Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
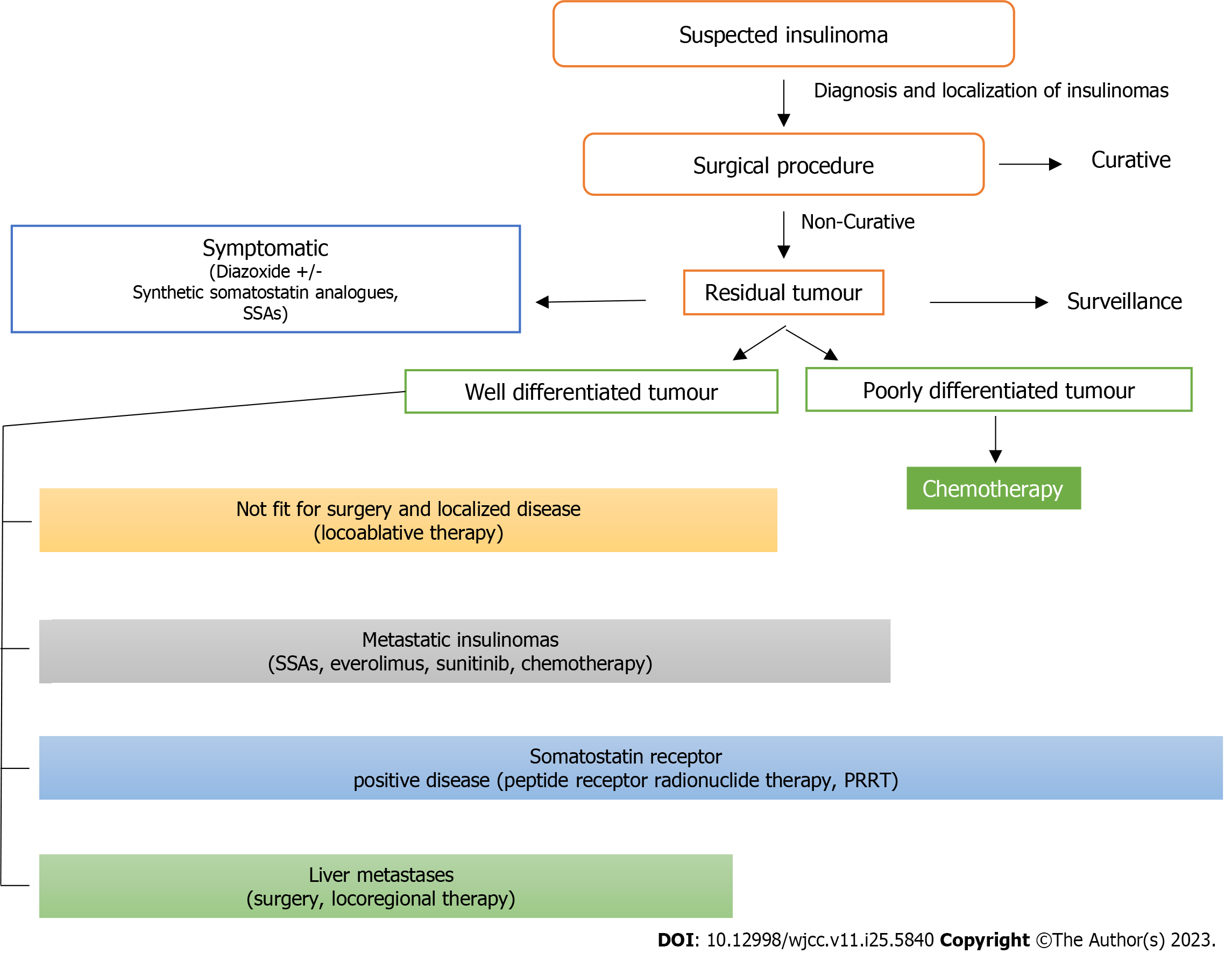
Figure 1 Different treatment options based on suspected aggressiveness of insulinomas[33].
SSAs: Supramolecular self-associating amphiphiles; PRRT: Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy.
