Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2022; 10(30): 11004-11009
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11004
Published online Oct 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11004
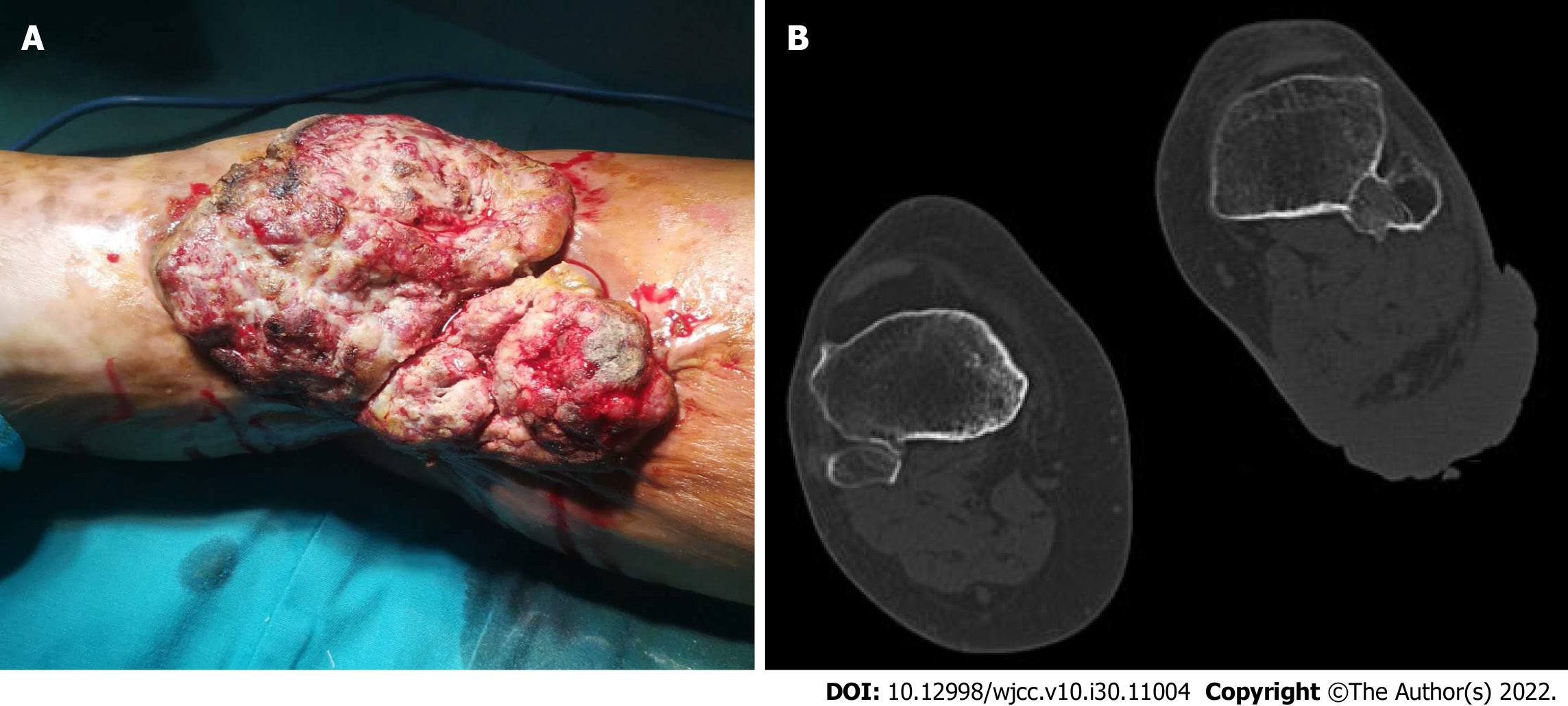
Figure 1 Before the surgery.
A: A huge erythematous nodular ulcerative skin tumor, measuring approximately 15 cm × 20 cm, was located on the left popliteal fossa; B: Computed tomography scan of the popliteal fossa.
