Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2022; 10(26): 9510-9517
Published online Sep 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9510
Published online Sep 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9510
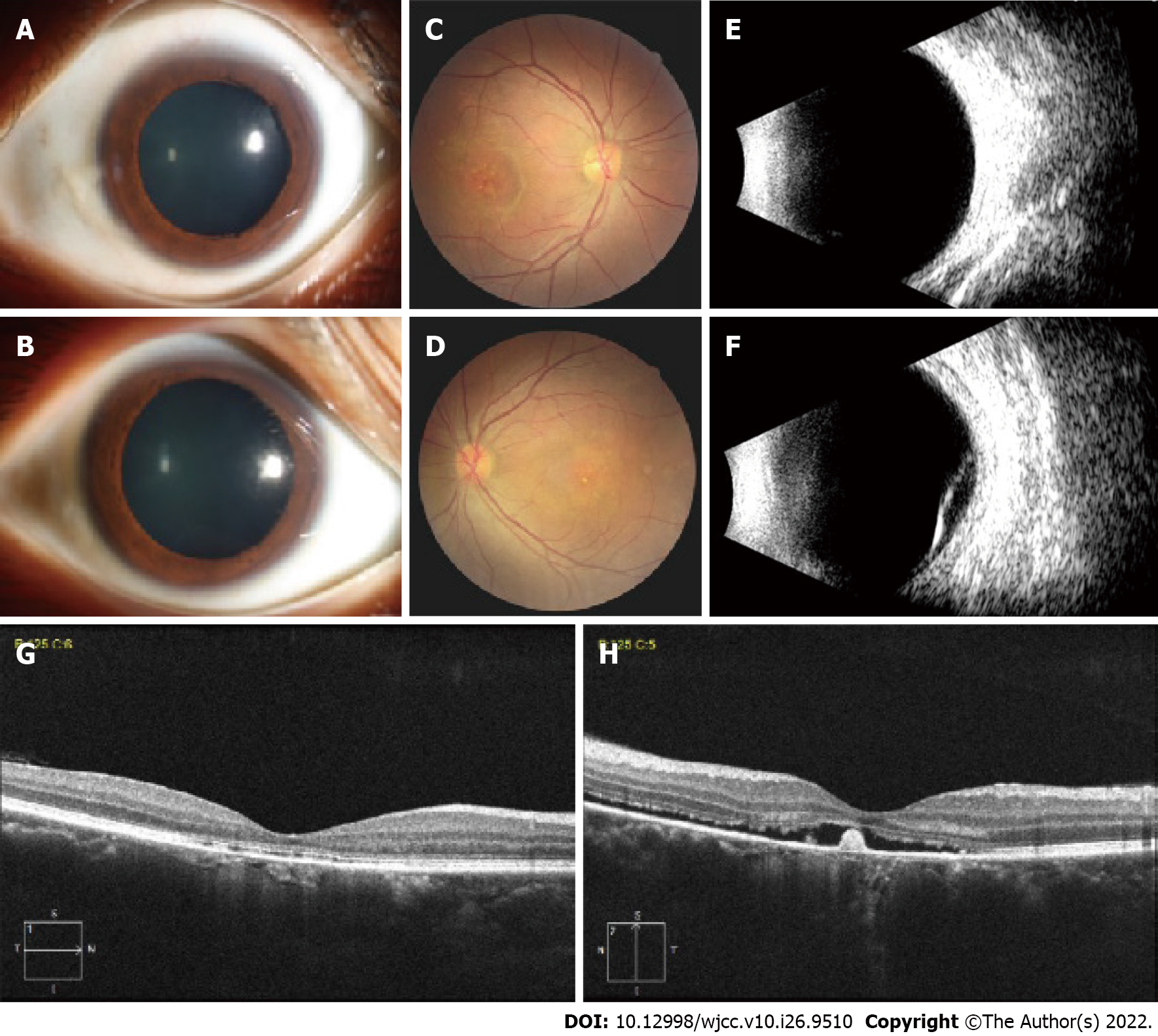
Figure 1 Anterior segment and fundus photograph, ophthalmic B-scan ultrasonography, and optical coherence tomography examination of the patient.
A: The anterior segment of the right eye is normal (dilated); B: The anterior segment of the left eye is normal (dilated); C: Fundus photograph shows white-yellow subretinal exudates in the posterior pole of the right eye; D: Fundus photograph of the left eye shows inferior exudative retinal detachment with subretinal exudation (fibrin) inferior to the macula; E: B-scan ultrasonography of the right eye is normal; F: B-scan ultrasonography confirms the bullous retinal detachment in the left eye; G: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) shows a discontinuous band of retinal pigment epithelium in the right eye; H: OCT shows neurosensory detachment at the fovea, with some hyperreflective material suggestive of fibrin in the left eye.
