Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2023; 11(10): 2213-2225
Published online Apr 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2213
Published online Apr 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2213
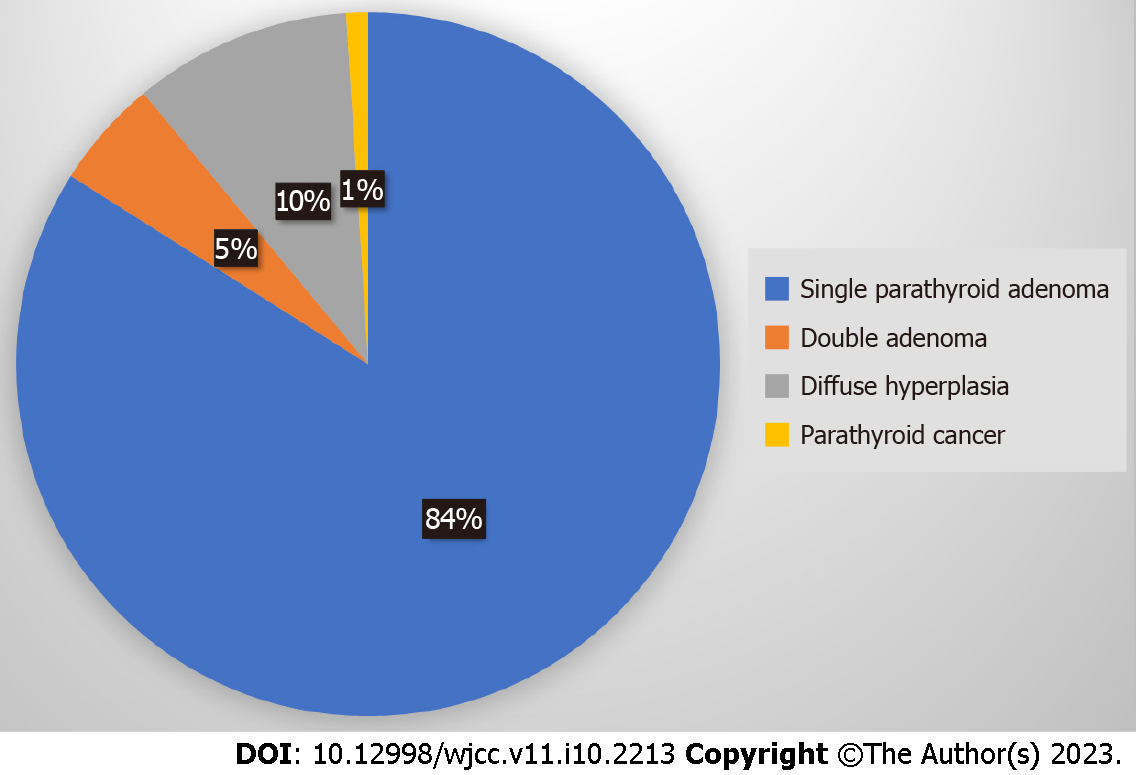
Figure 1 Causes of primary hyperparathyroidism.
Single parathyroid adenoma (80%-85%), double adenoma (4%-5%), diffuse hyperplasia (10%-15%), parathyroid cancer (< 1%).
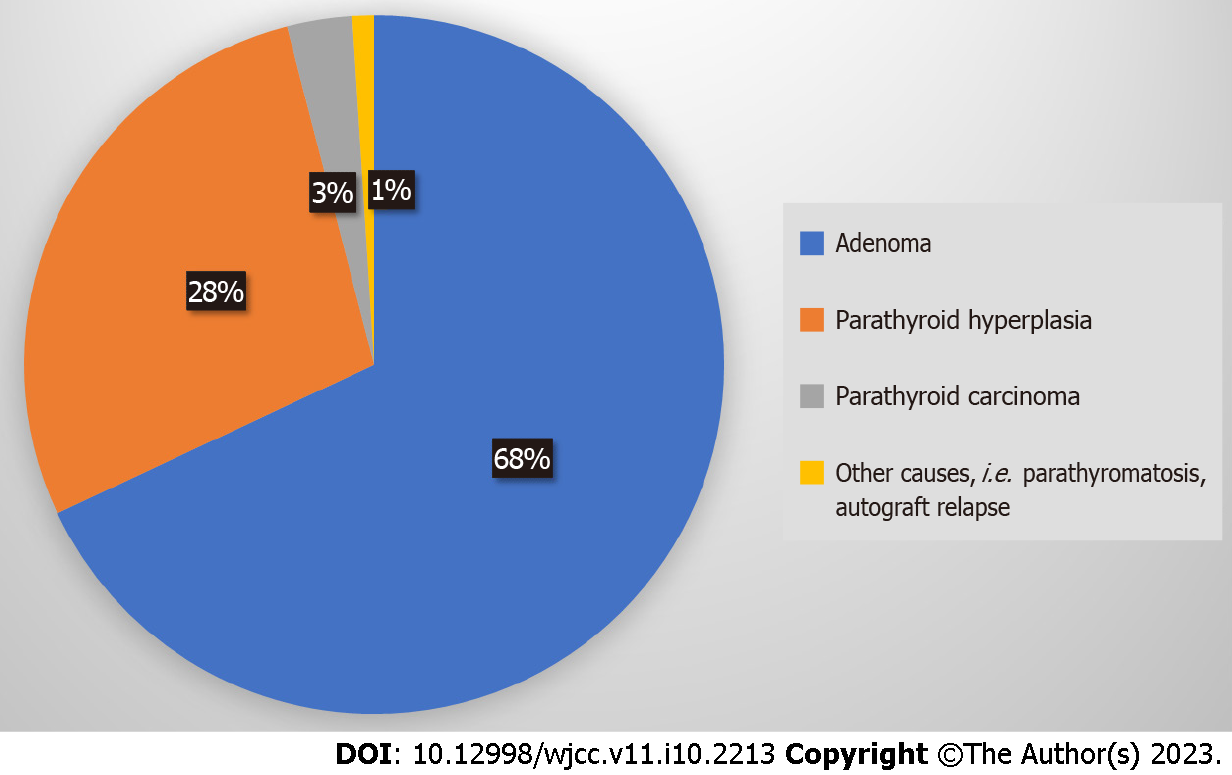
Figure 2 Causes of persistent-recurrent primary hyperparathyroidism.
