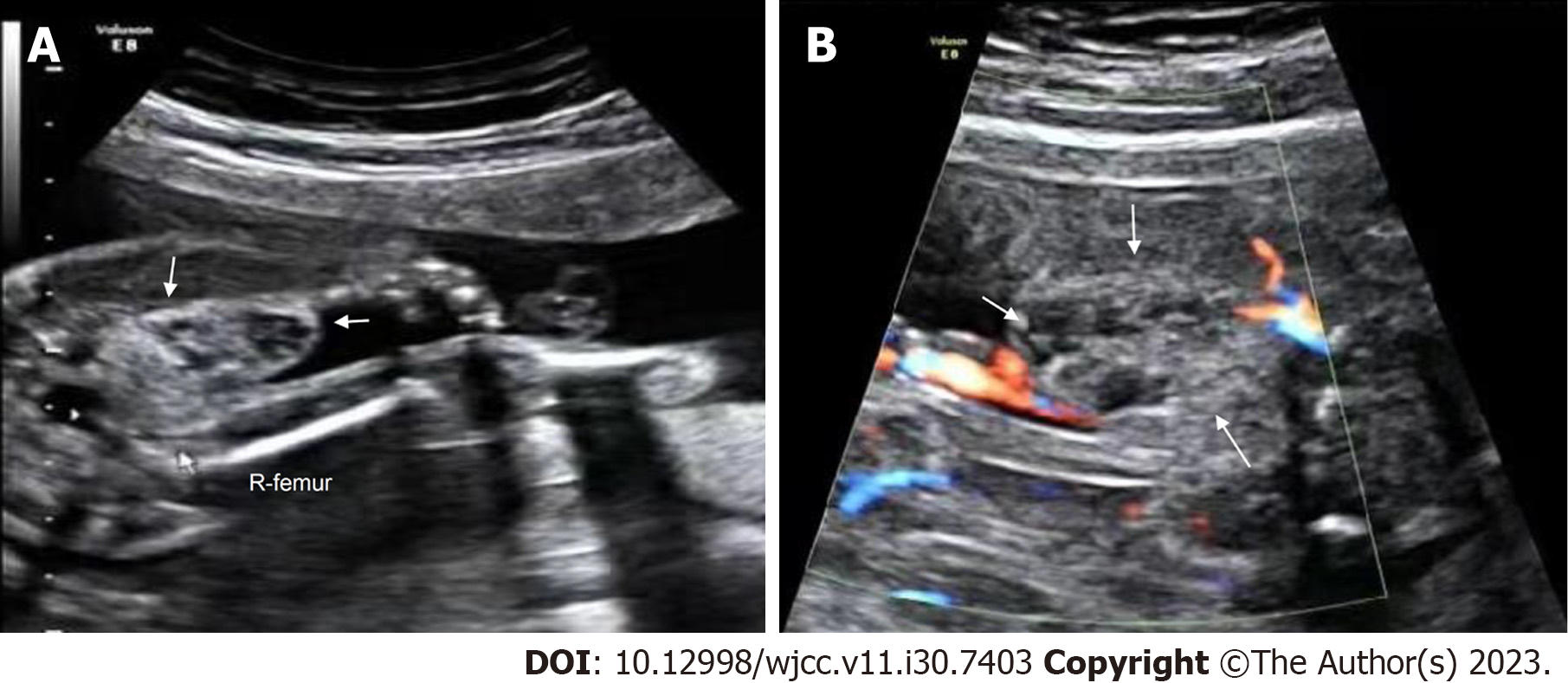
Figure 3 Prenatal ultrasonic imaging of the congenital hemangioma in Case 2.
A: Prenatal two-dimensional ultrasound image revealing a well-defined, heterogeneous mass at the root of the right thigh of the fetus at 23+1 wk of gestation. White arrow, the mass; R-femur, the right femur of the fetus; B: CDFI of the mass at the root of the right thigh of the fetus at 23+1 wk of gestation showing sparse punctate blood flow around the mass. White arrow, the mass.