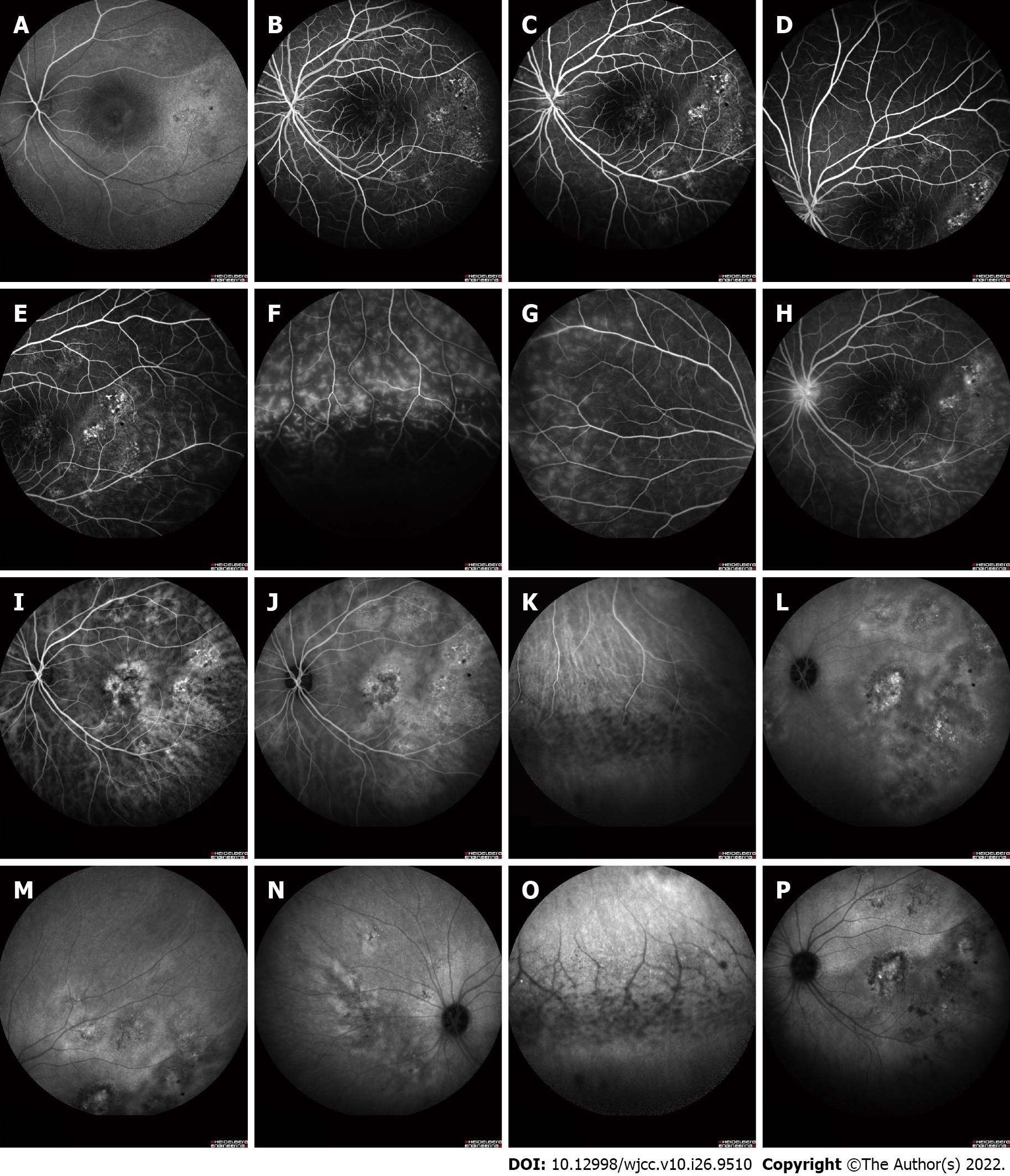
Figure 2 Fundus fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography photograph of the left eye.
