Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2023; 11(17): 4019-4025
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4019
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4019
Figure 1 Elastic fiber staining was categorized into four grades according to the elastic fibers' dissolution degree and destruction.
A: Grade I: Disorganized arrangement of elastic fibers in the lesion without significant dissolution (×200); B: Grade II: Partial breakage of elastic fibers in the lesion with mild dissolution (×200); C: Grade III: Partial dissolution of elastic fibers in the lesion, but small, discontinuous elastic fibers are still visible (×200); D: Grade IV: Complete dissolution and disappearance of elastic fibers in the lesion (×200).
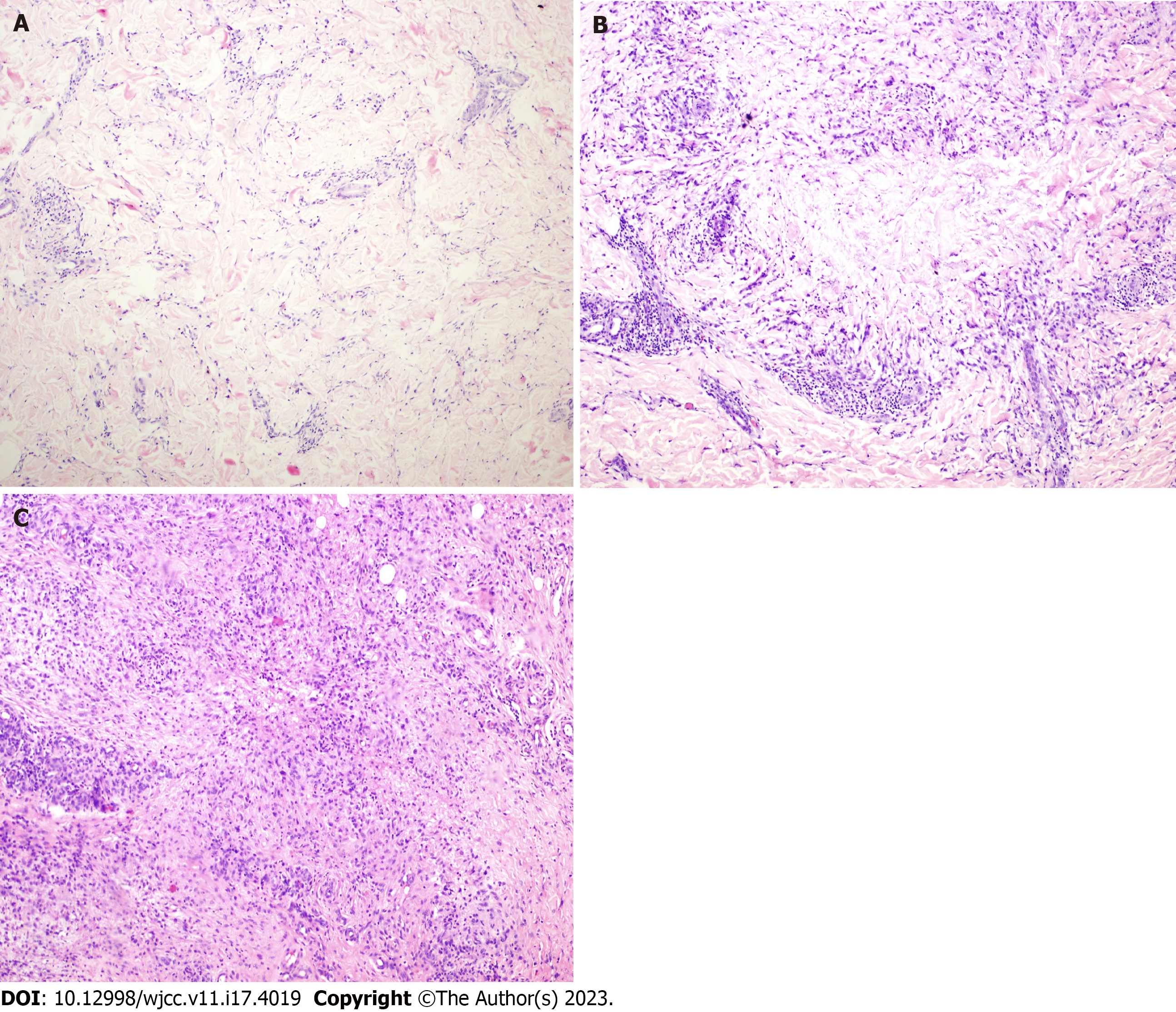
Figure 2 Granuloma annulare was classified into four types: Palisading granuloma, histiocytic infiltrative, epithelioid nodular, and mixed histologic types.
A: Histiocytic infiltration type granuloma annulare (GA): Progressive necrosis is mild with incomplete degeneration of collagen fibers (×100, HE); B: Palisading granuloma type GA: progressive necrosis is evident with complete degeneration of collagen fibers in the lesion (×100, HE); C: Epithelioid nodular type GA: histiocytes aggregate to form epithelioid nodules with multinucleated giant cells mixed in the nodules and surrounded by lymphocytes (×100, HE).
- Citation: Zhang DY, Zhang L, Yang QY, Xie YC, Jiang HC, Li JZ, Shu H. Elastic fiber degradation in the development of pediatric granuloma annulare: Report of 39 cases. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(17): 4019-4025
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i17/4019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4019