Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2022; 10(24): 8450-8462
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8450
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8450
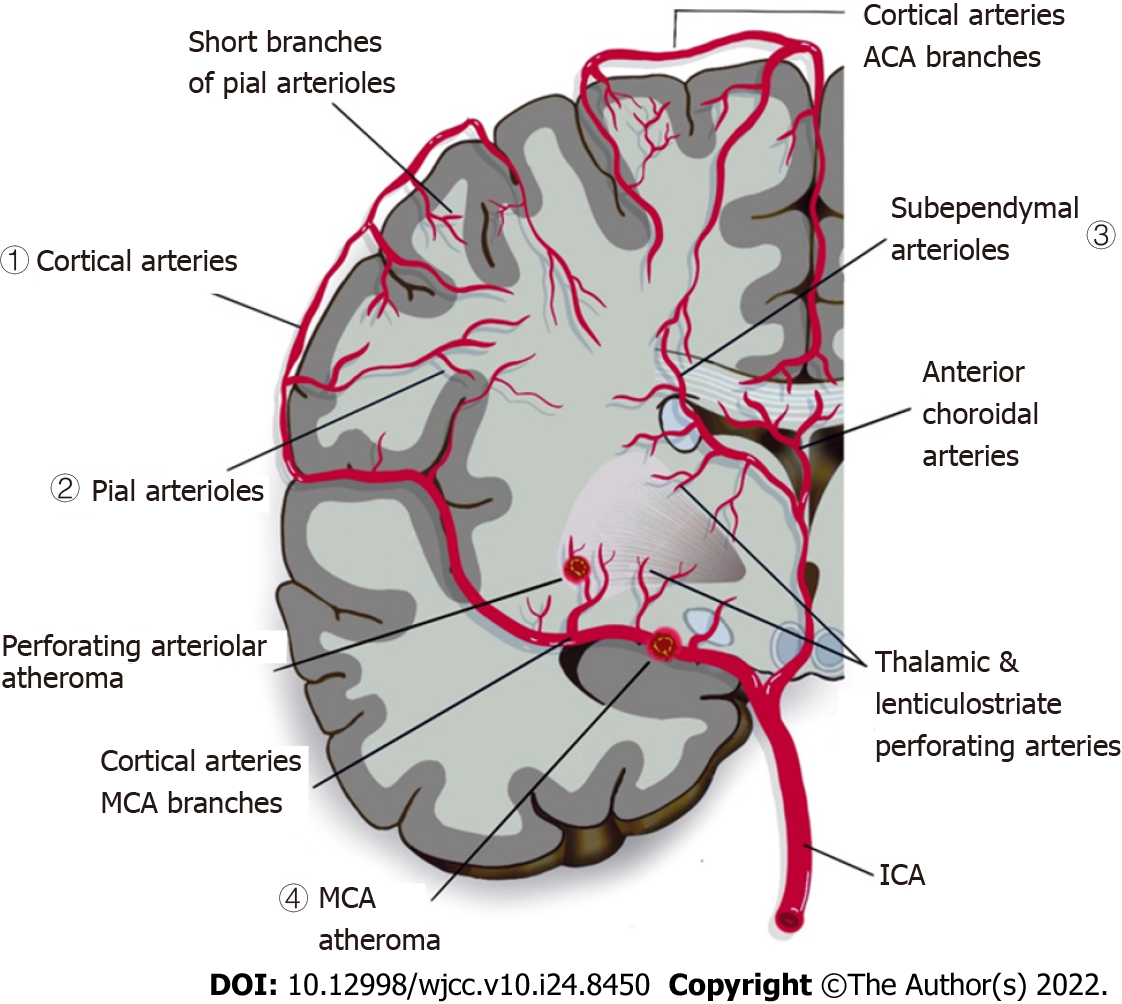
Figure 1 Illustration of cerebral vasculature and general pathophysiology of cerebral small vessel disease.
Different branches of cerebral arteries and their territories supplying the cerebral white matter: (1) cortical arteries, (2) pial arterioles that supply deep white matter, (3) short branches of anterior choroidal arteries that branch into sub-ependymal arteries, arterioles of sub-ependymal, and (4) middle cerebral artery (MCA) that branches into thalamic and lenticulostriate perforating arteries. The picture also shows branches of MCA penetrate the subcortical region of white matter and grey matter. In cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), a thromboembolism in the MCA eventually occludes the lenticulostriate arteries, resulting in a lacunar lesion in basal ganglia. If the atheroma in the parent artery is positioned at the opening of its penetrating branches, it could lead to an acute occlusion of one or several penetrating arteries hence causing a lacunar infarct. A more extensive small vessel disease may lead to a diffused disruption of the blood-brain barrier[3]. ACA: Anterior Cerebral Artery; MCA: Middle Cerebral Artery: ICA: Internal Carotid Artery.