Adenoma (68%), parathyroid hyperplasia (28%), parathyroid carcinoma (3%), other causes: i.e. parathyromatosis, autograft relapse (1%).
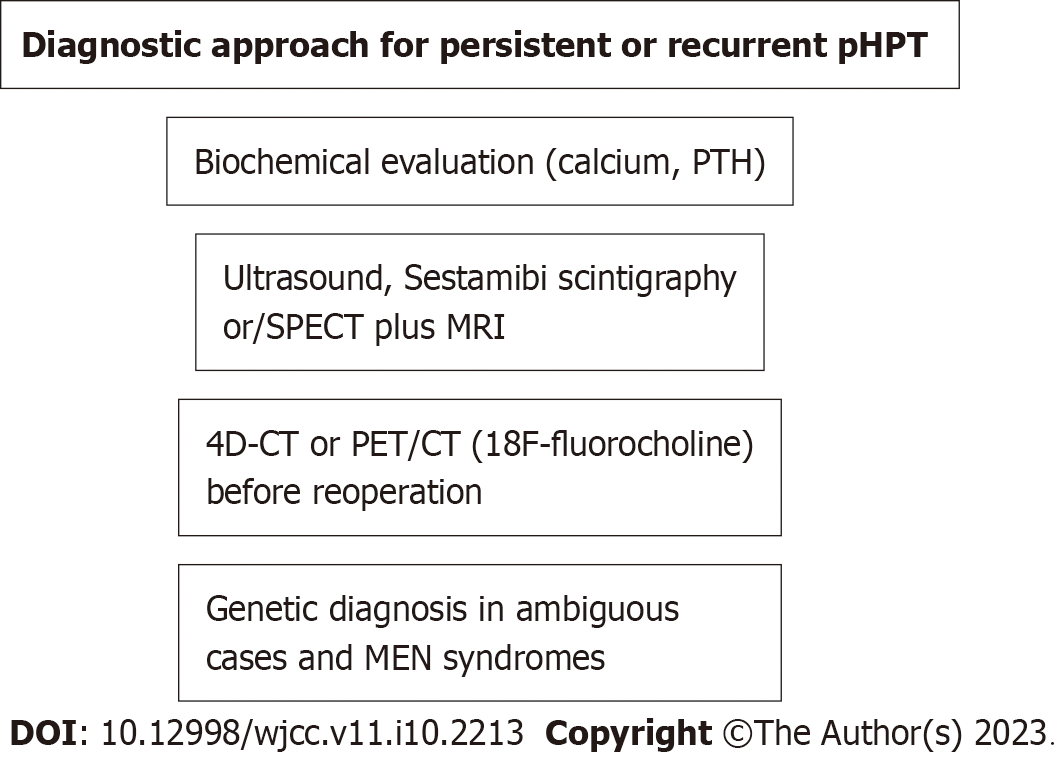
Figure 3 Scheme of diagnostic approach for persistent or recurrent primary hyperparathyroidism.
pHPT: Primary hyperparathyroidism; PTH: Parathyroid hormone; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; CT: Computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.