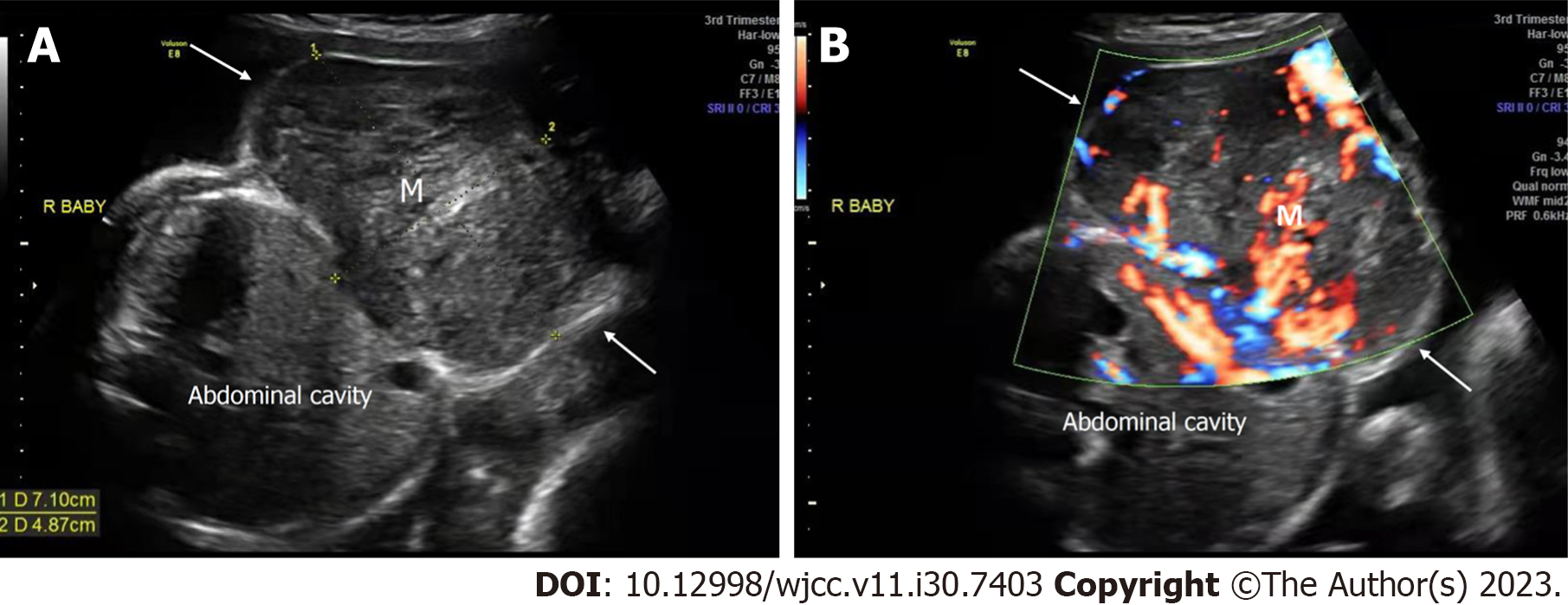
Figure 4 Prenatal ultrasonic imaging of the congenital hemangioma of the affected twin fetus in Case 3 at 30+0 wk of gestation.
A: Two-dimensional ultrasound of the abdominal horizontal cross-section of the mass of the affected fetus revealing a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with a clear boundary, protruding outward from the abdominal wall; B: CDFI in the horizontal cross-section of the fetal abdomen revealed abundant blood flow within the mass. R: Right; M: Mass; white arrow, the mass.
