Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 16, 2022; 10(32): 11921-11928
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11921
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11921
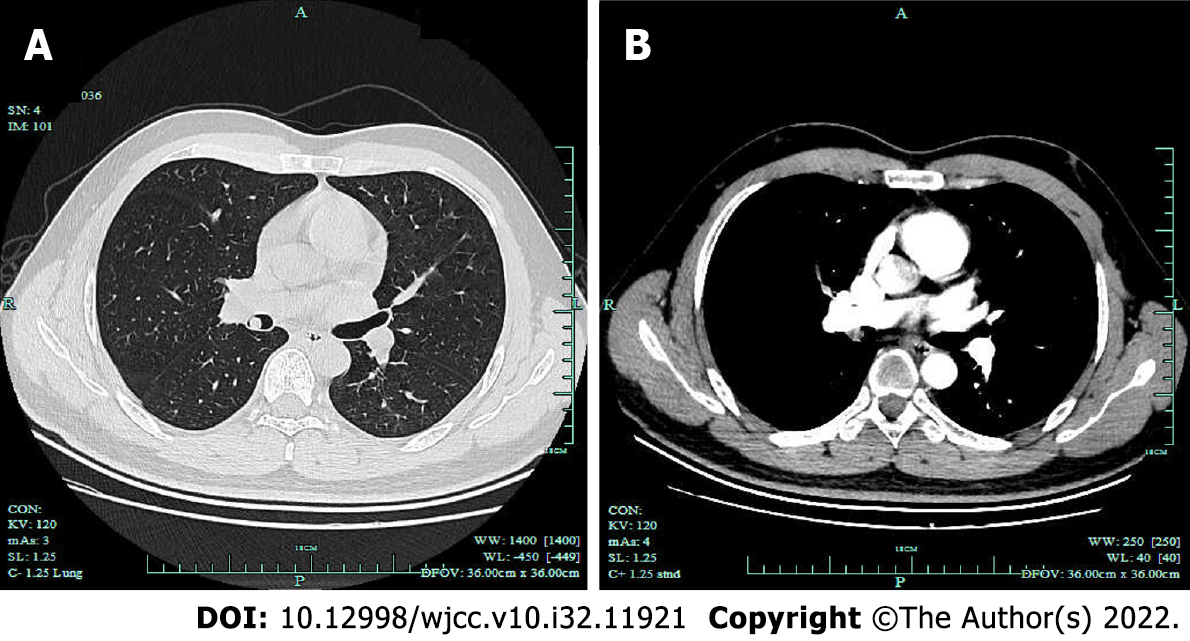
Figure 1 Chest computed tomography showed an intraluminal nodule.
Chest computed tomography showed a 9-mm intraluminal nodule in the bronchus intermedius with homogeneous density, well-defined margin and moderate enhancement. A: Lung window; B: Mediastinal window.
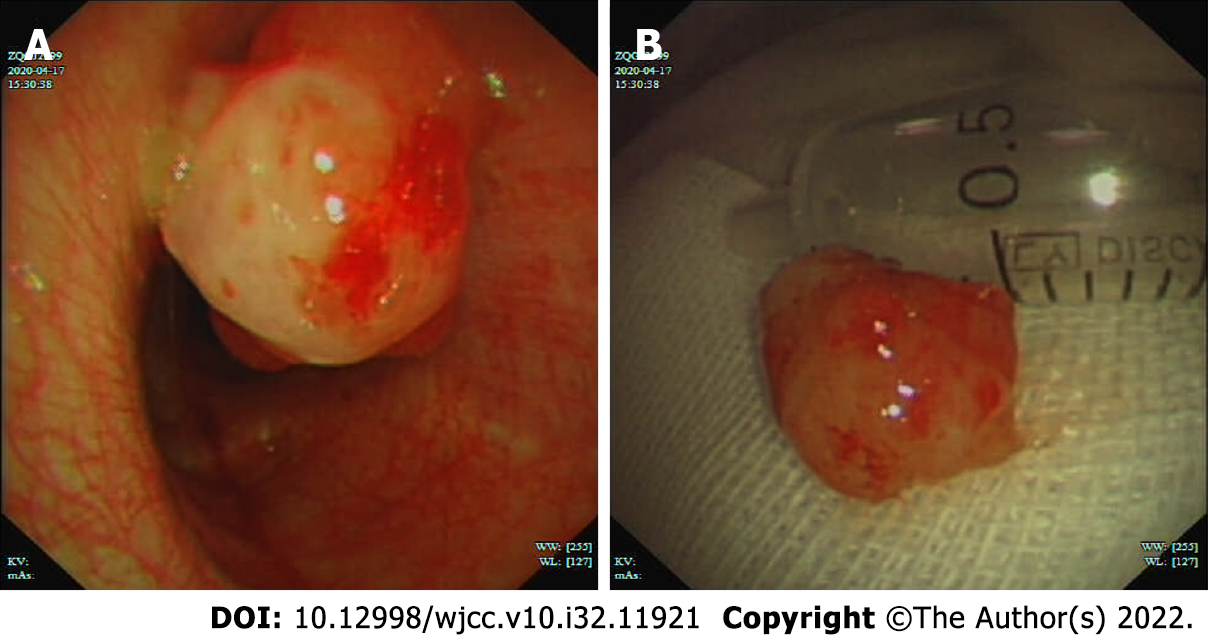
Figure 2 Interventional bronchoscopic therapy for the bronchial Mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
A: Bronchoscopy revealed an endobronchial pedunculated confined to the bronchus intermedius; B: Interventional bronchoscopy was performed, and the mass was removed successfully.
