Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2022; 10(8): 2591-2603
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2591
Published online Mar 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2591
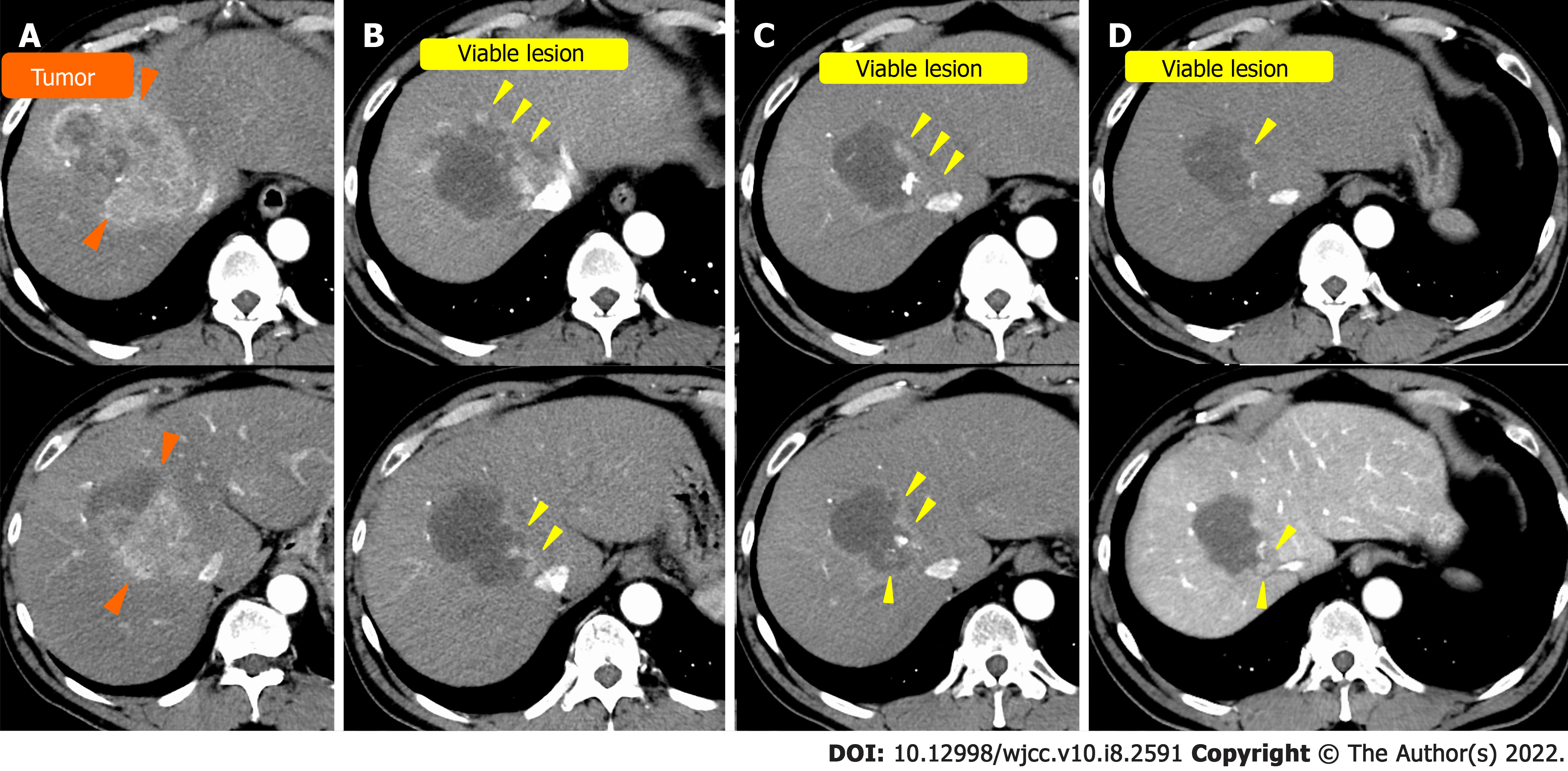
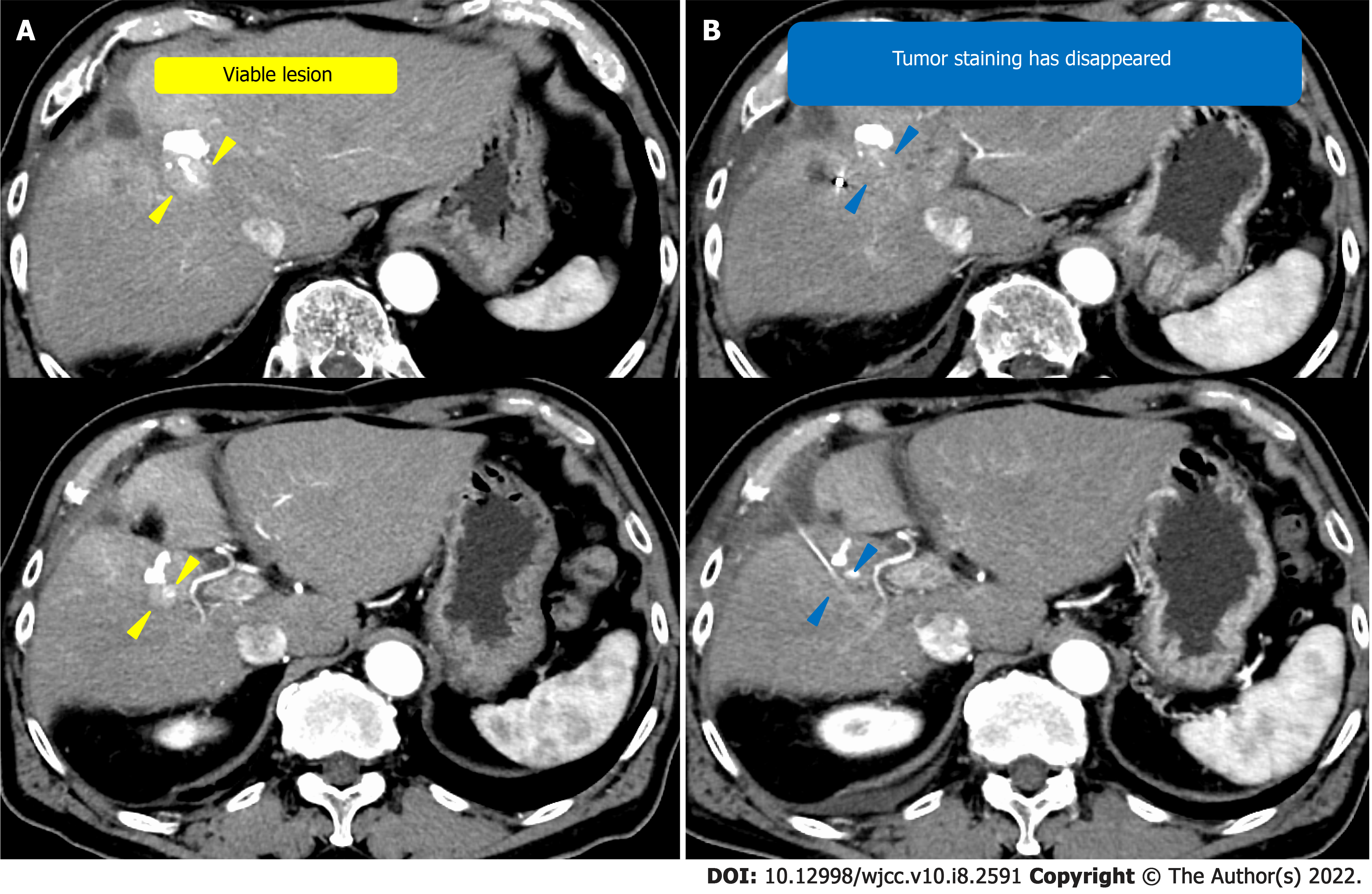
Figure 1 Computed tomography of case 1.
A: On admission; B: After the first transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE); C: After the second TACE; D: After the third TACE. Orange arrowhead: Hepatocellular carcinoma before TACE; yellow arrowhead: Viable lesion after TACE.
