Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2022; 10(8): 2622-2628
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2622
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2622
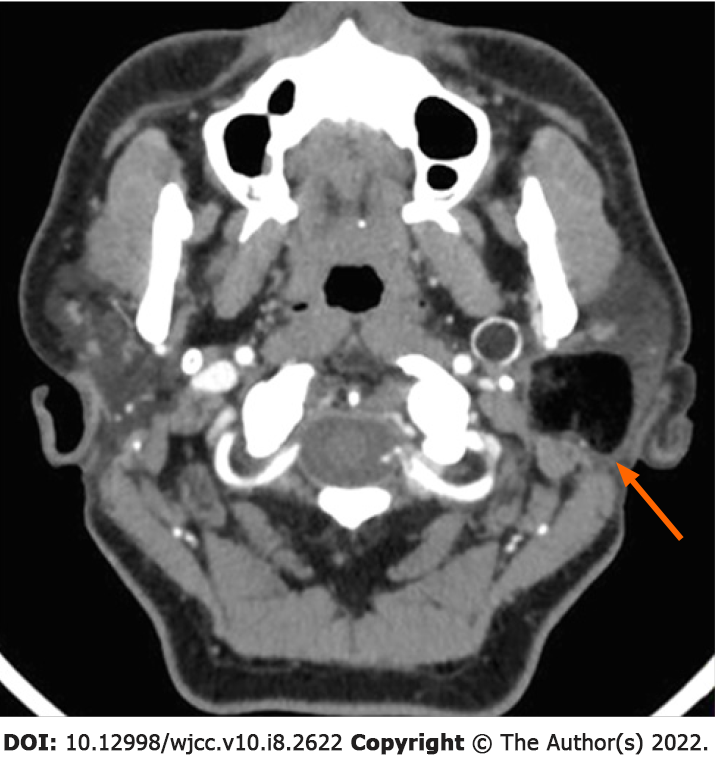
Figure 1 Axial-view contrast-enhanced computed tomography image.
The mass was located in the deep lobe of the left parotid gland. The medial part extended to the parapharyngeal space. Eggshell-like calcification was observed in the cyst wall. The cyst components were in different density, including a large amount of fat and a small number of keratinized substances.
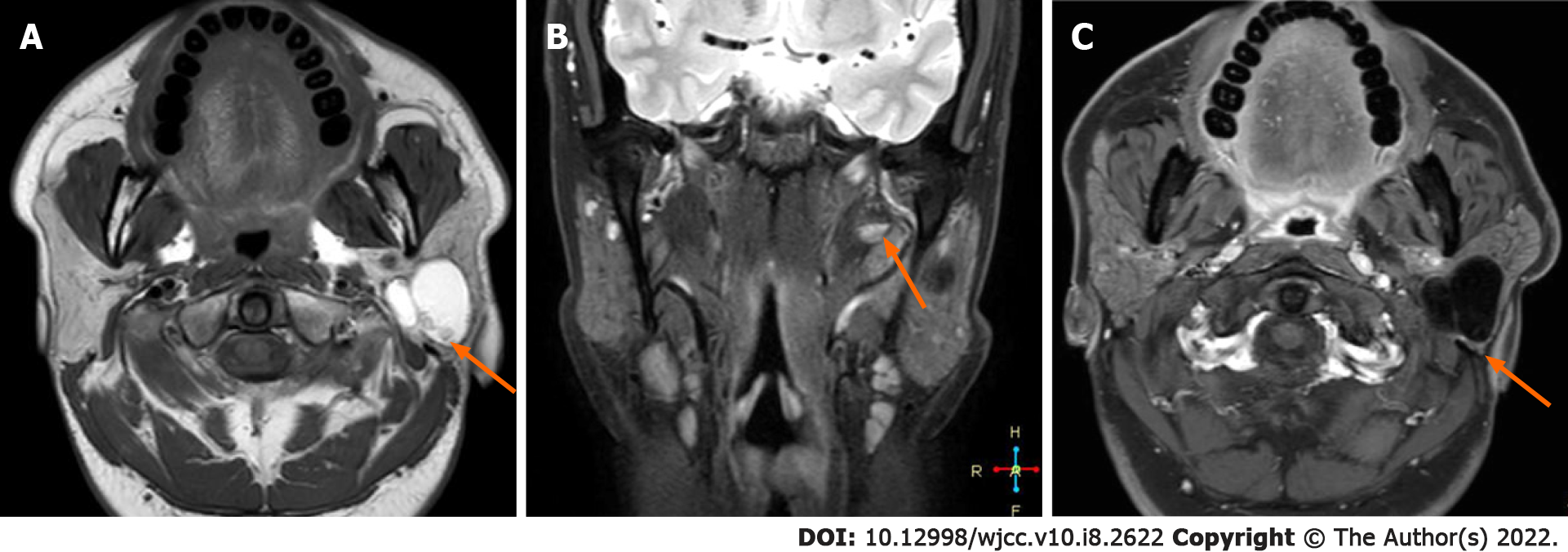
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging images.