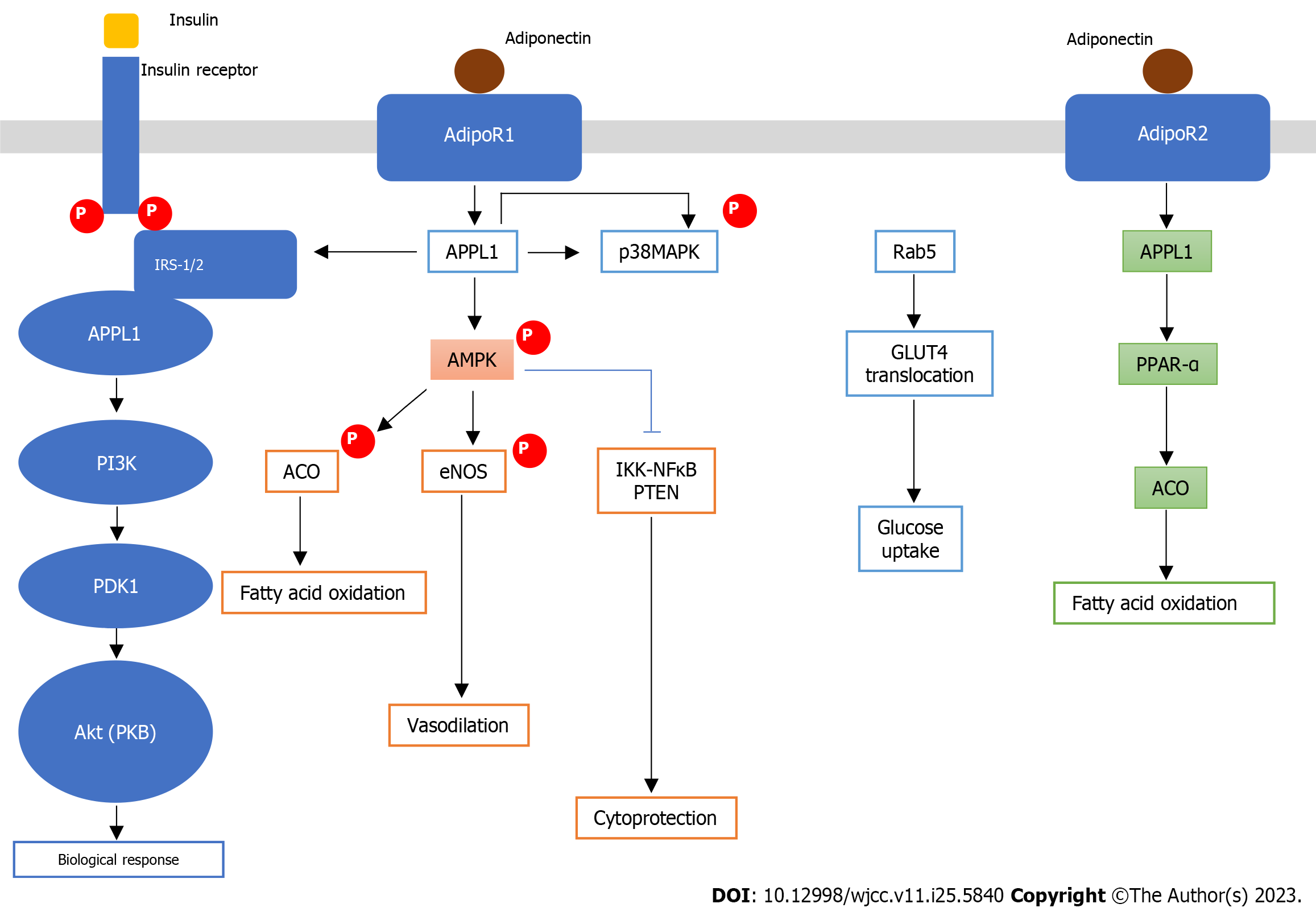
Figure 2 Schematic representation showing downstream signaling events in cross-talk between adiponectin signal transduction and insulin signaling pathway[67].
IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; APPL1: Adaptor protein containing a pleckstrin homology domain, phosphotyrosine binding domain, and leucine zipper motif; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; ACO: Asthma-COPD overlap; GLUT: Glucose transporter; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PDK: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinases; PKB: Protein kinase B; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; IKK: IkappaB kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear transcription factor-kappa B; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10.