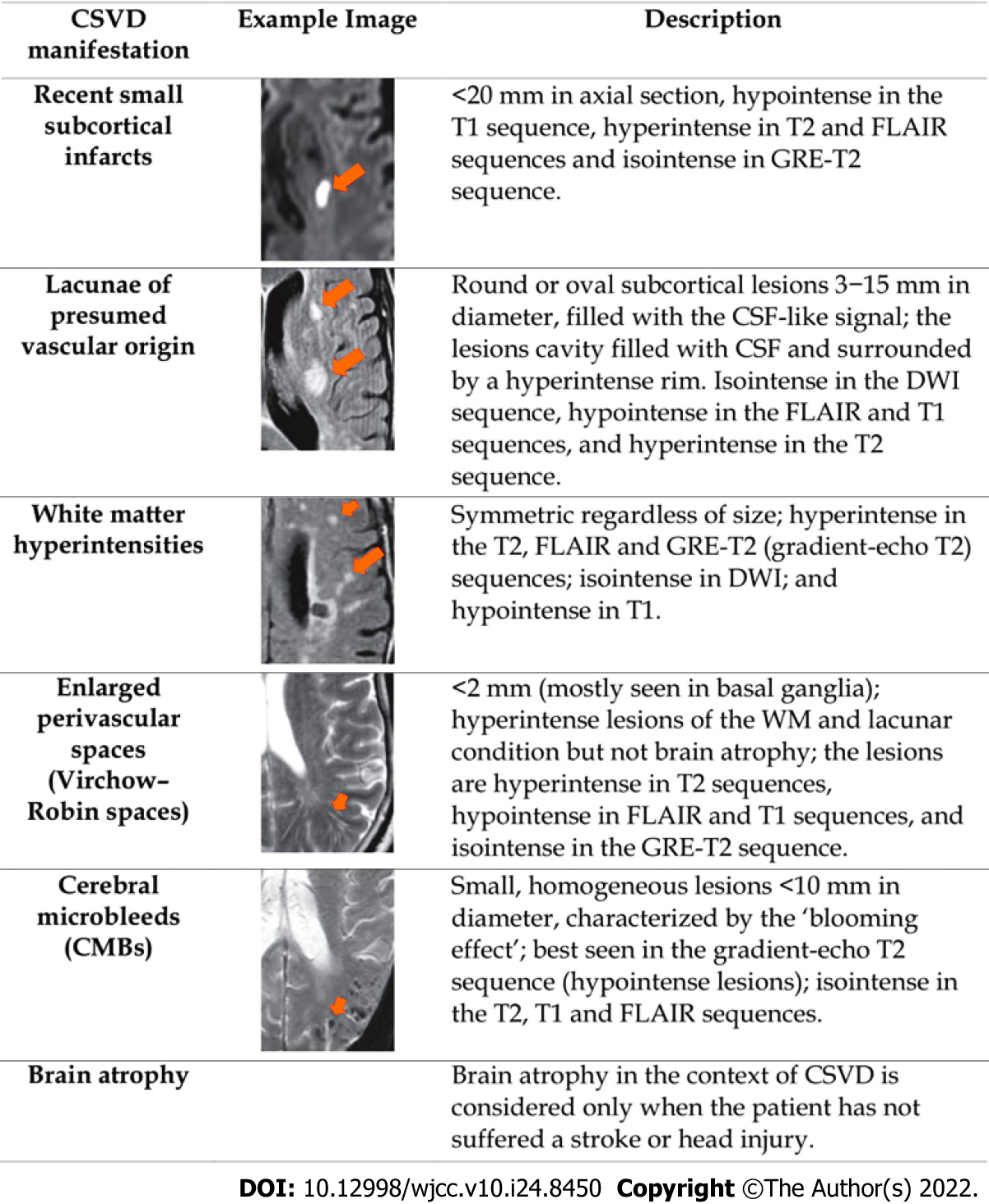
Figure 2 Several cerebral small vessel disease manifestations according to standards for reporting and imaging of small vessel disease[63].
CSVD: Cerebral small vessel disease; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; WM: White matter; DWI: Diffuse-weighted imaging; FLAIR: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; GRE: Gradient recalled echo; CMBs: Cerebral microbleeds.
