Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2022; 10(6): 1981-1990
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1981
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1981
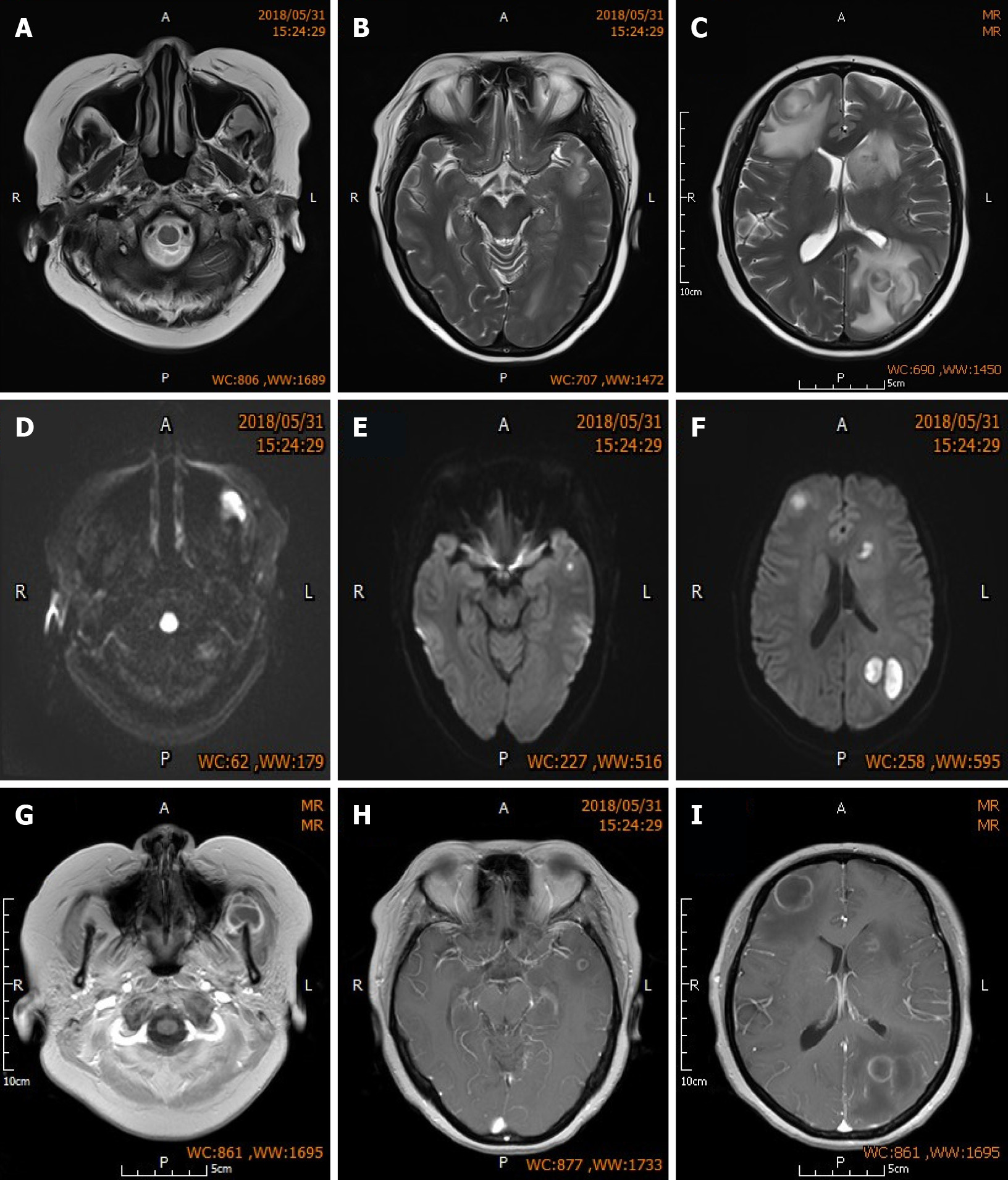
Figure 1 Brain magnetic resonance imaging of the patient.
A-C: Sequential MR-T2WI of both frontal lobes, left parietal lobe, and left masseteric space. Images show multiple nodular lesions with significant perilesional edema; D-F: Sequential MR-DWI show high level of lesion signal change; G-I: Sequential enhanced MR-T1WI showing low lesion signals that are slightly higher than the cerebrospinal fluid signal, and uniform, intact and round annular enhancement around the lesions.