A: T1W1 axial view; B: Coronal view of fat-saturated sequence in T2WI; C: T1W1 enhancement. The lesion had a complete capsule and presented as short T1 and long T2 signals, combined with medium T1 and T2 signals and line-like short T2 separation. It had a complete capsule showing low signal in the fat saturation sequence. It was accompanied by fat-liquid level, which was not significantly enhanced on enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
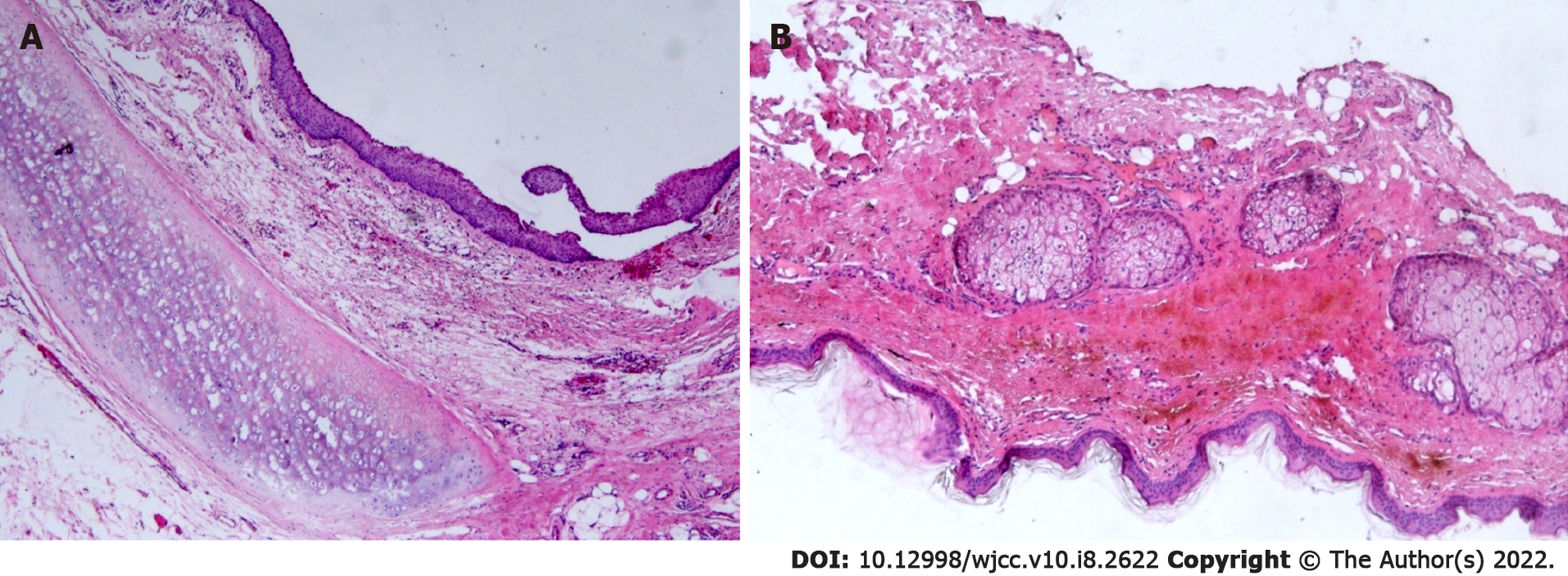
Figure 3 Histopathological analysis of the teratoma.
A and B: The cyst wall was lined with a stratified squamous epithelium. Hyaline cartilage, sebaceous glands, and fat tissue were seen in the fibrous capsule wall (HE × 50).
- Citation: Liu HS, Zhang QY, Duan JF, Li G, Zhang J, Sun PF. Cystic teratoma of the parotid gland: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(8): 2622-2628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i8/2622.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2622