A-H: Fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) revealing multifocal and diffuse leakage and hyperpermeable retinal vessels of the left eye; A: Early FFA angiograms; B-E: Middle FFA; F-H: Late FFA; I-P: Indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) revealing hyperpermeable and dilated choroidal vessels and multifocal and diffuse leakage of the left eye; I-J: Early ICGA; K-N: Middle ICGA; O-P: Late ICGA.
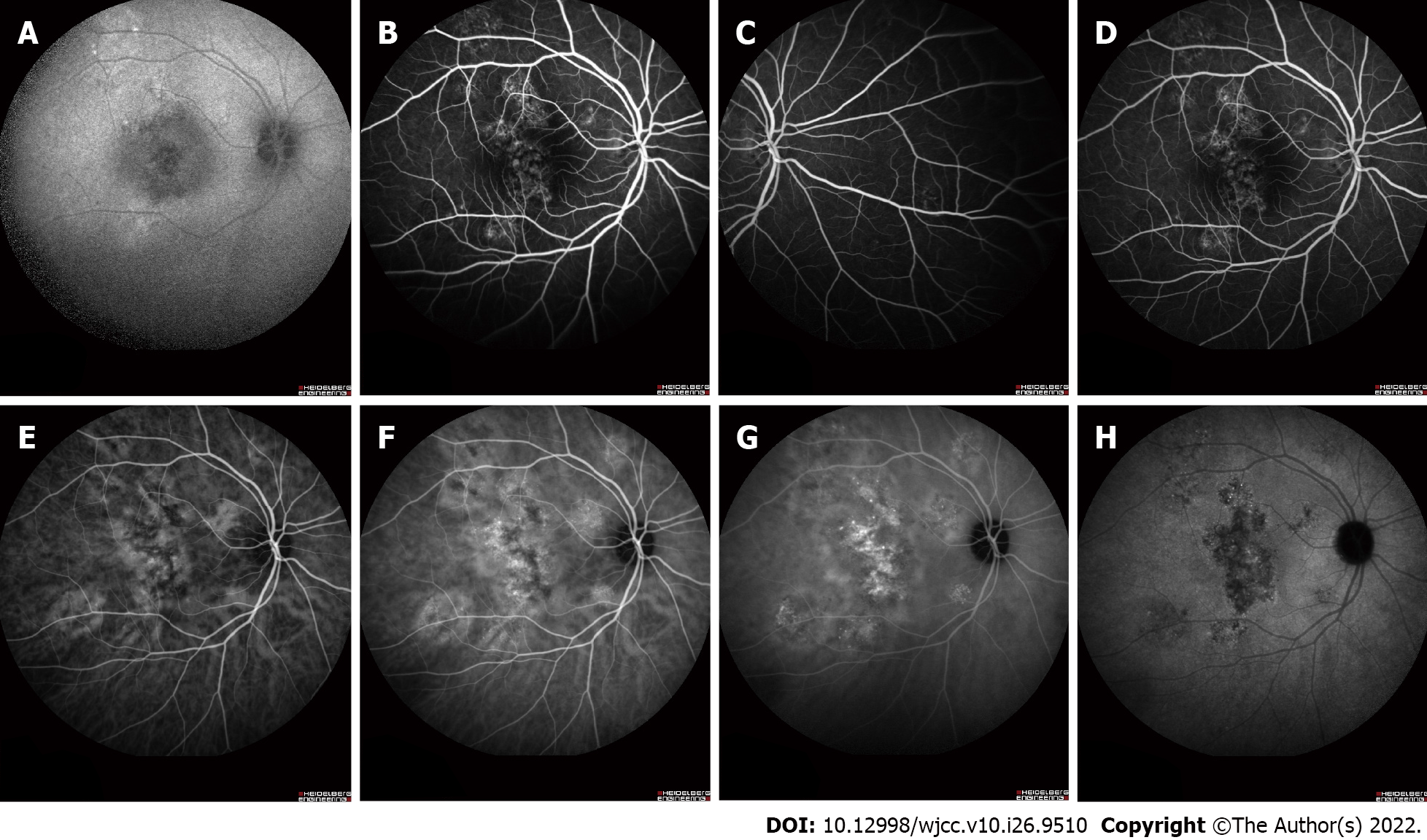
Figure 3 Fundus fluorescein angiography and indocyanine green angiography revealing some areas of transmission hyperfluorescence and dilated choroidal vessels of the right eye.
A: Fundus autofluorescence; B-D: Middle and late fundus fluorescein angiography; E-H: Early and late indocyanine green angiography.