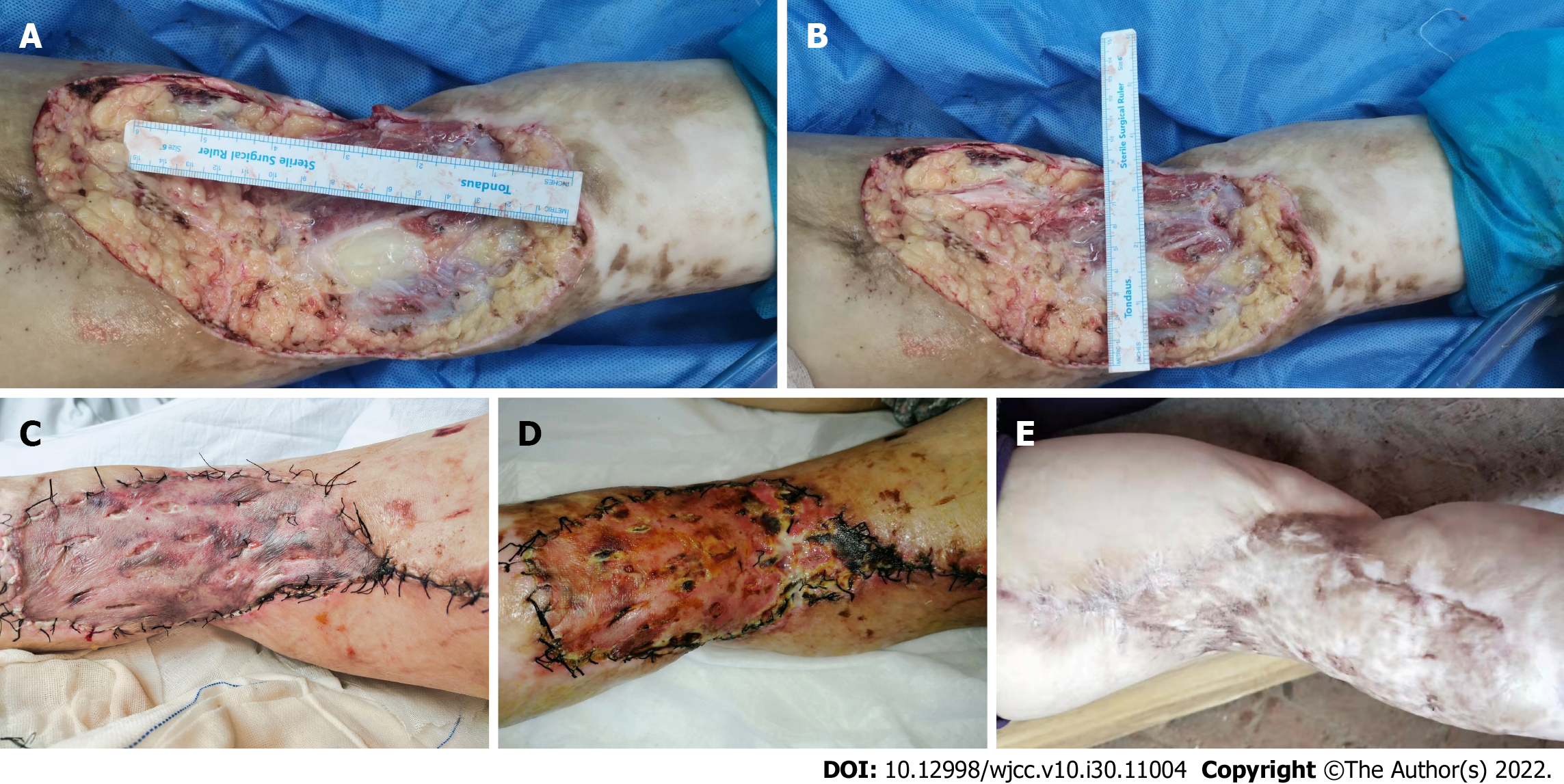
Figure 2 After extirpating the tumor, the final surgical defect on the left popliteal fossa measured 25 cm × 15 cm.
A: The surgical defect in the left popliteal fossa was 25 cm long; B: The surgical defect in the left popliteal fossa was 15 cm wide; C: As seen on day 4 after reconstruction, the surgical defect on the left popliteal fossa was repaired by full-thickness skin grafting; D: Appearance of the full-thickness skin repair of the left popliteal fossa on day 15 after reconstruction; E: Appearance of the full-thickness skin repair of the left popliteal fossa at the 1-year follow-up.