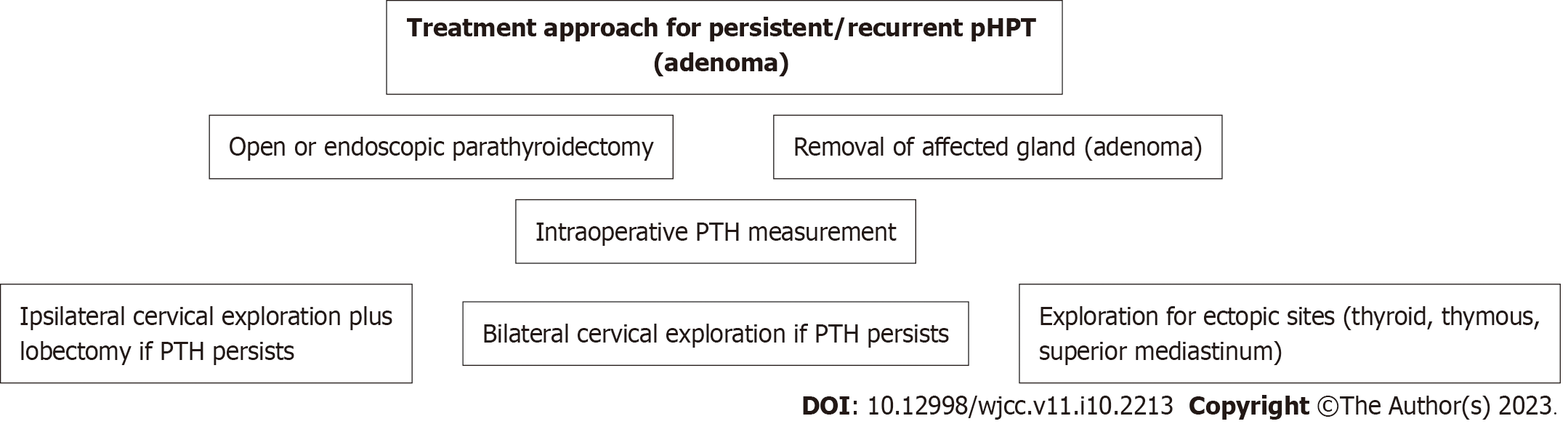
Figure 4 Scheme of treatment approach for persistent or recurrent primary hyperparathyroidism (adenoma).
pHPT: Primary hyperparathyroidism; PTH: Parathyroid hormone.
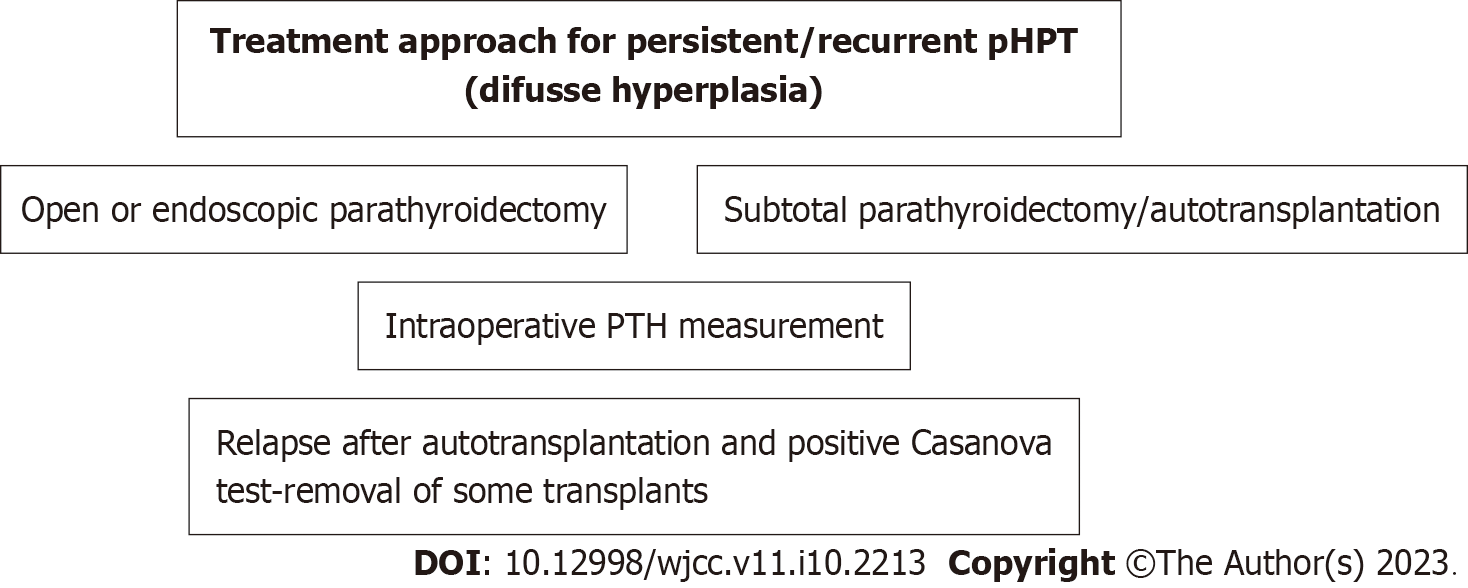
Figure 5 Scheme of treatment approach for persistent or recurrent primary hyperparathyroidism (diffuse hyperplasia).
pHPT: Primary hyperparathyroidism; PTH: Parathyroid hormone.
- Citation: Pavlidis ET, Pavlidis TE. Update on the current management of persistent and recurrent primary hyperparathyroidism after parathyroidectomy. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(10): 2213-2225
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i10/2213.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2213