Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2023; 11(13): 3062-3069
Published online May 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i13.3062
Published online May 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i13.3062
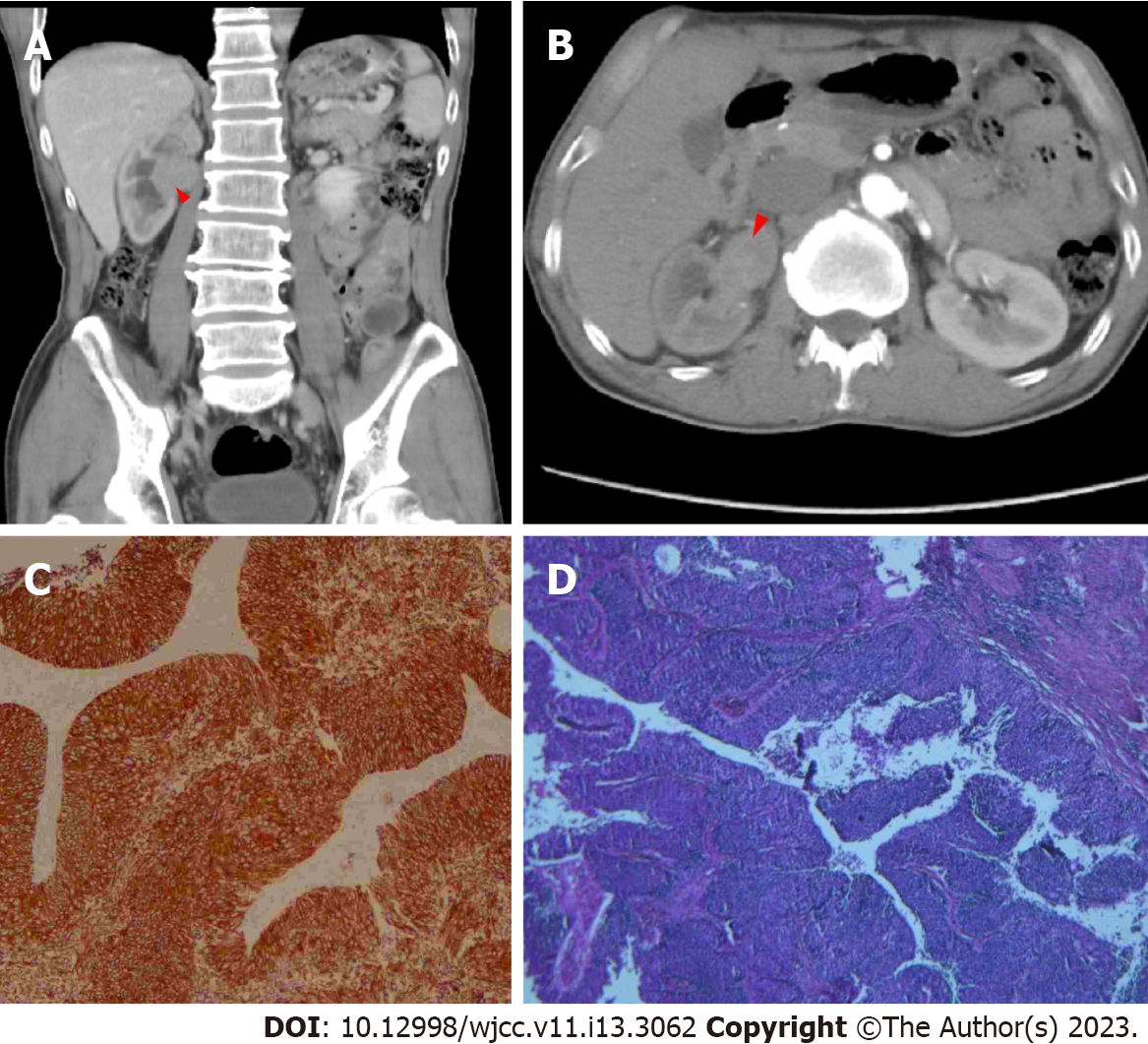
Figure 1 Radiological and histological analysis of the patient at the first hospitalization.
A: Computed tomography (CT) identified a mass in the right pelvis in longitudinal section (red arrowhead); B: CT identified a mass in the right pelvis in cross-section (red arrowhead); C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining indicated the tumor was a urothelial carcinoma; D: CK7 staining indicated the tumor was a urothelial carcinoma.