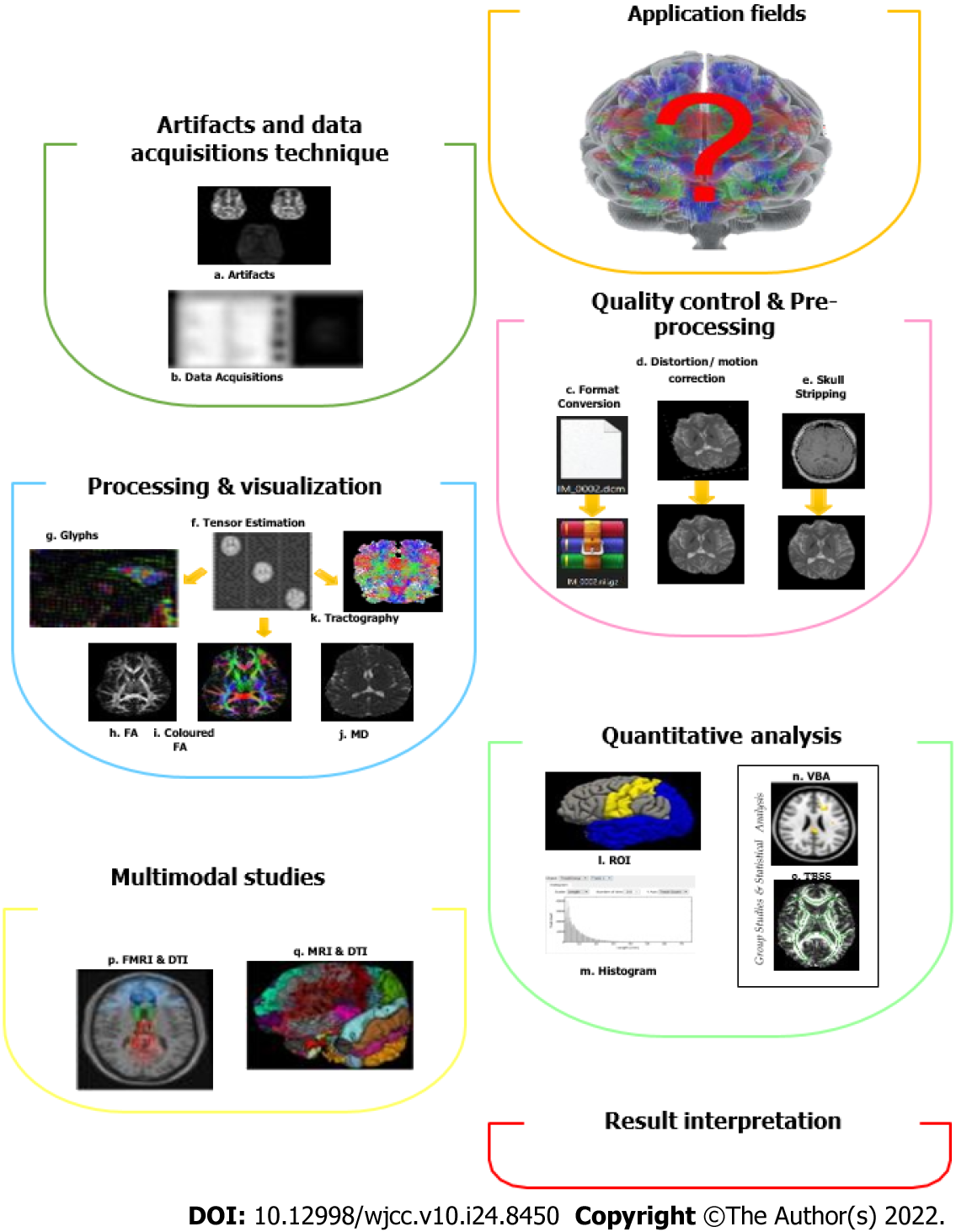
Figure 3 Typical diffusion tensor imaging workflow[63].
The general technique in diffusion tensor imaging pipeline processing and analysis involves a few steps that include artifacts and data acquisition technique, quality control and pre-processing, processing and visualization, quantitative analysis; these can involve multimodal studies, and lastly, result interpretations. FA: Fractional Anisotropy; MD: Mean diffusivity; ROI: Region of interest; VBA: Voxel based analysis; TBSS: Tract based spatial statistics.