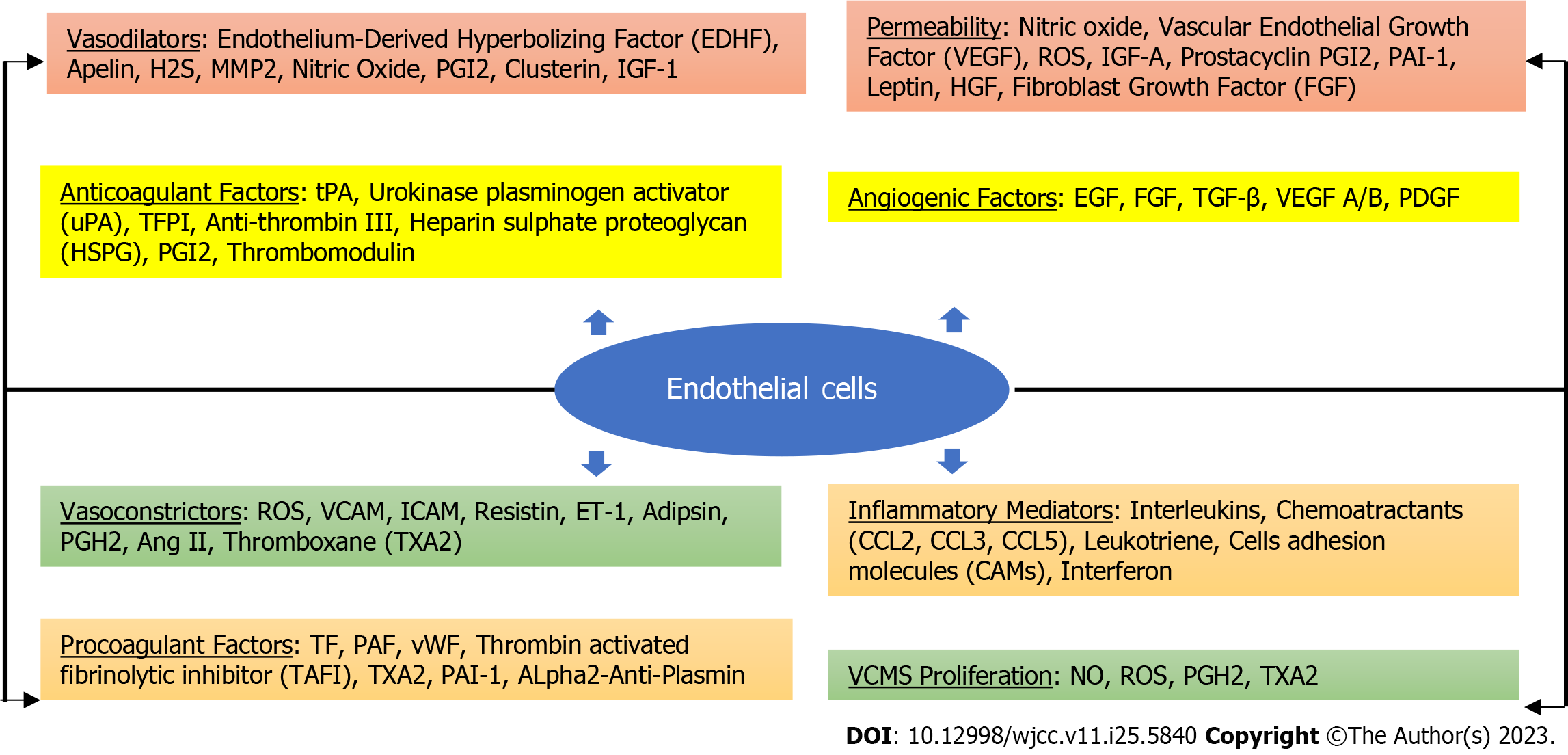
Figure 3 Important molecular functions of endothelial cells and the link between obesity-induced inflammation and endothelial dysfunction[74].
MMP2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2; PGI2: Prostacyclin; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1;ROS: Reactive oxygen species; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; tPA: Tissue plasminogen activator; TFPI: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; ET-1: Endothelin-1; PAF: Platelet activating factor; vWF: von Willebrand factor; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; NO: Nitric oxide.
