Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2022; 10(27): 9904-9910
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9904
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9904
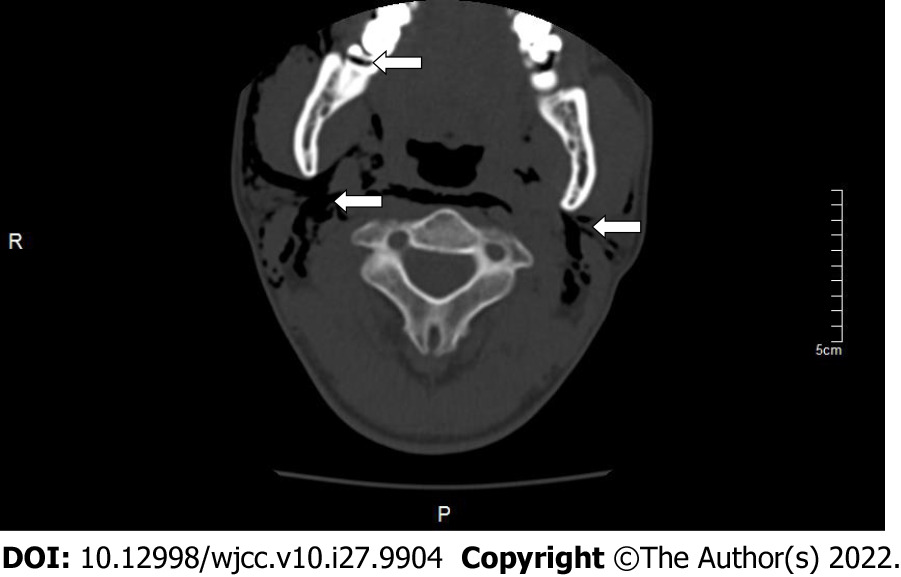
Figure 1 Computed tomography scan showing the right mandibular third molar level of impact, fusion root, buccal and lingual to the crown, and range of emphysema in patient 1 when the emphysema occurred.
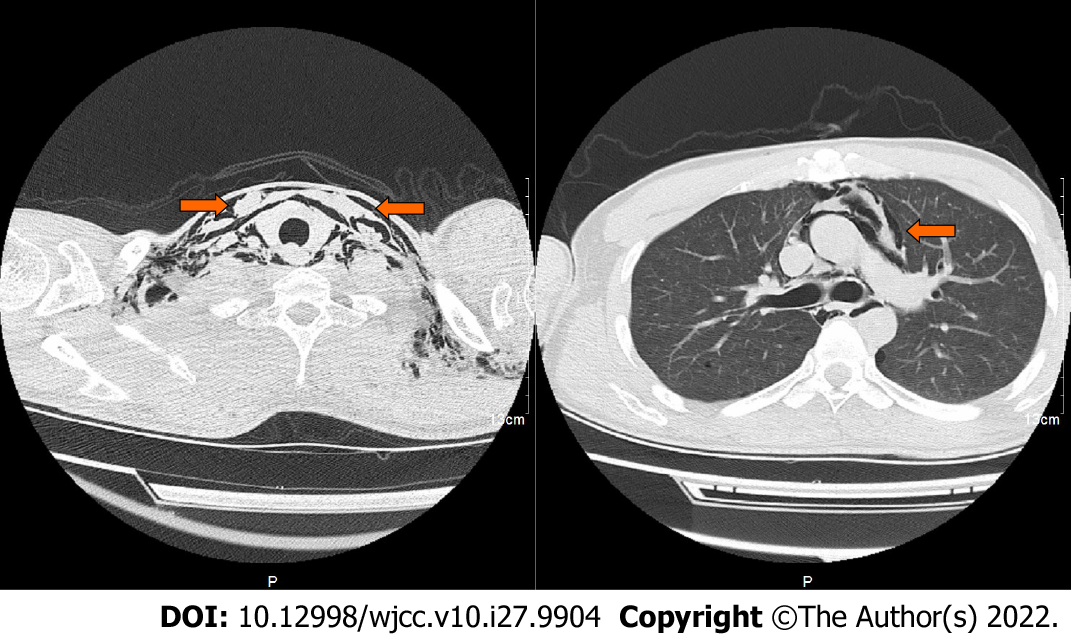
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan showed a large amount of gas in the neck, chest wall, and mediastinum in patient 1 when emphysema occurred.
