Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2022; 10(30): 11116-11121
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11116
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11116
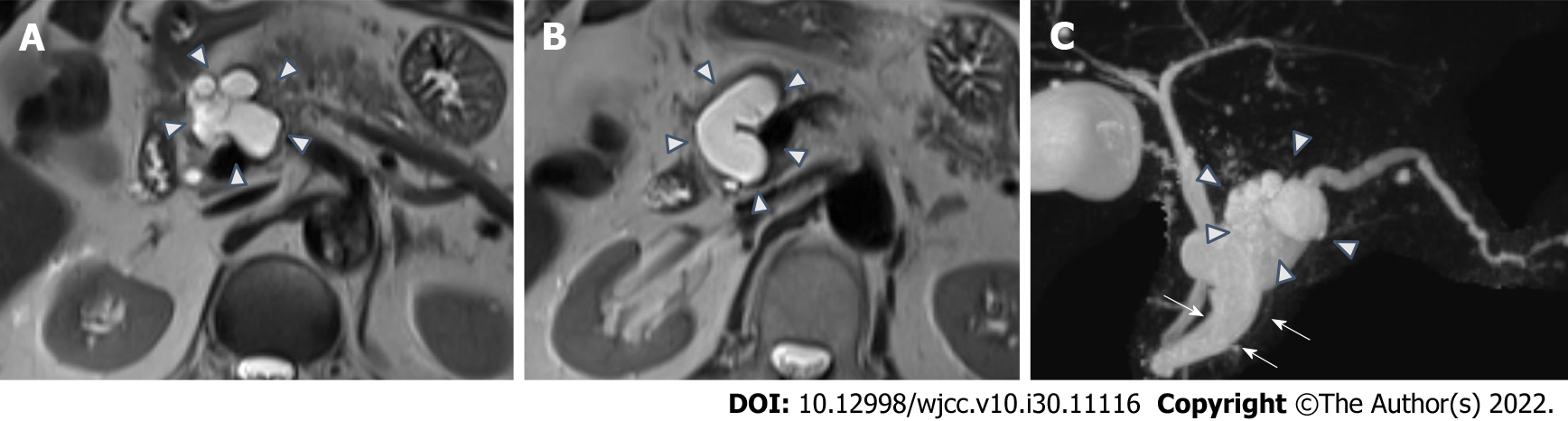
Figure 1 Pancreas magnetic resonance imaging scan at referral 5 years ago.
A: Axial T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) image shows a multilobular tumor in the head of pancreas (arrow head); B: T2WI image shows pancreatic duct dilatation (arrow head); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows a multilobular tumor (arrow head) and pancreatic duct dilatation (arrow).
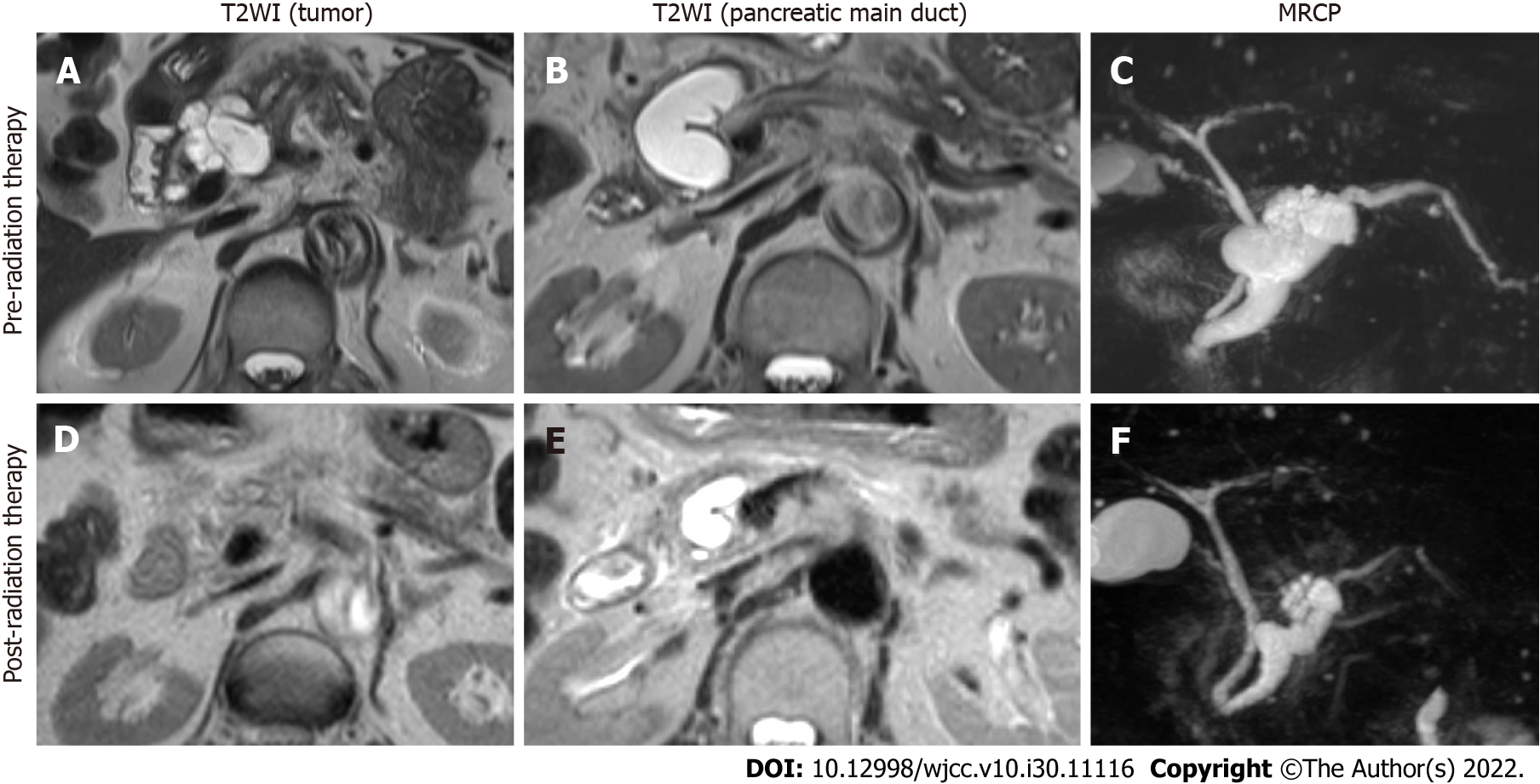
Figure 2 Pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging scans of pre- and post-radiation therapy.