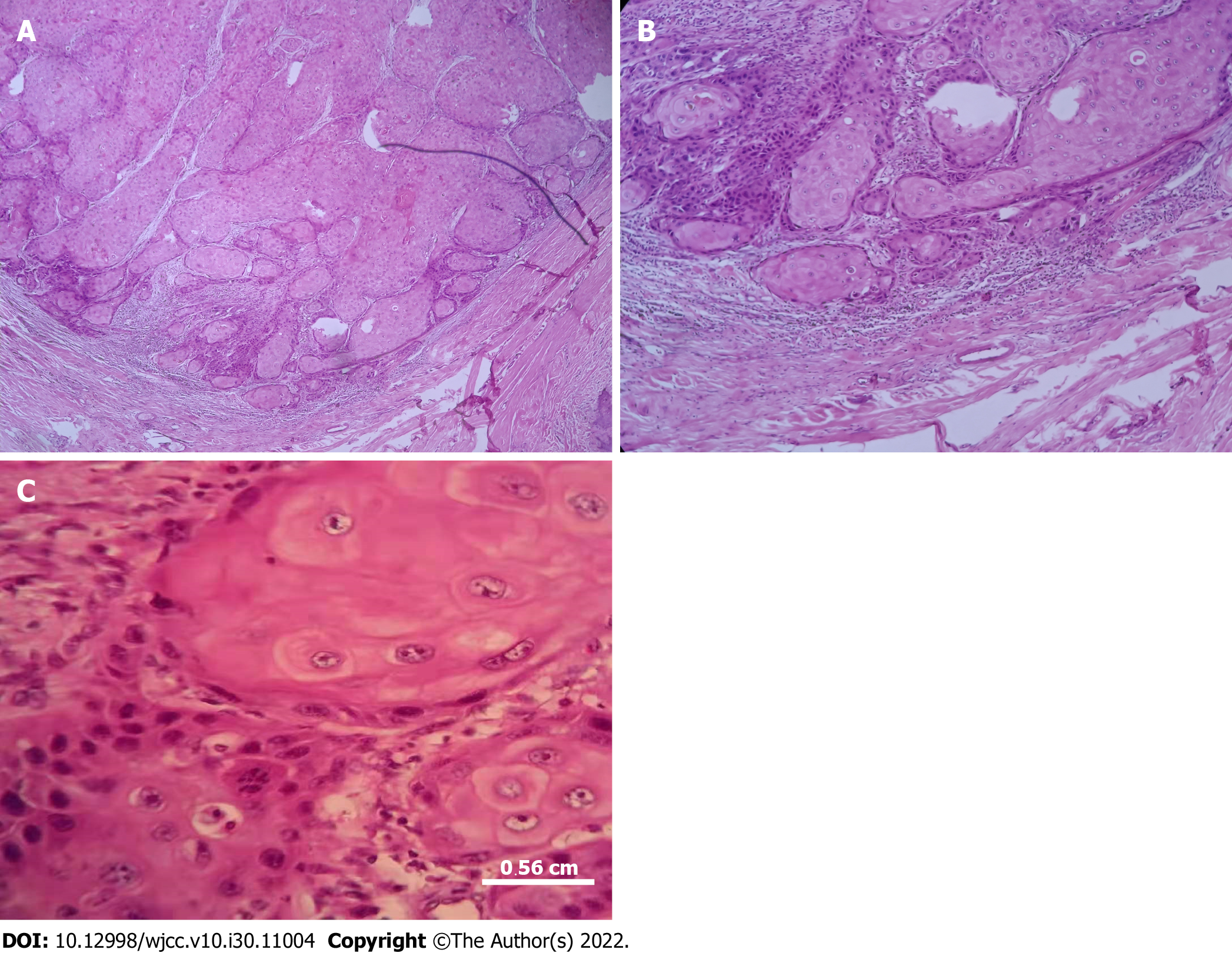
Figure 3 Photomicrographs of the tumor.
A: Scattered squamous cells with dyskeratosis and mitotic infiltrates (H&E staining, 40 × magnification); B: Numerous squamous cells with dyskeratosis and mitotic infiltrates (H&E staining, 100 × magnification); C: Squamous cells in the periphery of the tumor (H&E staining, 400 × magnification).
- Citation: Wang K, Li Z, Chao SW, Wu XW. Giant cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the popliteal fossa skin: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(30): 11004-11009
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i30/11004.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.11004