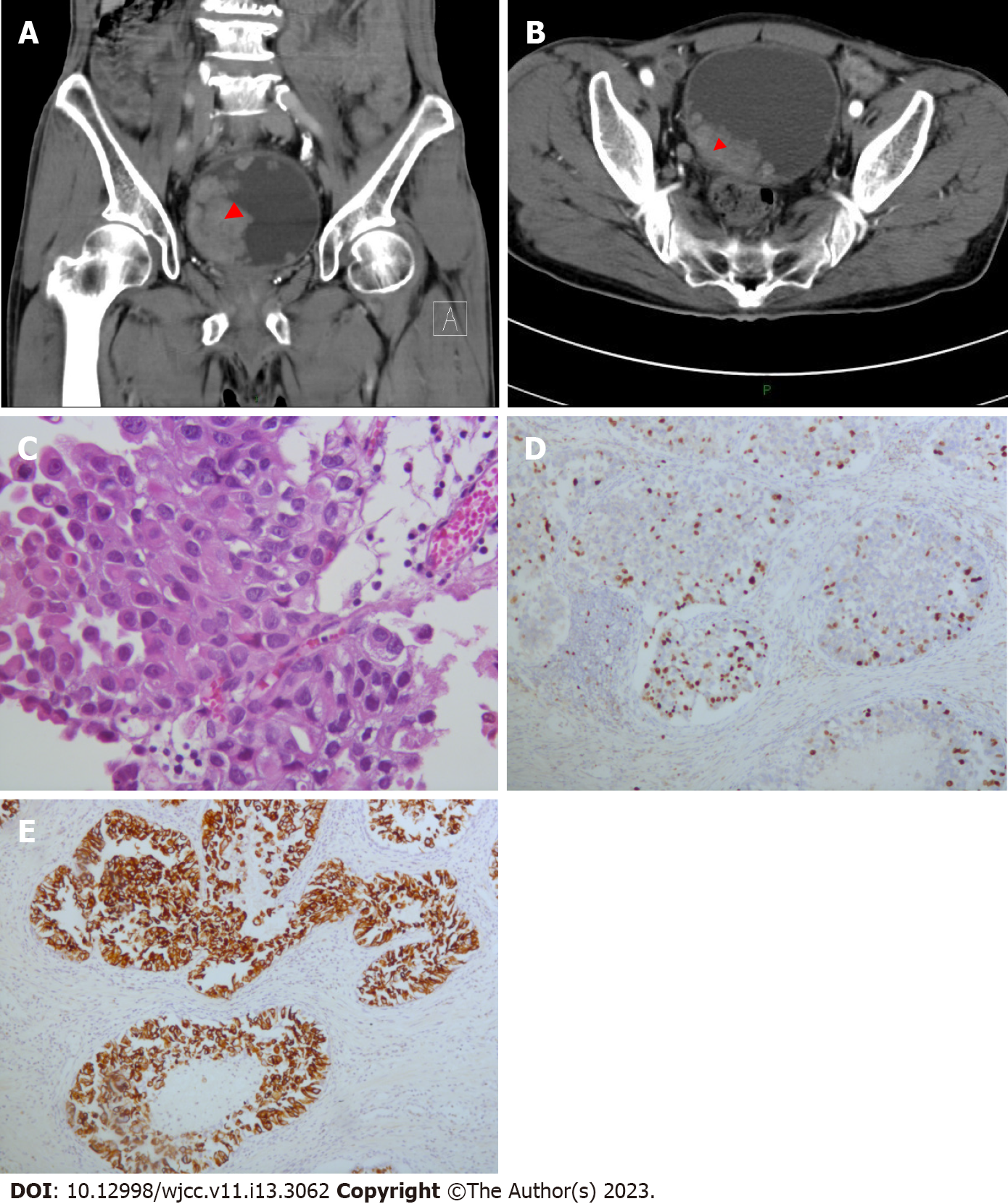
Figure 2 Radiological and histological analysis of the patient at the second hospitalization.
A: Computed tomography (CT) showed multiple neoplasms in the bladder in longitudinal section (red arrowhead); B: CT showed multiple neoplasms in the bladder in cross-section (red arrowhead); C-E: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (C) and positive staining for Ki-67 (D) and CK7 (E) confirmed urothelial carcinoma.
Figure 3 Treatment timeline of the patient.
UC: Urothelial carcinoma.
- Citation: Zhang JQ, Duan Y, Wang K, Zhang XL, Jiang KH. Metachronous urothelial carcinoma in the renal pelvis, bladder, and urethra: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(13): 3062-3069
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i13/3062.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i13.3062