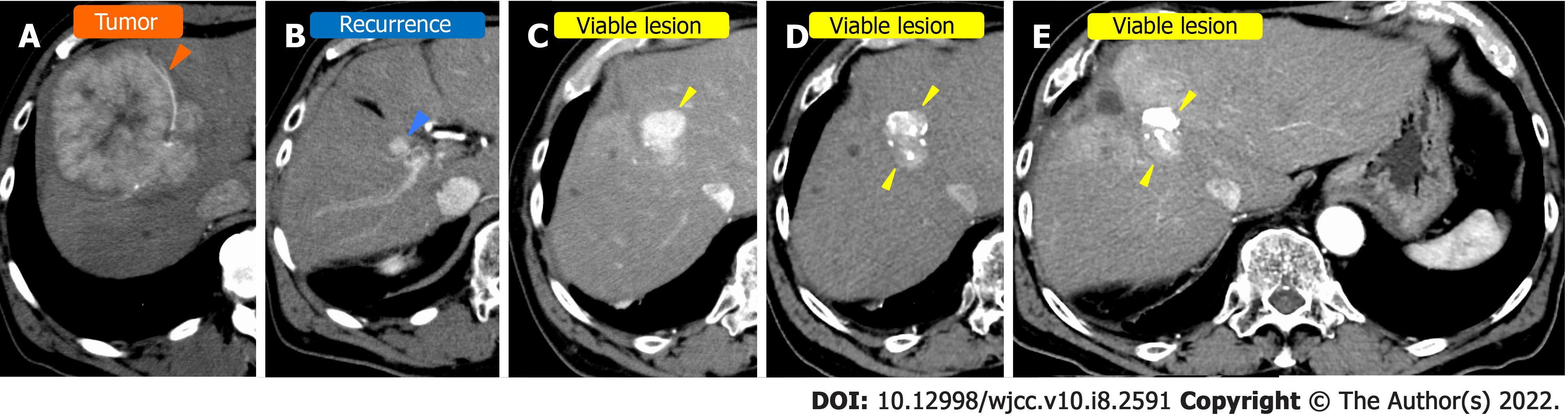
Figure 2 Computed tomography in case 2.
A: Before surgical resection at a nearby hospital; B: At the time of recurrence; C: Before Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) at our hospital; D: After the first TACE at our hospital; E: After the third TACE at our hospital. Orange arrowhead: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) before