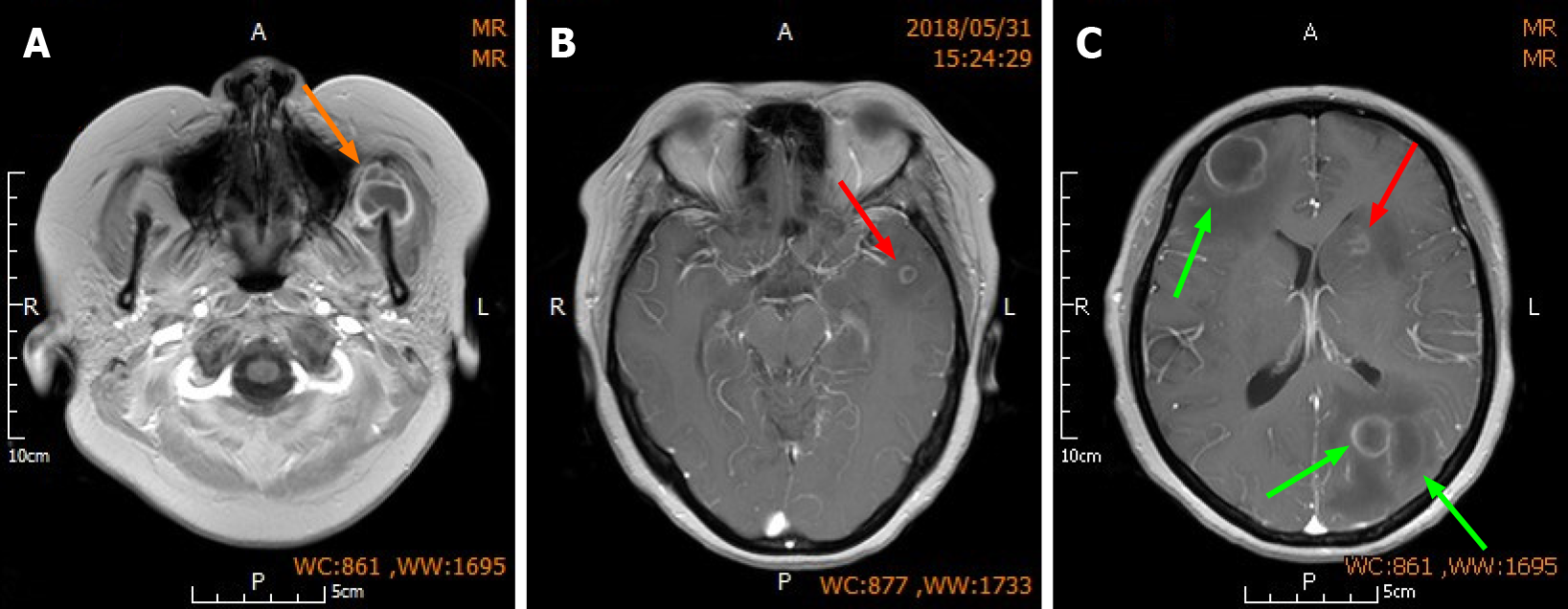
Figure 2 Surgical strategy.
A: Orange arrow indicates the left maxillofacial lesion on which puncture aspiration was performed; B and C: Red arrow indicates the smaller non-resected lesions located in the deeper parts of the left frontal and temporal lobes; Green arrows indicate the larger lesions with greater perilesional edema in the right frontal lobe and left parietal lobe which were resected.