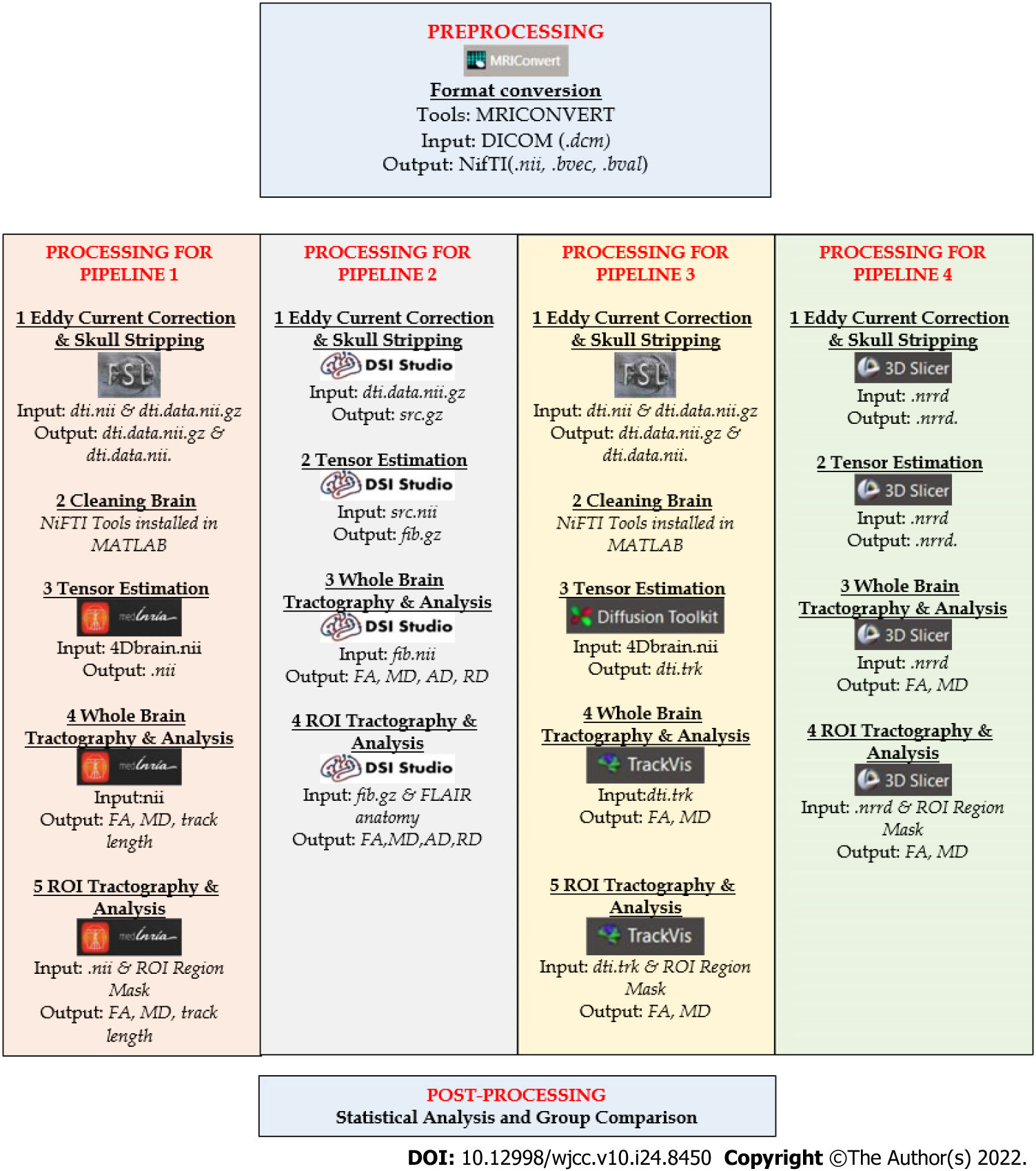
Figure 4 Summarize processing for different pipeline processing.
General methods for four pipelines processing that includes white matter hyperintensities detection and evaluation, pre-processing, processing, and post-processing. WMH: White Matter Hyperintensities; ROI: Region of interest; FA: Fractional anisotropy; MD: Mean diffusivity; AD: Axial diffusivity; RD: Radial diffusivity.
- Citation: Safri AA, Nassir CMNCM, Iman IN, Mohd Taib NH, Achuthan A, Mustapha M. Diffusion tensor imaging pipeline measures of cerebral white matter integrity: An overview of recent advances and prospects. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(24): 8450-8462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i24/8450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8450