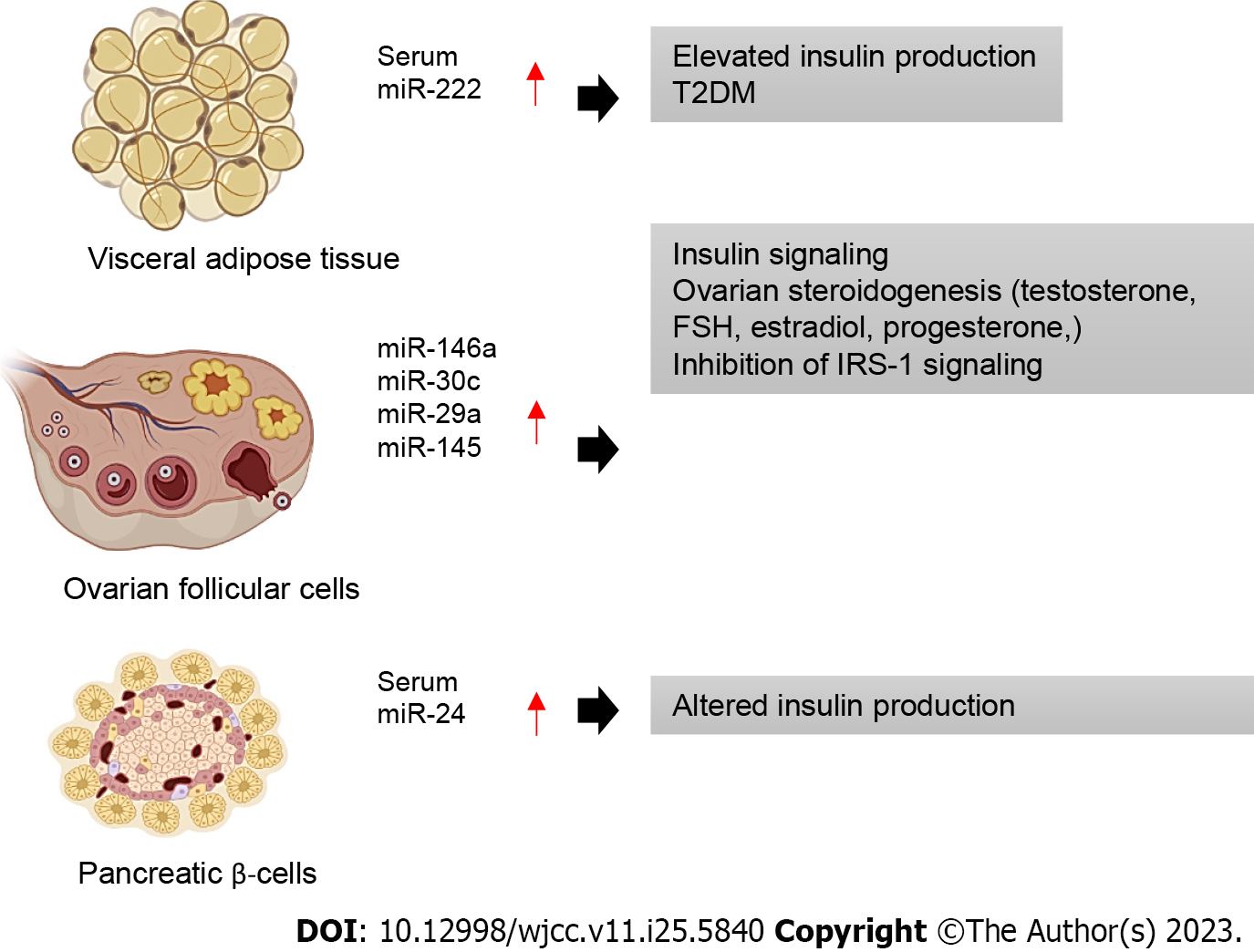
Figure 4 Schematic diagram summarizing the involvement of clinically relevant microRNAs expressed in major tissues in regulating insulin signaling pathways implicated in polycystic ovary syndrome.
T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; FSH: Follicle-stimulating hormone; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate.