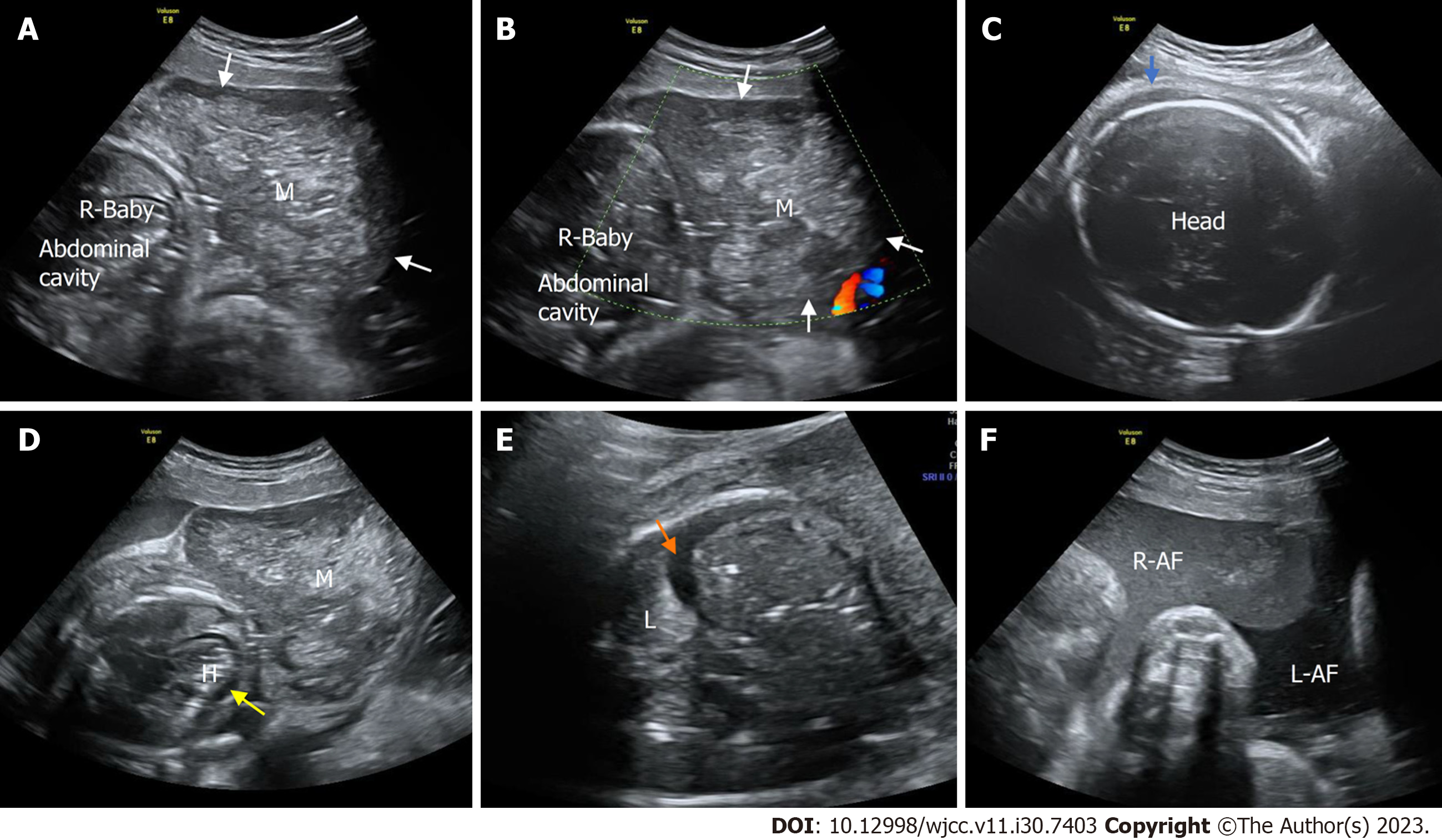
Figure 5 Prenatal ultrasonic imaging of the congenital hemangioma of the affected twin fetus in Case 3 at 33+0 wk of gestation.
A: Two-dimensional ultrasound of the abdominal horizontal cross-section of the mass of the affected fetus revealing that the mass was enlarged and heterogeneous; B: CDFI of an abdominal horizontal cross-section of the mass showing no blood flow signal within the mass. M: Mass; R: Right; white arrow, the mass; C: A two-dimensional ultrasound image of the fetal head showing subcutaneous edema (blue arrow); D: A two-dimensional transverse section of the fetal chest showing intrapericardial fluid collection (yellow arrow). H, heart; M, mass; E: A two-dimensional thoracic horizontal cross-section of the affected fetus showing fetal pleural effusion (orange arrow). L: Lung; M: Mass; R: Right; white arrow, the mass; F: Two amniotic cavities on two-dimensional ultrasound showing that the amniotic fluid of the affected fetus (R-AF) was not clear. R-AF: Right amniotic fluid. LAF left amniotic fluid.