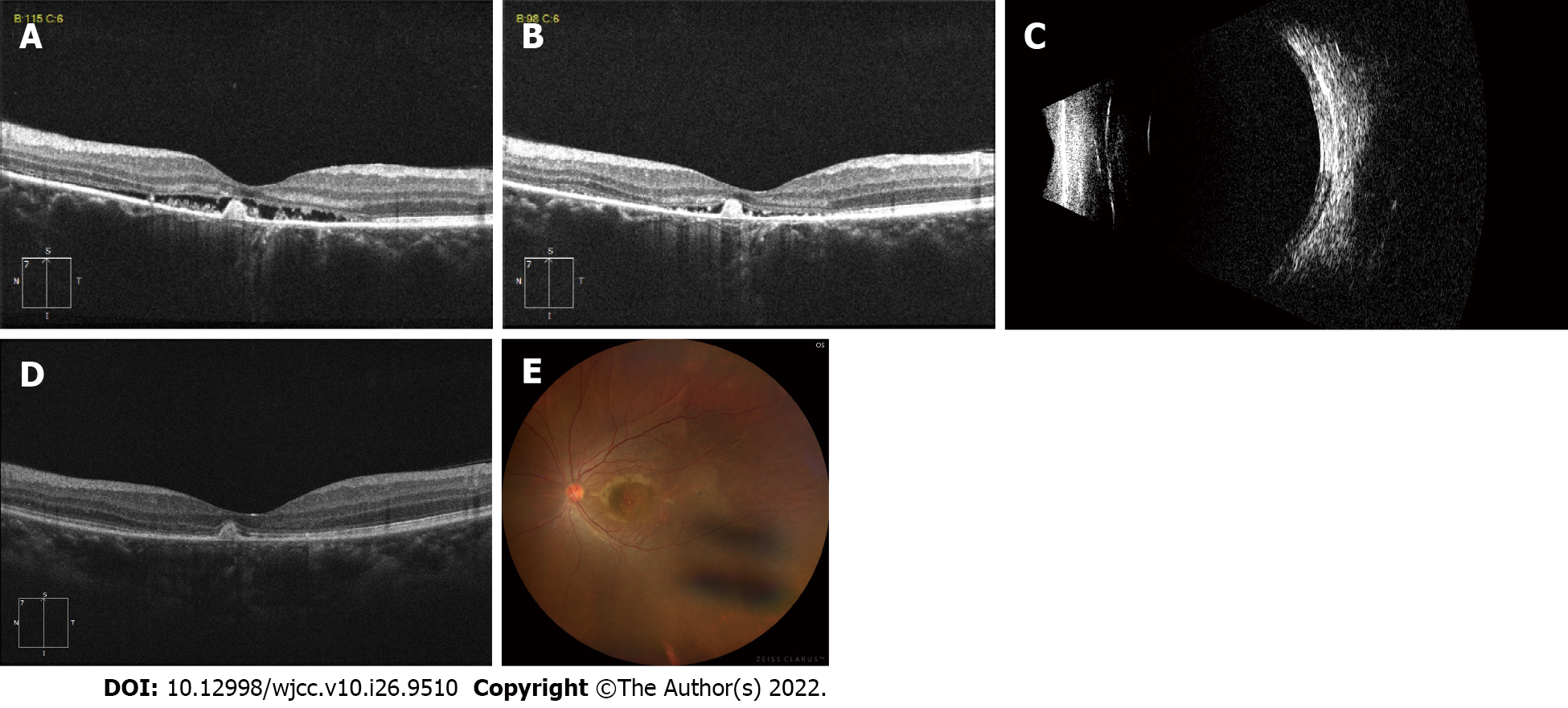
Figure 4 Examination images after the first and second intravitreal injections of conbercept.
A: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showing a decrease in subretinal fluid with persistence of hyperreflective subretinal fibrin 1 mo after the first injection; B: OCT revealing a small amount of subretinal fluid with persistence of hyperreflective subretinal fibrin 1 mo after the second injection; C: B-scan ultrasonography revealing clear resolution of bullous retinal detachment 1 mo after the second injection; D: OCT revealing resolution of subretinal fluid with persistence of the hyperreflective subretinal fibrin 6 mo after the second intravitreal injection of conbercept; E: Fundus photograph of the left eye shows total resolution of the exudative detachment with subretinal exudation (fibrin) at the posterior pole 6 mo after the second intravitreal injection of conbercept.
- Citation: Xiang XL, Cao YH, Jiang TW, Huang ZR. Intravitreous injection of conbercept for bullous retinal detachment: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(26): 9510-9517
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i26/9510.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9510