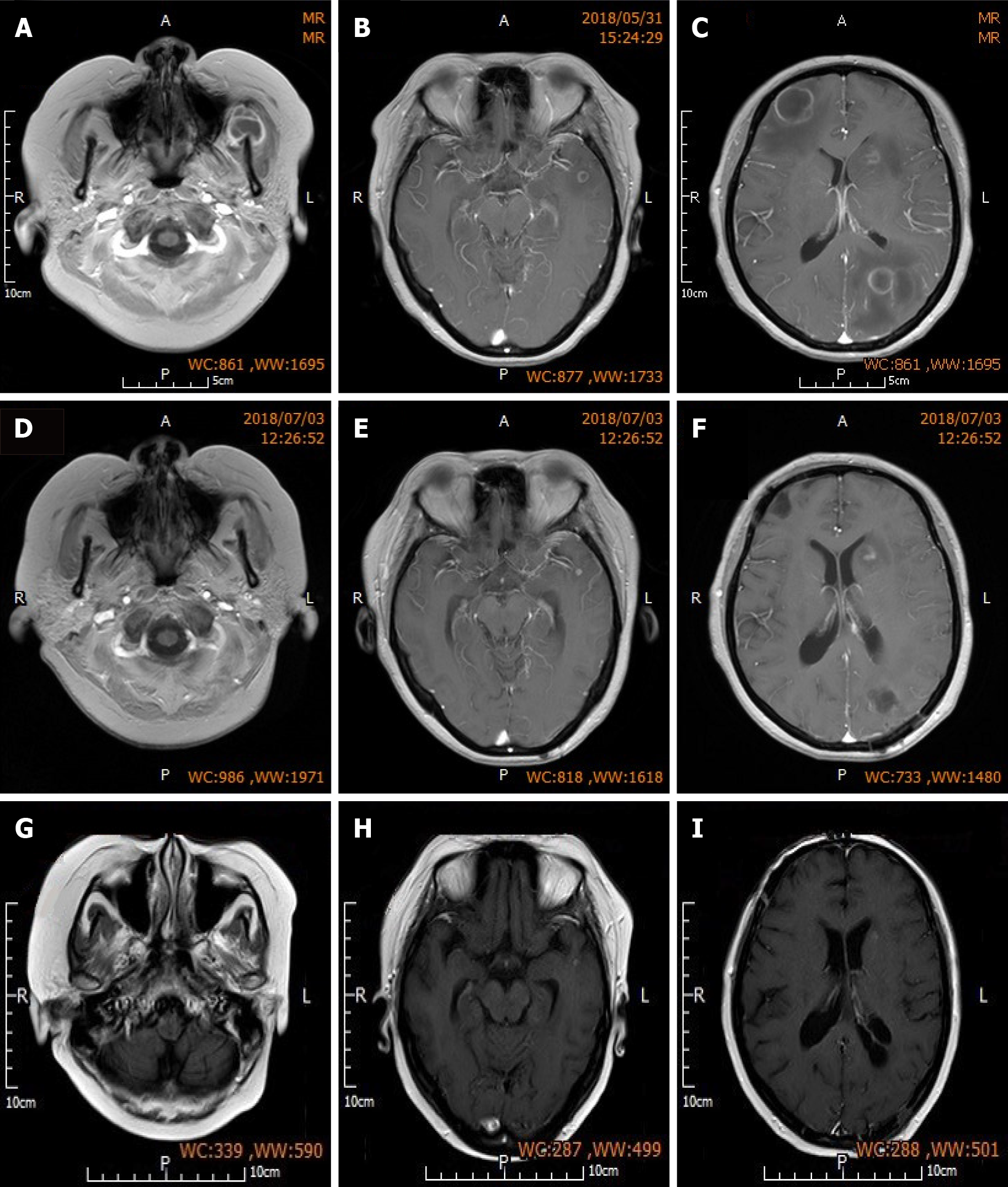
Figure 3 Preoperative and postoperative brain magnetic resonance imaging.
A-C: Sequential preoperative enhanced MR-T1WI showing low lesion signals that are slightly higher than cerebrospinal fluid signal, and uniform, intact and round annular enhancement around the lesions. There are also low perilesional edema signals that are slightly higher than the cerebrospinal fluid signal; D-F: Sequential MR-T1WI at 1 mo post-surgery showing absence of the resected lesions in the right frontal lobe and left parietal lobe, and formation of soft lesions. Lesion in the left maxillofacial region on which puncture aspiration was performed was also absent. Non-resected lesions in the left frontal and temporal lobes were reduced in size, and low edema signals can be observed around the lesions in the left temporal lobe; G-I: Sequential MR-T1WI at three months post-surgery showing further reduction in the size of non-resected lesions in the left frontal and temporal lobes compared with those at 1 mo post-surgery. Edema was absorbed and dissipated.