surgical resection at a nearby hospital; blue arrowhead: recurrence of HCC; yellow arrowhead: Viable lesion after TACE.
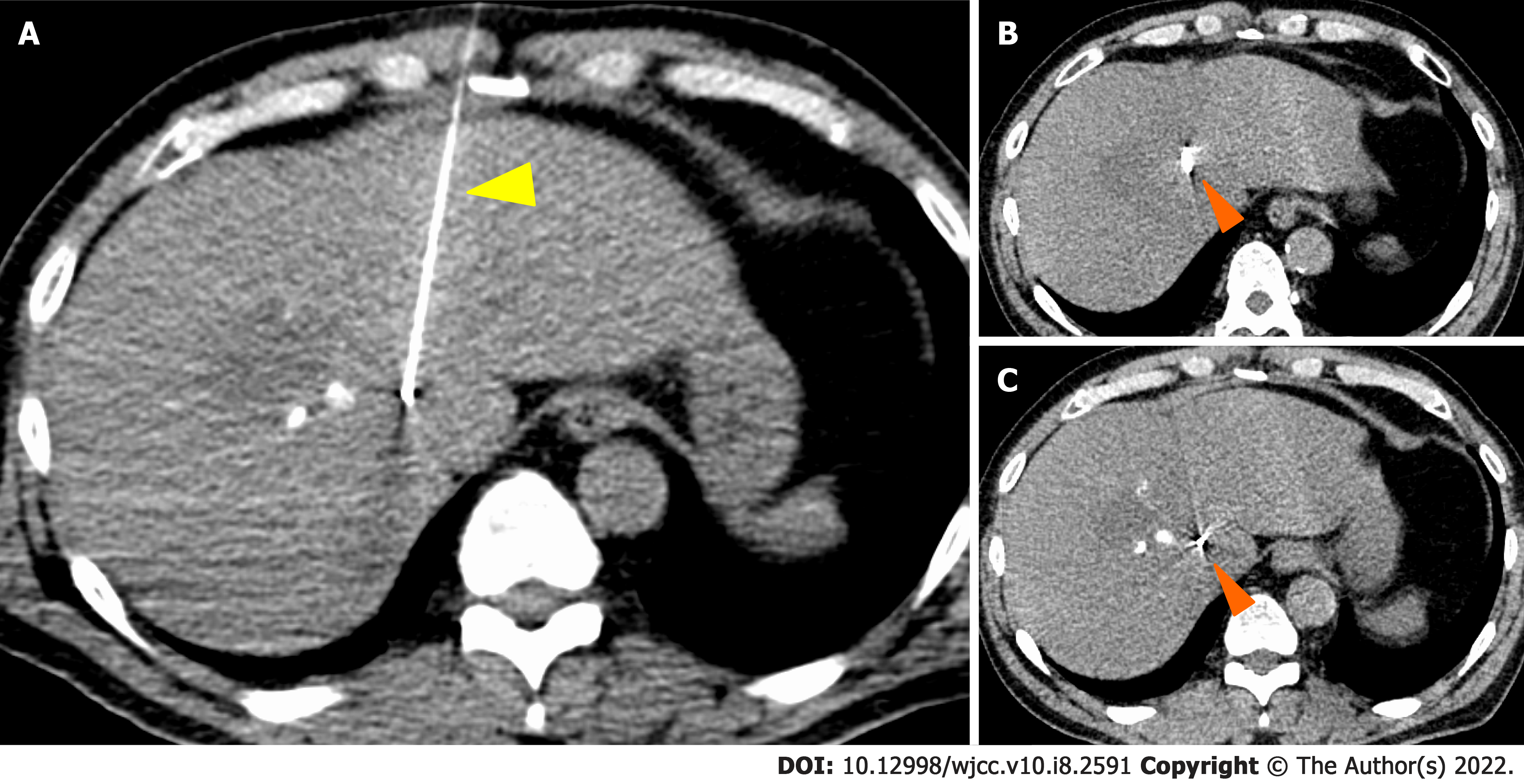
Figure 3 Gold Anchor® placement in case 1.
Orange arrowhead: Gold Anchor® (GA); yellow arrowhead: Puncture needle of GA.
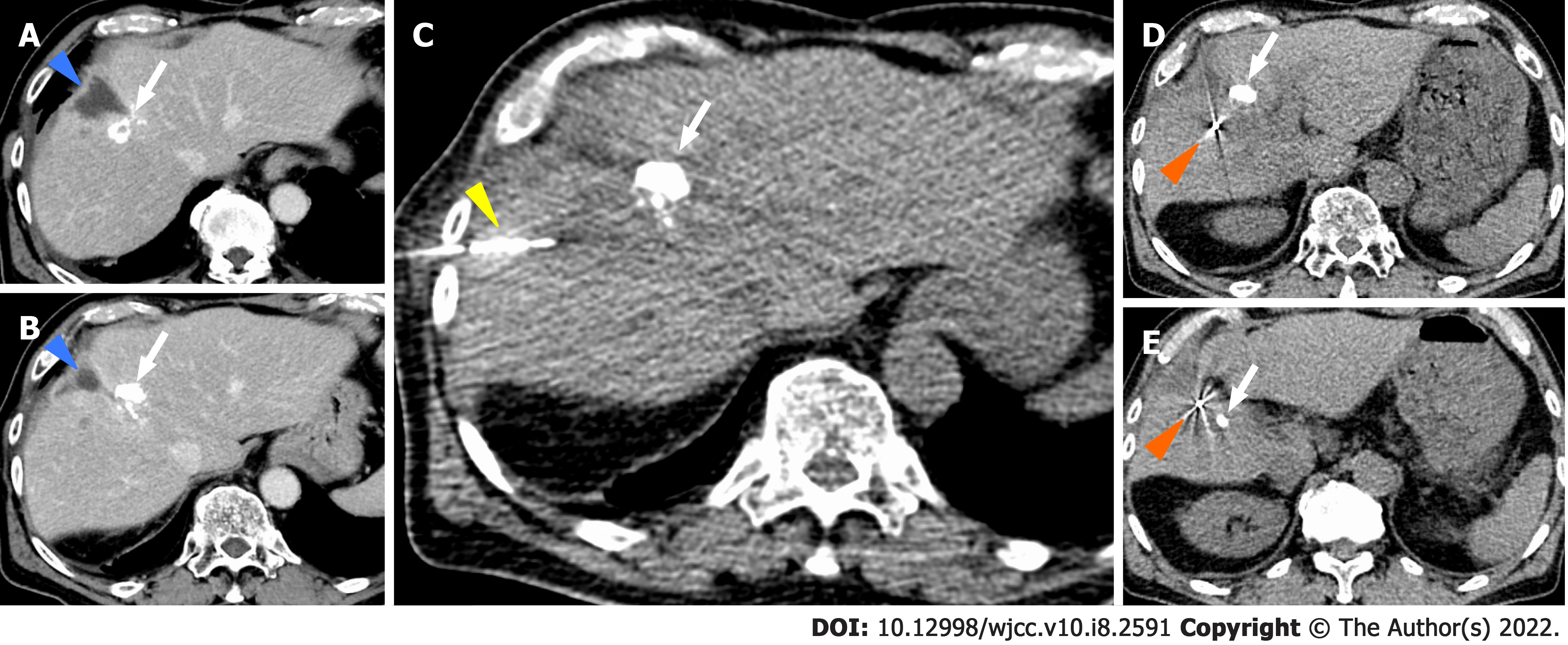
Figure 4 Gold Anchor® placement in case 2.