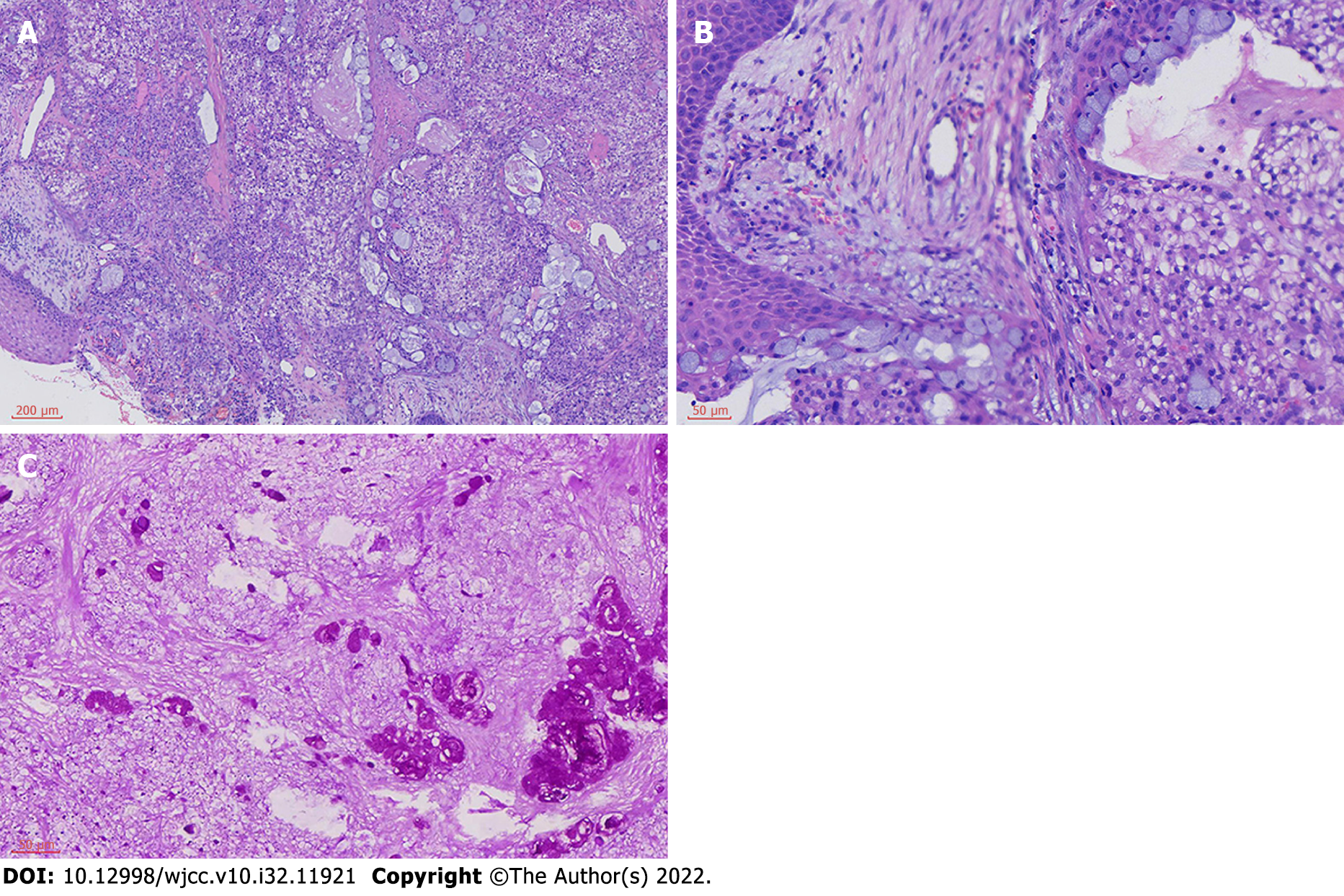
Figure 3 Histopathological analysis indicated characteristics of mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
The tumor is comprised of glands, tubules and cysts containing mucin separated by a fibrous stroma (Hematoxylin and eosin staining; A: ×100; B: ×400). Periodic acid schiff staining showed moderate mucin expression in the tumor mass. (C: ×400).