A-C: T2-weighted imaging single scans and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) taken one month before radiation therapy; D-F: Magnetic resonance imaging scans and MRCP taken three months after radiation therapy. T2WI: T2-weighted imaging; MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
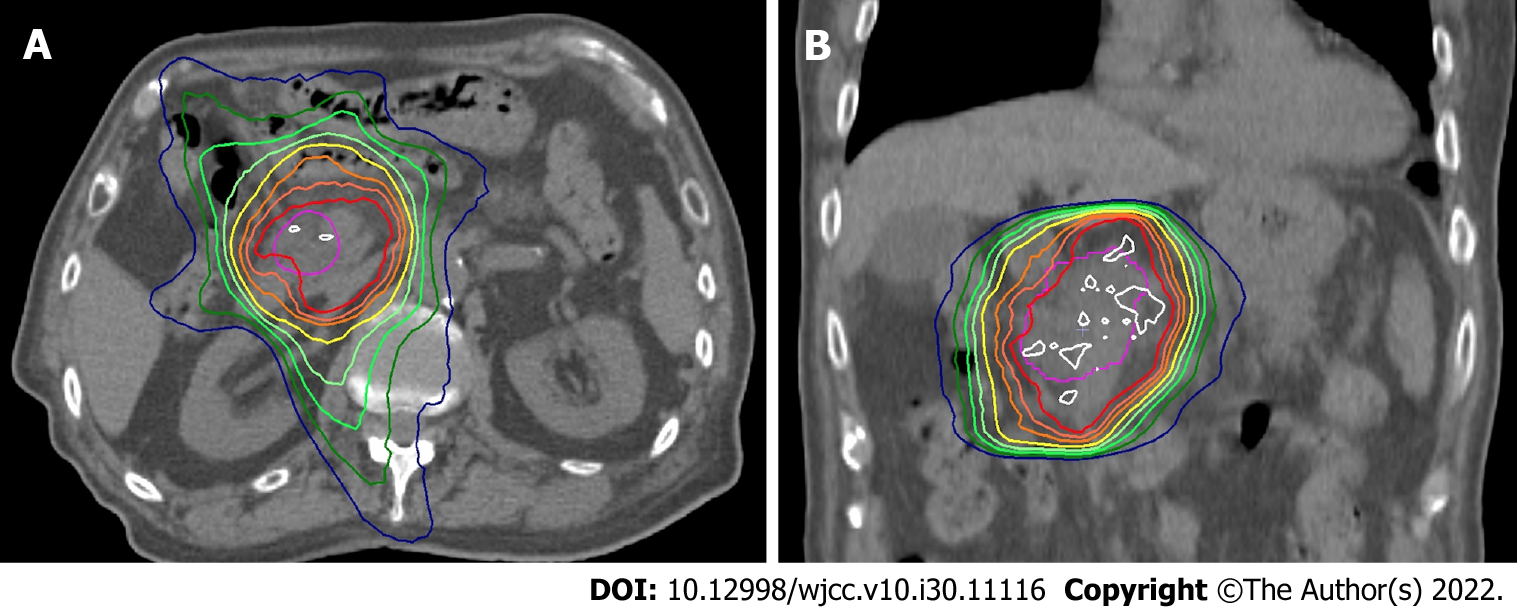
Figure 3 Computed tomography image with dose distribution of radiation therapy.
A: An axial image; B: A coronal image. White, red, inner-orange, outer-orange and yellow lines show 52.5 Gy, 50 Gy, 47.5 Gy, 45 Gy and 42.5 Gy, respectively.
- Citation: Harigai A, Kume K, Takahashi N, Omata S, Umezawa R, Jingu K, Masamune A. Favorable response after radiation therapy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms manifesting as acute recurrent pancreatitis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(30): 11116-11121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i30/11116.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11116