A and B: Blue arrowhead; Biloma complicated with surgical resection at the previous hospital, white arrow; Ethyl ester of iodinated poppyseed oil fatty acid (lipiodol) after Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, C: white arrow; Ethyl ester of iodinated poppyseed oil fatty acid (lipiodol) after Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, yellow arrowhead; Puncture needle of GA, D and E: Orange arrowhead; Gold Anchor® (GA), white arrow; Ethyl ester of iodinated poppyseed oil fatty acid (lipiodol) after Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
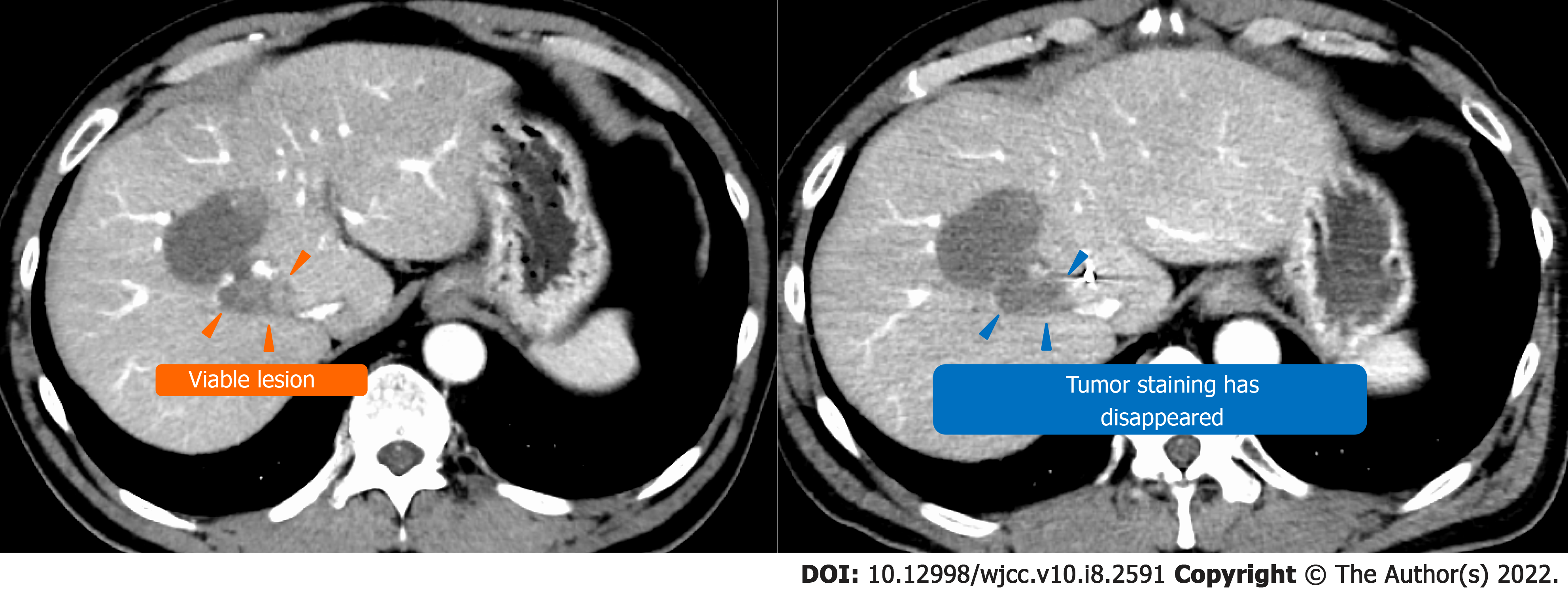
Figure 5 Computed tomography before and after stereotactic body radiation in case 1.
