Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2023; 11(17): 4179-4186
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4179
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4179
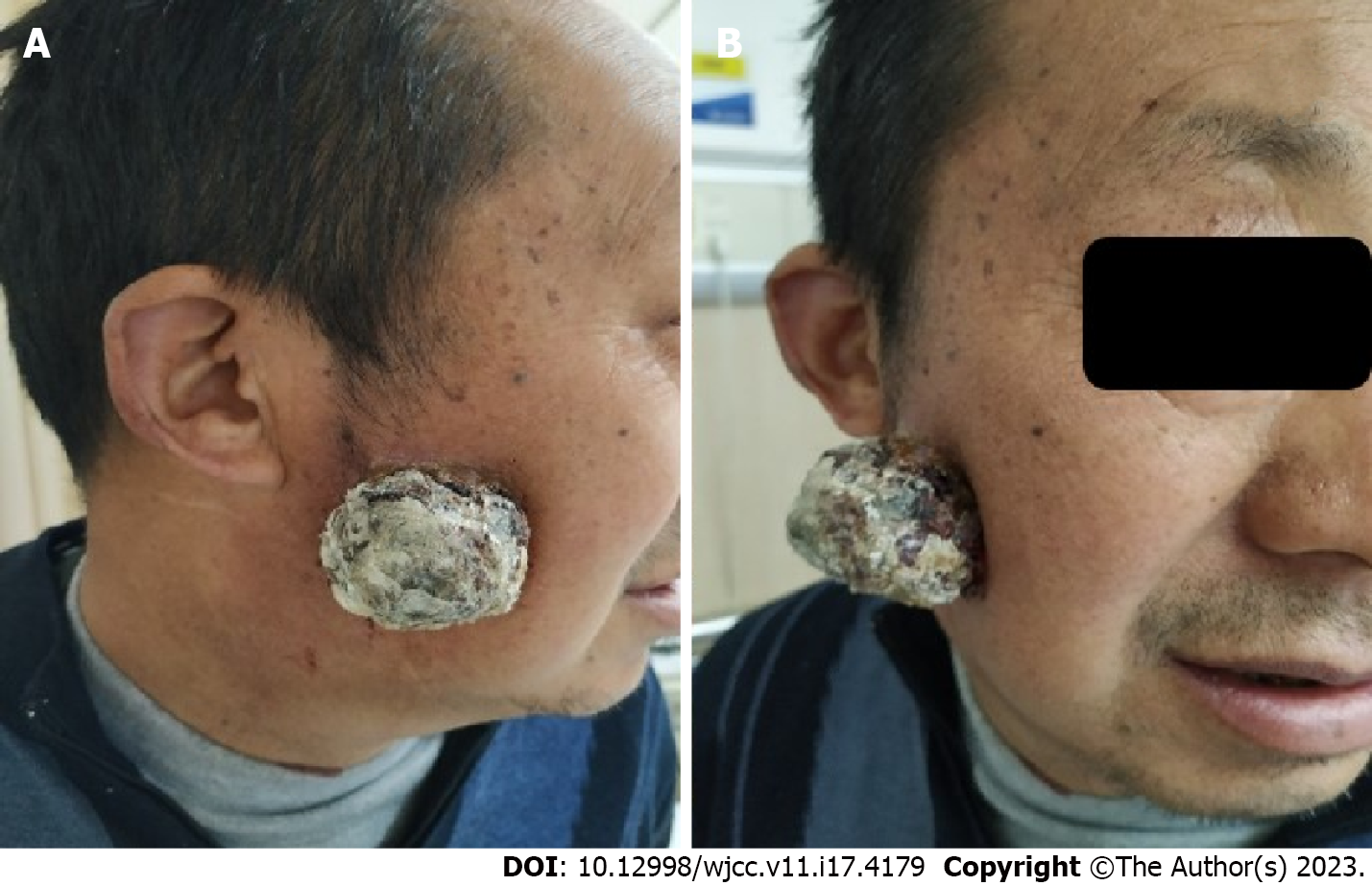
Figure 1 A 56-year-old Asian male who has reported a significant mass on the right cheek of the patient.
Physical examination revealed a 4.5 cm × 4.5 cm mass with an irregular surface and foul-smelling discharge on the right cheek of the patient. A: Side view; B: Front view.
Figure 2 The lump was subjected to fine-needle aspiration cytology.
A and B: Fine needle aspiration cytology of Wright staining revealing diffuse tumor cells with scant cytoplasm and loose chromatin (red arrow, original magnification, × 1000).