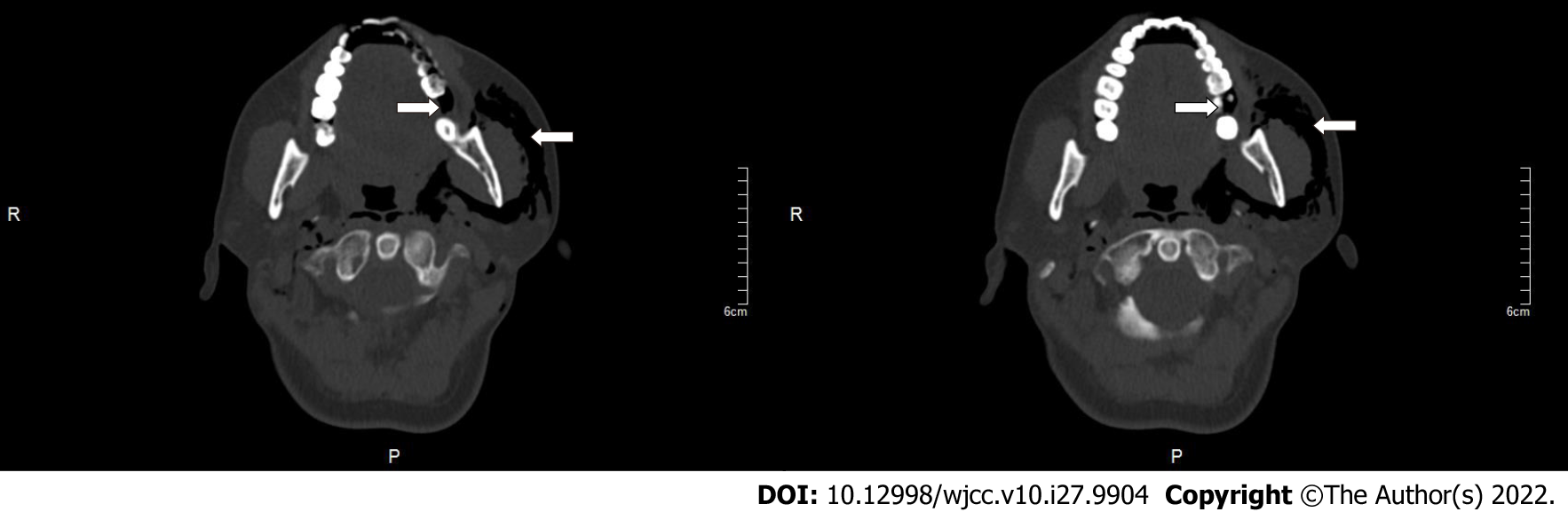
Figure 3 Computed tomography scan showed the left mandibular third molar removal and range of emphysema in patient 2 when emphysema occurred.