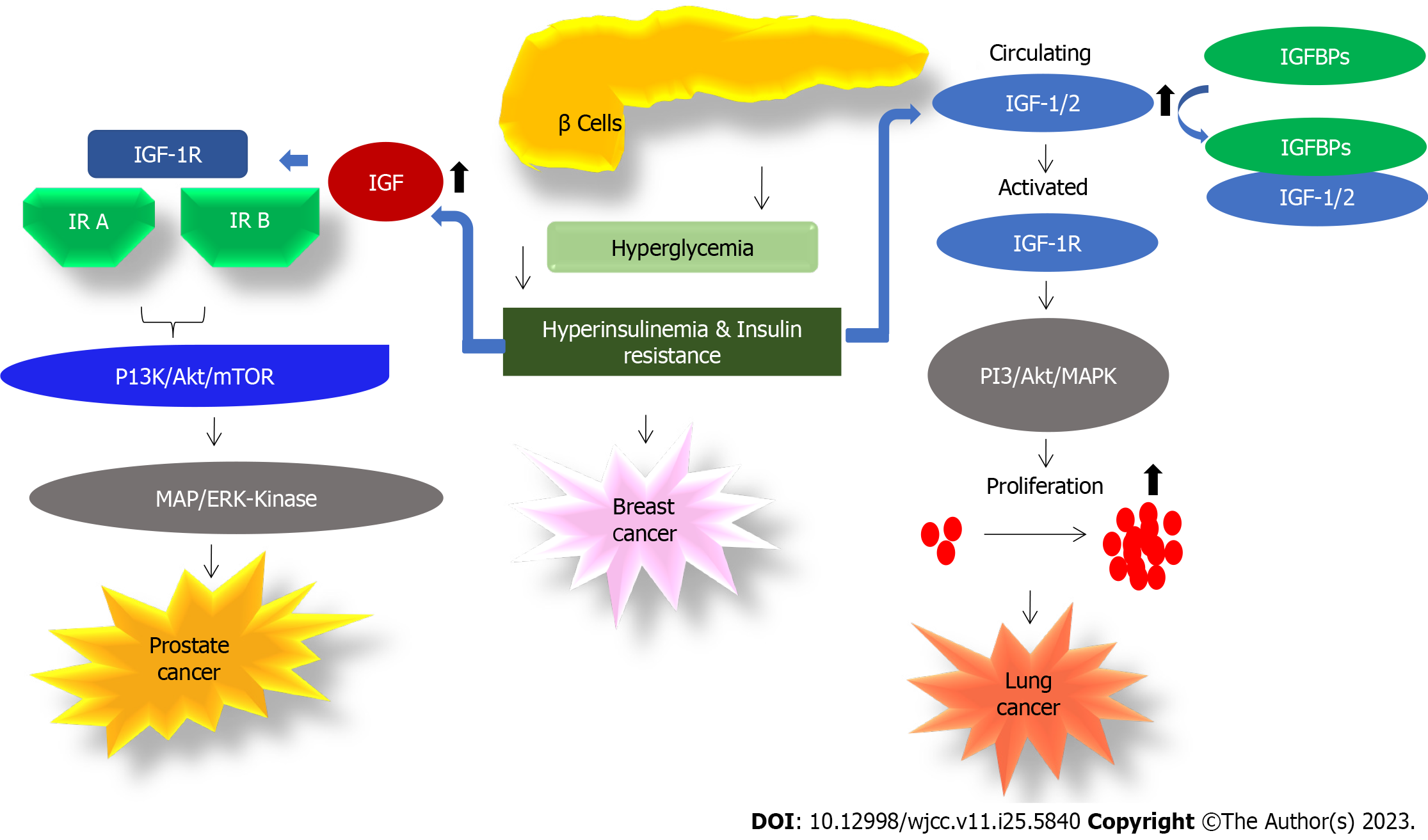
Figure 5 Molecular association of hyperinsulinemia/hyperglycaemia and cancer.
Increased insulin-like growth factor (IGF) due to hyperinsulinemia increases IGF-1R activation which in turn activates downstream signaling and causes prostate cancer[135]. Hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance may lead to breast cancer[129]. Increased insulin in diabetic patients increases IGF-1/IGF-2 circulating levels which interact with IGF-1R present on lung cells. Thus, the activation of the receptor and thereby activated downstream signaling increase carcinogenesis in lung cells. Most of the IGF binding proteins are known to bind circulating IGF-1/IGF-2 and thereby interrupt their interaction with IGF-1R[133,137]. IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; IGFBPs: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; MAP: Mitogen-activated protein; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IR: Insulin receptor.
- Citation: Kumar S, Senapati S, Bhattacharya N, Bhattacharya A, Maurya SK, Husain H, Bhatti JS, Pandey AK. Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i25/5840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840