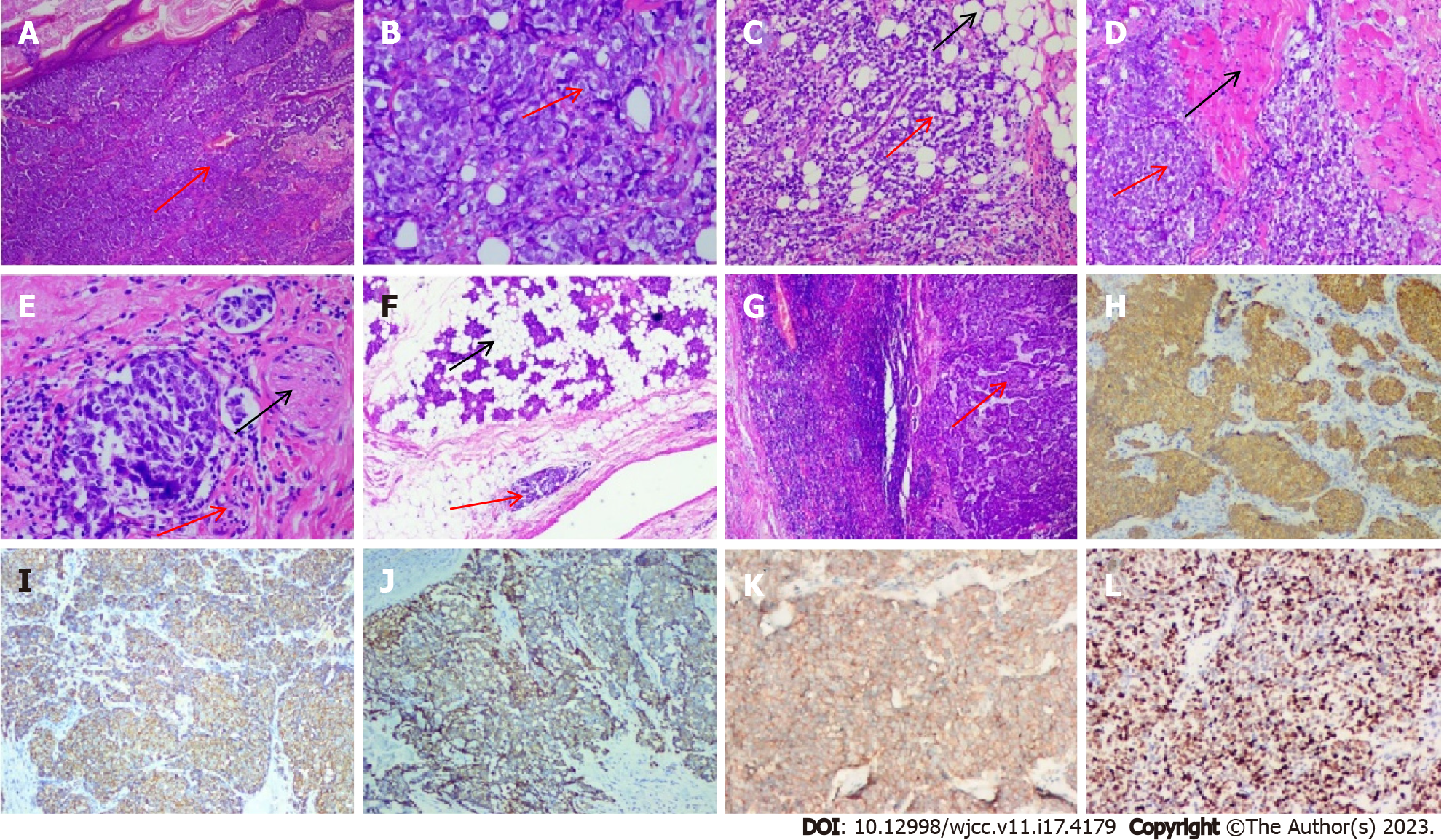
Figure 3 Histopathological findings of Merkel cell carcinoma.
A and B: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining revealed a monotonous population of small round basophilic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei, sparse cytoplasm (red arrow, original magnification: A × 4; B × 100); C: Microscopy examinations finding the Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) cells invaded adipose tissue (original magnification: × 20); D: Microscopy examinations finding the MCC cells invaded muscle (original magnification: × 20); E: Microscopy examinations finding the MCC cells invaded nerve (original magnification: × 40); F: Microscopy examinations finding the MCC cells invaded parotid gland (original magnification: × 10); G: Microscopy examinations finding the MCC cells invaded lymph nodes (original magnification: × 10); H: Immunohistochemical staining revealed that the MCC cells demonstrated strong paranuclear dot-like cytoplasmic staining for cytokeratin 20 (CK20) (riginal magnification × 10); I: Immunohistochemical analysis found that the tumor cells were positive for CgA (original magnification × 10); J: Immunohistochemical analysis found that the tumor cells were positive for CD56 (original magnification × 10); K: Immunohistochemical analysis found that the tumor cells were positive for Syn (original magnification × 10); L: Immunohistochemical analysis found that the tumor cells were positive for Ki67 (original magnification × 10) (The tumor is indicated by the red arrow and the black arrow indicates normal tissue; Cytokeratin, cluster of differentiation, chromogranin and synaptophysin for CK, CD, CgA and Syn).
Figure 4 Computed tomography scan head and neck.
A: Computed tomography (CT) scan head demonstrating a mass extending into the parotid gland (red arrow); B: CT scan neck demonstrating a swollen lymph node on the right side of the neck, presenting as a low-density shadow (red arrow).
- Citation: Ren MY, Shi YJ, Lu W, Fan SS, Tao XH, Ding Y. Facial Merkel cell carcinoma in a patient with diabetes and hepatitis B: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(17): 4179-4186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i17/4179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4179