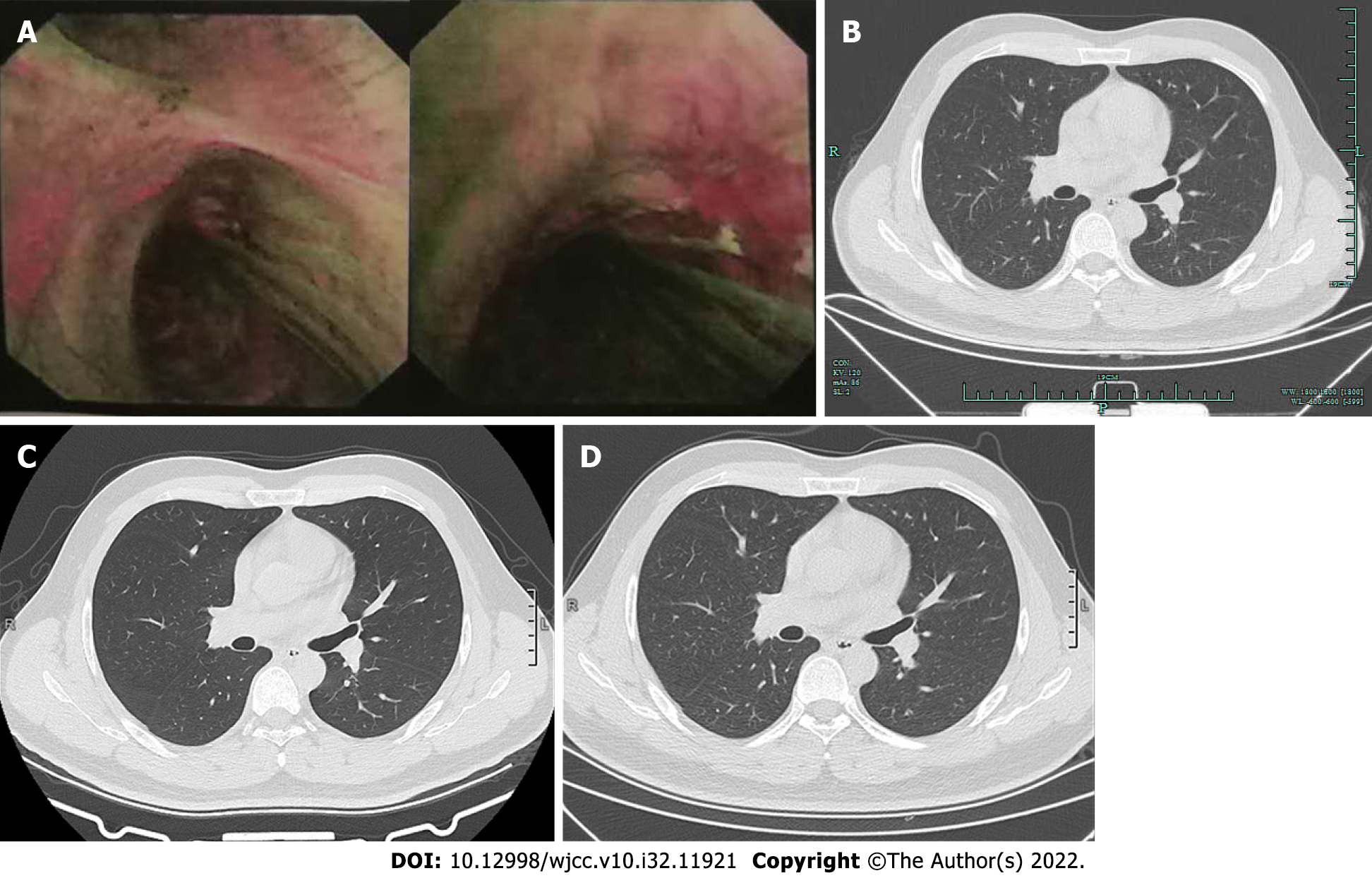
Figure 4 Fluorescence bronchoscopy and computed tomography during follow-up showed no relapse.
A: After 3 mo, the fluorescence bronchoscopy showed normal mucosa; B: After 6 mo, chest computed tomography (CT) showed normal airways with no obstruction; C: After 19 mo, chest CT showed normal airways; D: After 2 years, chest CT showed normal airways.
- Citation: Ding YM, Wang Q. Endoscopic resection of bronchial mucoepidermoid carcinoma in a young adult man: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(32): 11921-11928
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i32/11921.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11921