Yellow arrowhead: Viable lesion after the third transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; blue arrowhead: Disappearance of the contrast effect of the tumor after stereotactic body radiation.
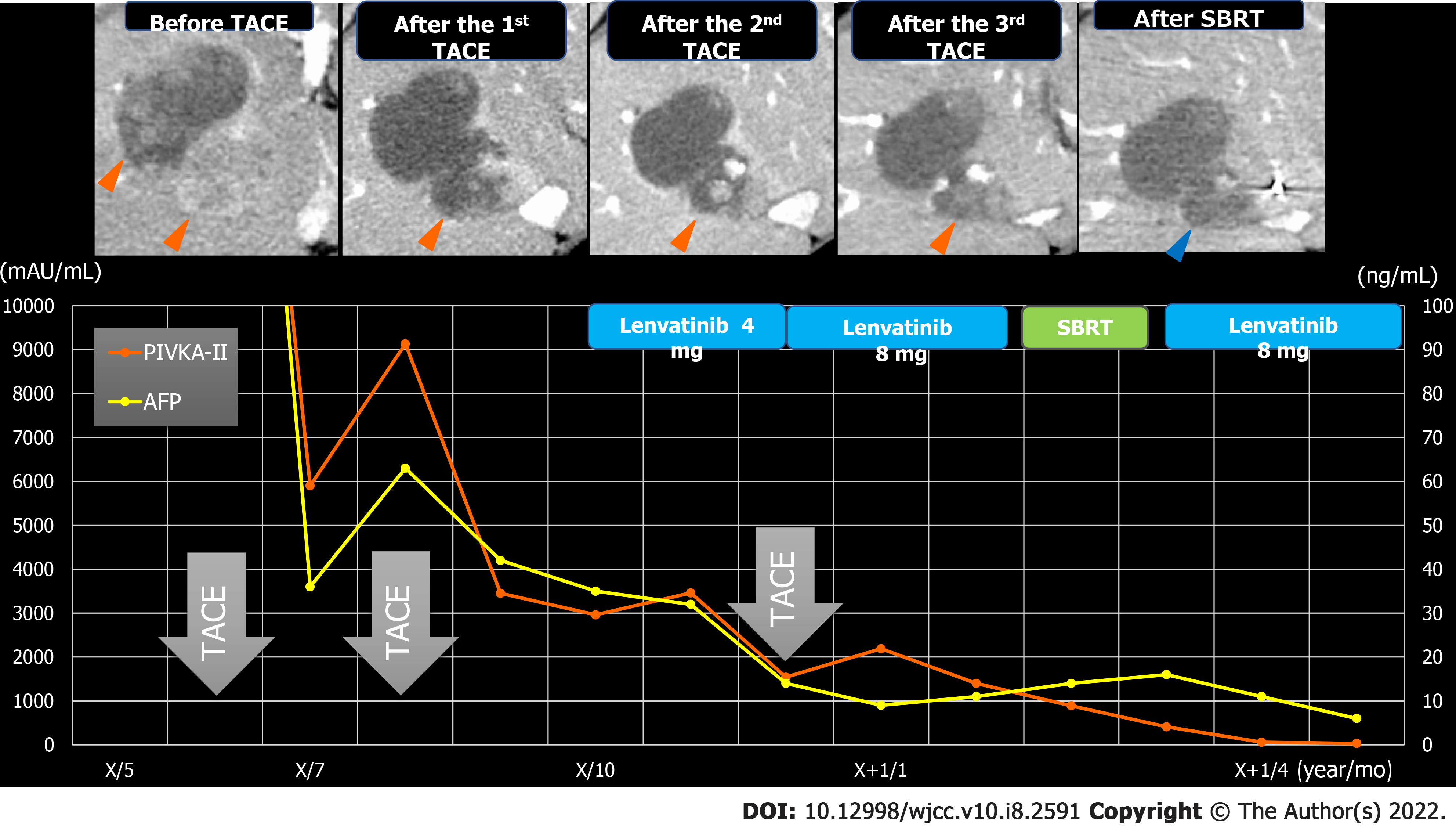
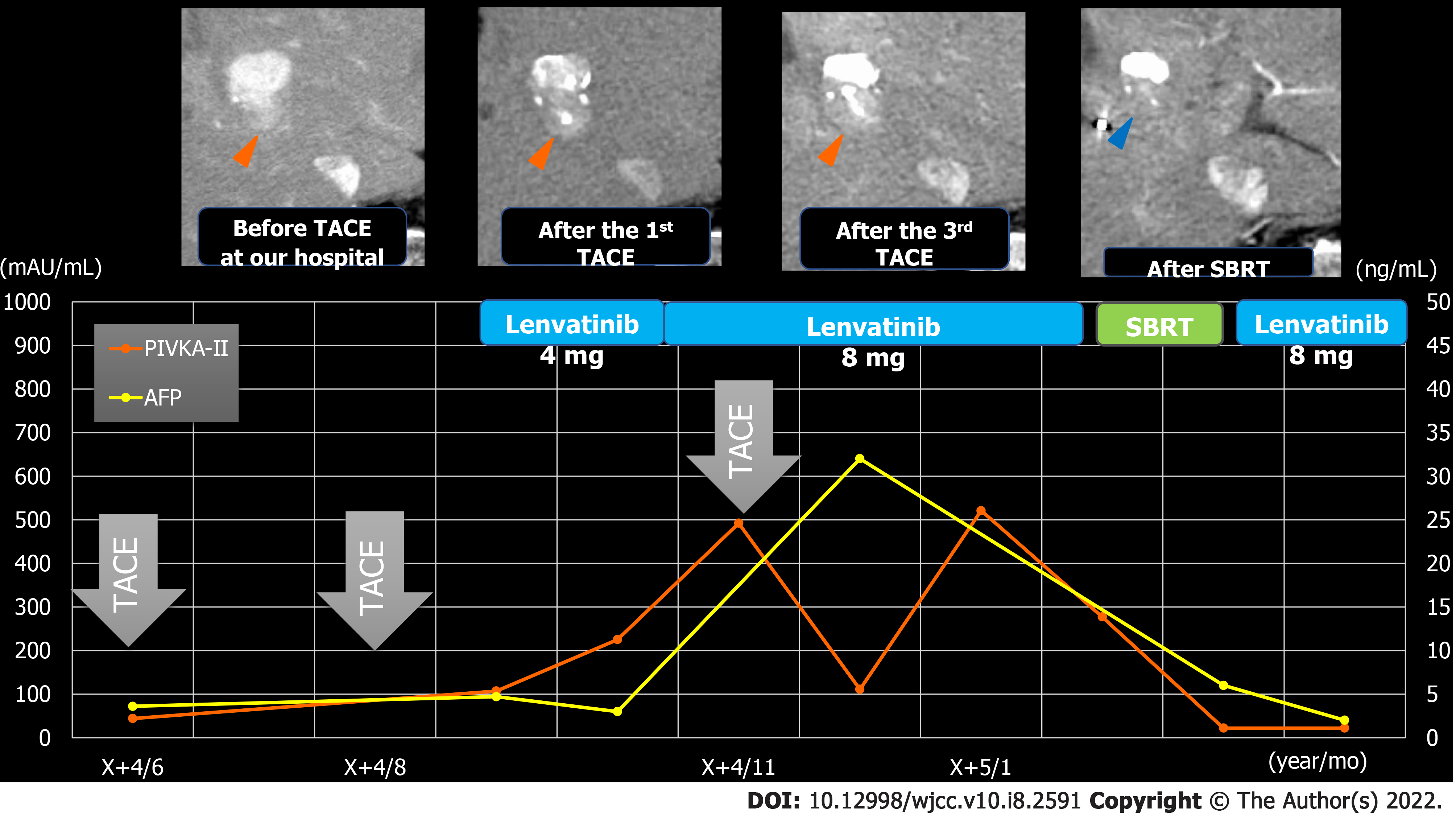
Figure 6 Clinical course in case 1.