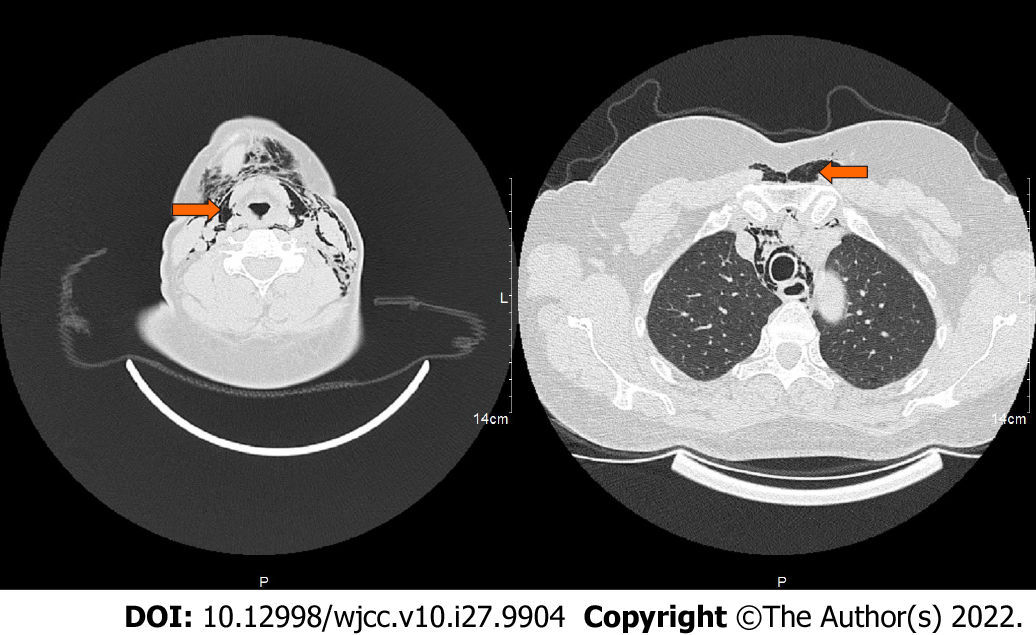
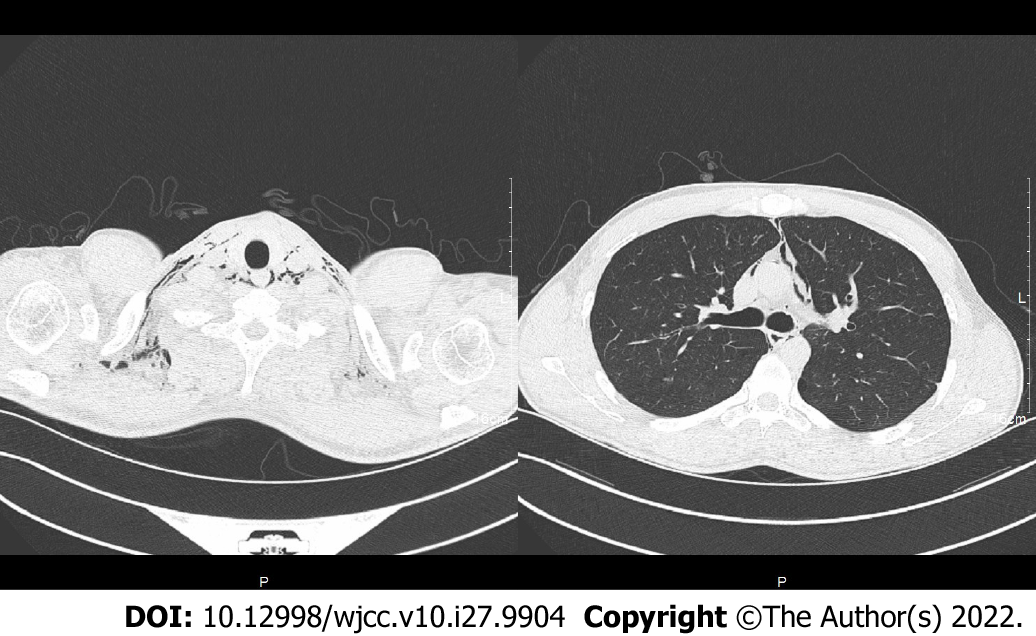
Figure 4 Computed tomography scan showed the neck root, chest wall, and mediastinal gas in patient 2 when emphysema occurred.
Figure 5 Computed tomography scan showed absorption of gas in the neck, chest wall, and mediastinum after 5 d of treatment in patient 1.
- Citation: Ye LY, Wang LF, Gao JX. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema secondary to dental extraction: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(27): 9904-9910
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i27/9904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9904