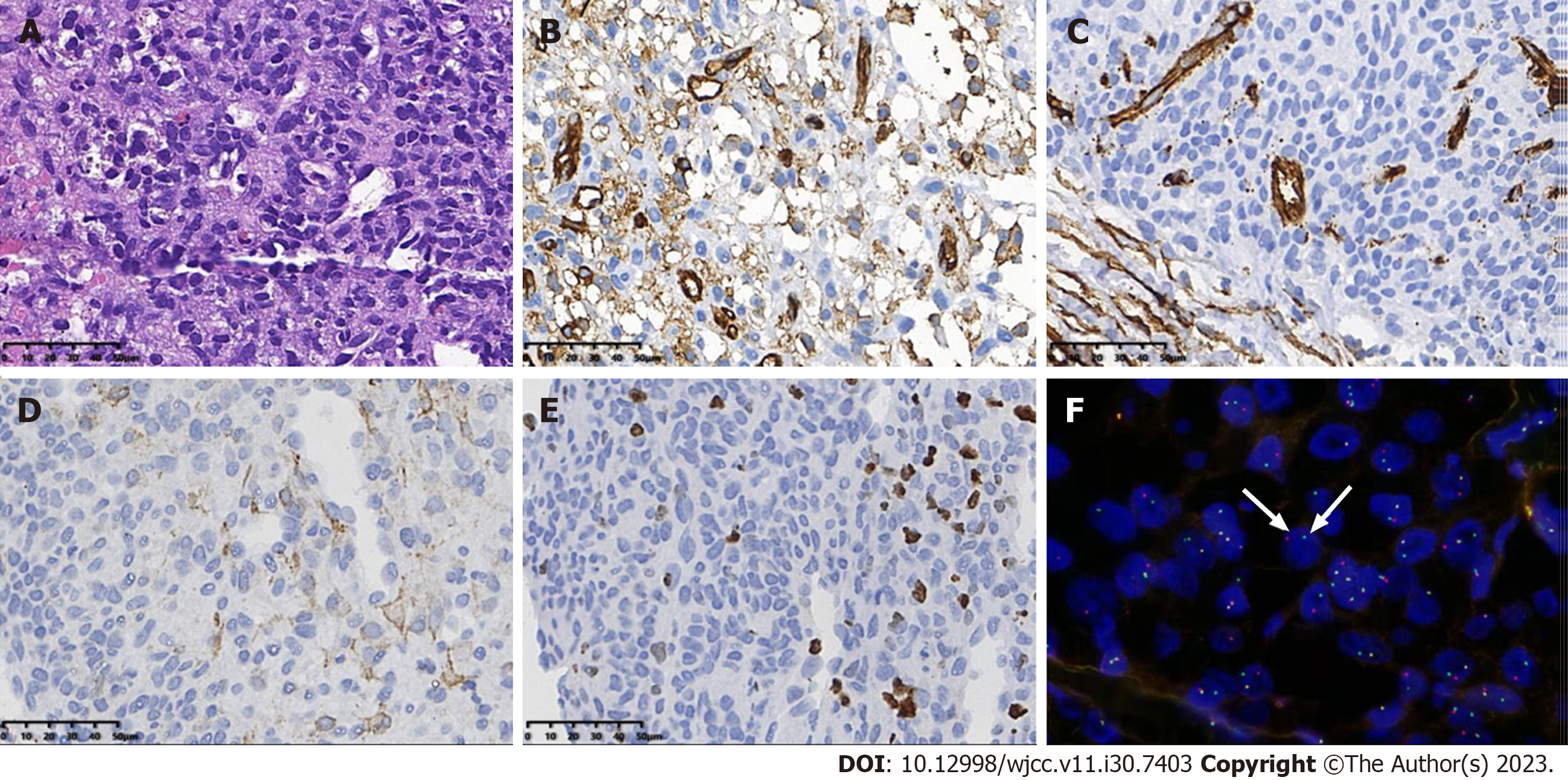
Figure 6 Pathological findings of the congenital infantile fibrosarcoma in Case 1.
A: H&E staining image. The tumor cells showing eosinophilic, diffuse sheets of monotonous round cells with fine chromatin, and indistinct nucleoli; B-D: Immunochemistry demonstrated the expression of smooth muscle actin, CD34, and CD31 in the tumor cells; E: The immunochemical study showed that the Ki-67 proliferation index was approximately 20%; F: Using fluorescence in situ hybridization, the tumor cells showed NTRK3 gene rearrangement, with break-apart green (telomeric) and red (centromeric) signals (white arrows).
- Citation: Liang RN, Jiang J, Zhang J, Liu X, Ma MY, Liu QL, Ma L, Zhou L, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhou Q, Yu SS. Prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of congenital infantile fibrosarcoma and congenital hemangioma: Three case reports. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7403-7412
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7403.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7403