Orange arrows: Viable lesion; blue arrows: Disappearance of the contrast effect of the tumor after stereotactic body radiation. AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; PIVKA-Ⅱ: Protein induced by vitamin K antagonists-Ⅱ; SBRT: Stereotactic body radiation; TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Figure 7 Computed tomography before and after stereotactic body radiation.
A: Computed tomography (CT) before stereotactic body radiation (SBRT); B: CT after SBRT. Yellow arrowhead: Viable lesion after the third transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; blue arrowhead: Disappearance of the contrast effect of the tumor after SBRT.
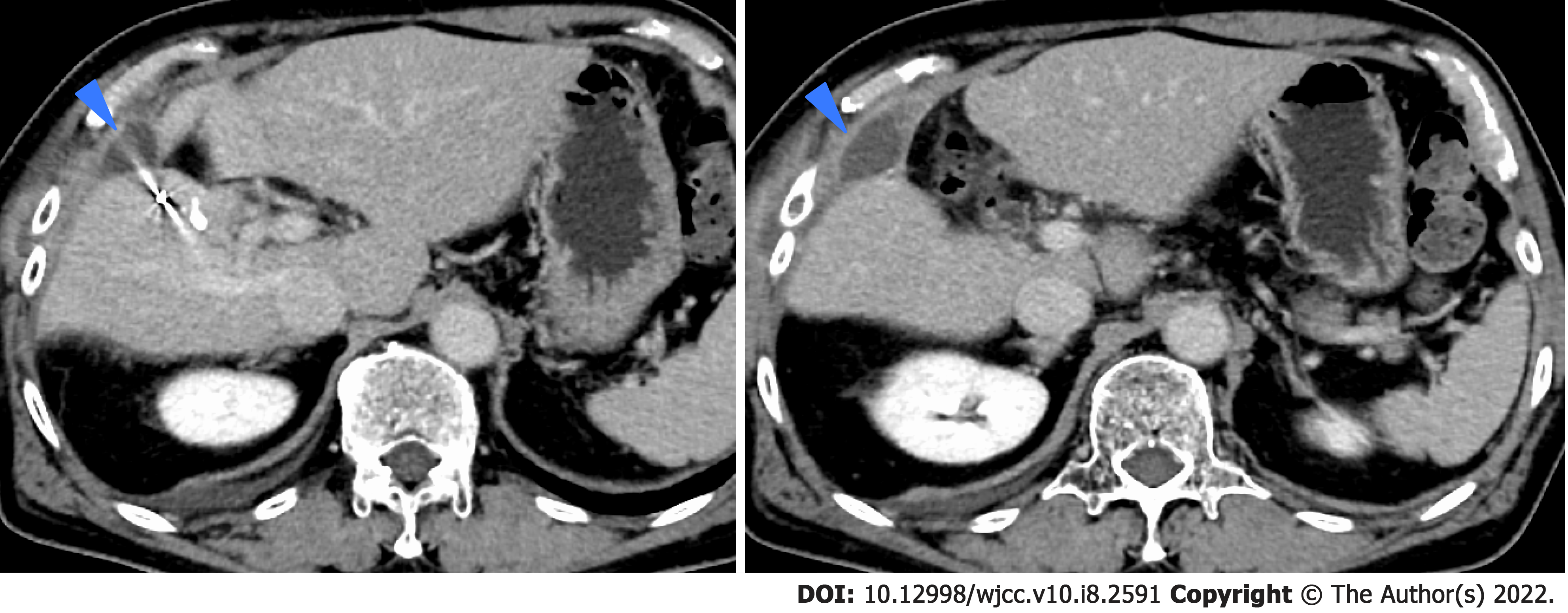
Figure 8 Computed tomography of infected biloma.
Blue arrows: Infected biloma.
Figure 9 Clinical course in case 2.
Red arrows: Viable lesion; blue arrows: Disappearance of the contrast effect of the tumor after stereotactic body radiation. AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; PIVKA-Ⅱ: Protein induced by vitamin K antagonists-Ⅱ; SBRT: Stereotactic body radiation; TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
- Citation: Masuda S, Tsukiyama T, Minagawa Y, Koizumi K, Kako M, Kinbara T, Haruki U. Hepatocellular carcinoma effective stereotactic body radiotherapy using Gold Anchor and the Synchrony system: Two case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(8): 2591-2603
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i8/2591.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2591