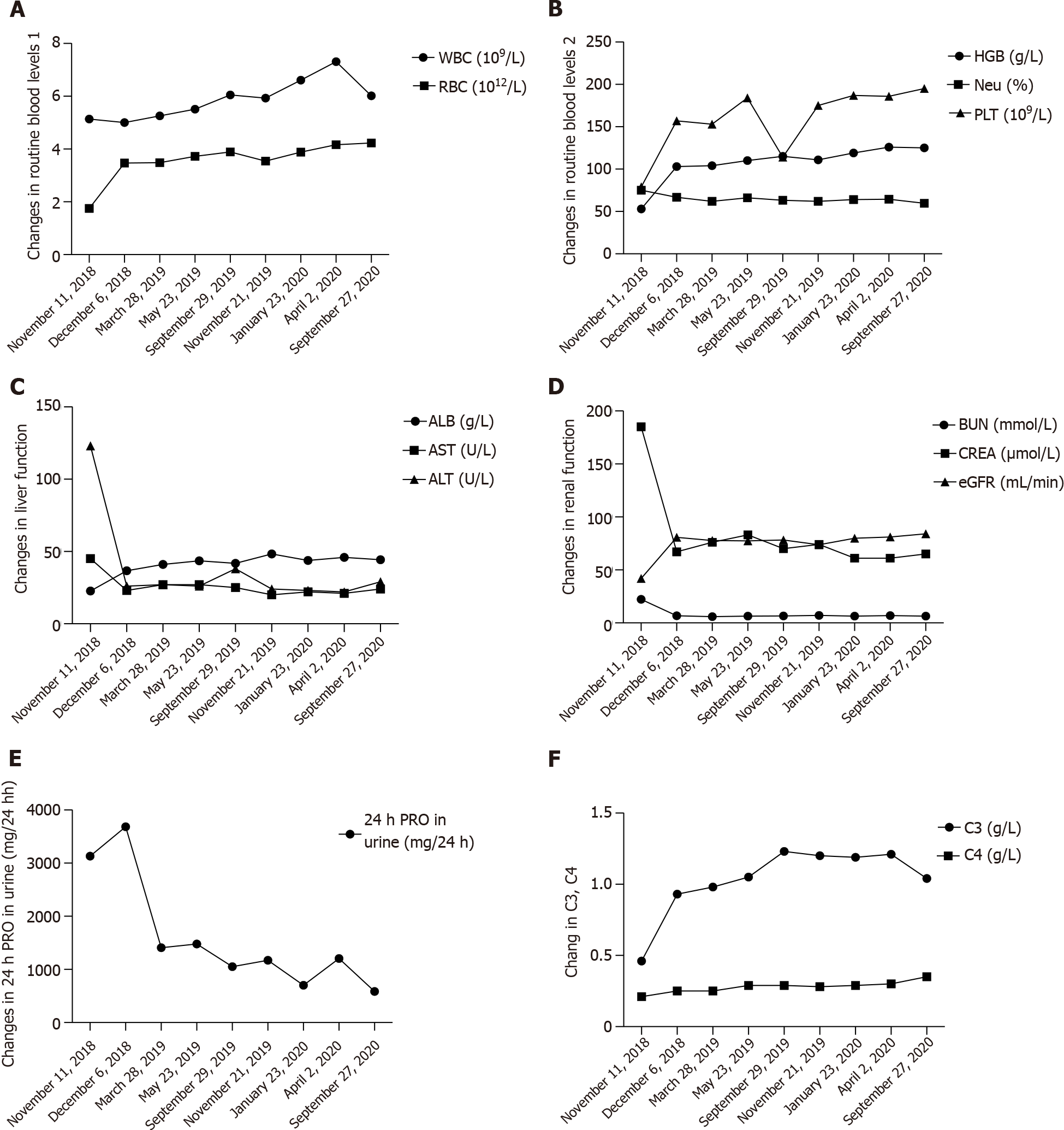
Figure 4 Systemic lupus erythematosus related indicators were followed up for 2 years after discharge.
A: Changes in routine blood levels 1; B: Changes in routine blood levels 2; C: Changes in liver function; D and E: Changes in renal function; F: Changes in C3, C4.
- Citation: Hu QD, Liao LS, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Liu J. Surgery and antibiotics for the treatment of lupus nephritis with cerebral abscesses: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(6): 1981-1990
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i6/1981.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1981